24+ Sample Report Format
-

Training Report Format
download now -

Annual Report Format
download now -

APA Report Format
download now -

HR Monthly Report Format
download now -

Handover Report Format
download now -

Report Format Example
download now -
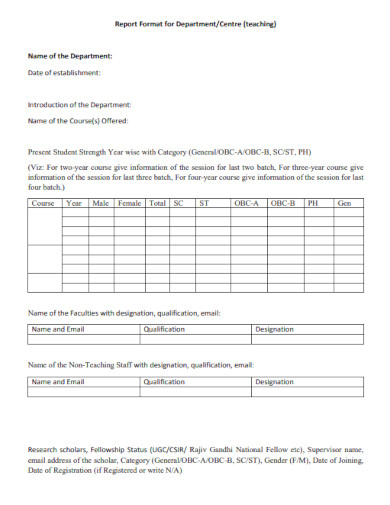
Report Format for Teaching Department
download now -
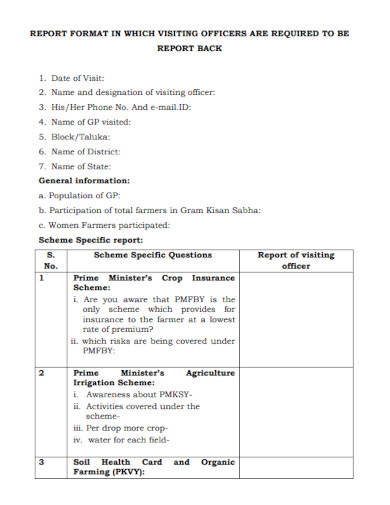
Printable Report Format
download now -

Detail Project Report Format
download now -

Medical Board Report Format
download now -
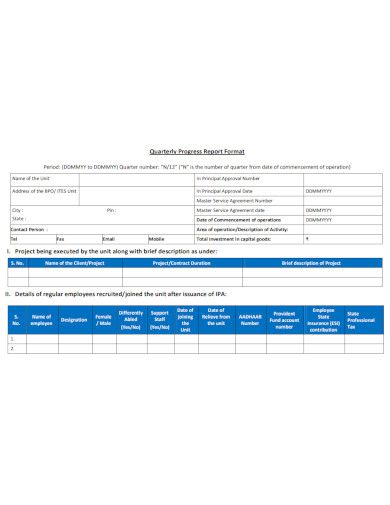
Quarterly Progress Report Format
download now -

Inspection Report Format
download now -
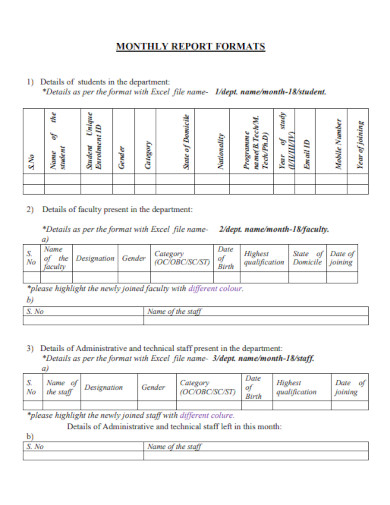
Sample Monthly Report Format
download now -
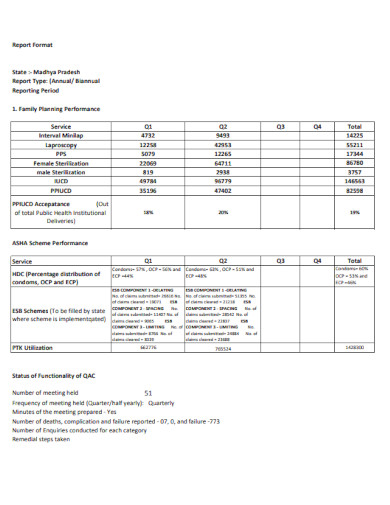
Simple Report Format
download now -
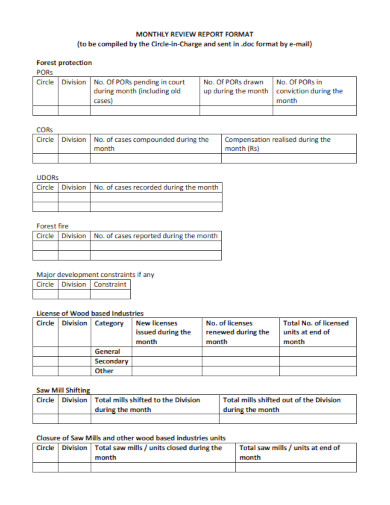
Review Report Format
download now -

Research Report Format
download now -

Project Report Format
download now -

Study Completion Report Format
download now -

Formal Report Formats
download now -
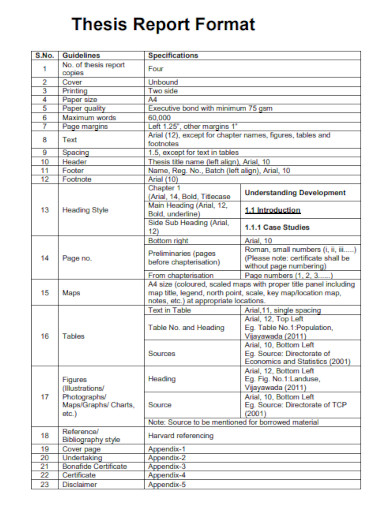
Thesis Report Format
download now -

Seminar Report Format
download now -
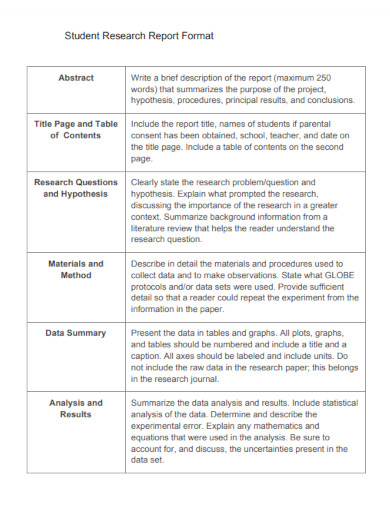
Student Research Report Format
download now -

Format for Technical Report
download now -

Industrial Training Report Format
download now -

Report Format of Death Events
download now
What Is a Report?
A report is a formal document that presents the results of an investigation or a project to a specific audience. Reports are typically used to educate, inform, and provide recommendations for further action in the workplace. Reports are prevalent in nearly every industry, including healthcare, business, academia, and science. Writing reports is an integral part of many professions today. Teachers are required to compose end-of-term reports on their students. Doctors must write reports describing their patient’s conditions and the optimal treatment. Supervisors are required to produce progress reports detailing the development of a particular project. Whether the report is technical or informative, it must be well-written and accurate.
Benefits of Reports
An academic, business, or scientific report presents and discusses facts regarding a specific topic. Reports also follow a structure and include tables, fishbone diagrams, and appendices to make the information easily digestible. Students must write reports for two primary reasons: communicating what they have learned and developing critical thinking skills. These are essential for preparing students for future professions and endeavors. If you are still intrigued, here are a few of its additional advantages:
How to Write a Report
Report writing is a common aspect of many occupations. Knowing how to write an effective report is a valuable talent that will make you an asset to any organization. However, to write professional reports, you must understand what they typically consist of and how to begin. If you’re still intrigued, the report creation steps are listed below.
1. Establish Parameters of Reference
Start by defining your scope of work. Clarify the report’s subject, purpose, date of writing, and justification for existence. Terms of reference typically appear in the first paragraph, allowing the reader to determine the report’s relevance without reading the body. Defining the words at the outset facilitates the development of a solid outline and keeps you on track as you write the report. Collect data that relates directly to the topic or issue you will be writing about. This information is available in your company’s database or archives. If your report requires investigating a case or trend, you may need to collect additional information and organize it meaningfully. Interpret and organize data so that readers can comprehend it. Utilize charts, graphs, or timelines that comprehensively convey the information. Cite pertinent sources and explain how you obtained the data.
2. Create an Outline
Create an outline for your report next. You can create a bulleted or numbered inventory of your document’s sections. Typical report introductions include a title and schedule of contents. The body has an introduction, terms of reference, procedure summary, findings, analysis, conclusion, and contacts. The order of these sections will depend on the type of report you are writing, its length, and formality requirements. Be sure to highlight all essential areas and eliminate anything that does not contribute to the value of your report.
3. Create the Initial Copy
You can compose the first draft now that you know how the report will be formatted. Transfer all pertinent information, thoughts, and data to a document that will ultimately serve as the final report. Refrain from being concerned with how it reads or appears. You will still have time to review and revise the content. As you construct the draft, you may discover informational or statistical gaps. Notate these, but wait to attempt to resolve them. Complete the draft, then revisit the issue during the final review.
4. Conduct Data Analysis and Report Findings
Every report is centered on its findings. This section contains your analysis of the data. The results could explain to a teacher why student performance declined during the previous school term. It could summarize for a marine biologist how global warming affects ocean acidification and how this impacts marine life. Ensure that the section of your report titled “Findings” contains pertinent information about the topic or issue you are addressing. If you conclude that the data you gathered was insufficient or the research methodology was flawed, be honest enough to acknowledge it and explain why. Although numerous groups, organizations, and experts have various data analysis approaches, most of them can be condensed into a single definition. Data analysis is the process of cleansing, modifying, and processing unprocessed data to extract relevant, actionable information that assists businesses in making advised decisions. The procedure aids in mitigating the inherent risks associated with decision-making by providing valuable insights and statistics, frequently presented in charts, images, tables, and graphs.
5. Proofread and Distribute
Before distributing your document, you must verify that it is free of typographical and grammatical errors. Use proofreading or a spell-checking program to identify any grammatical mistakes or blunders. In addition, double-check the accuracy of your data and citations. Read the document at least twice to ensure the information is coherent. Request a review to present the report to a public audience. There are numerous methods for disseminating your written report. You can deliver it verbally during a meeting agenda, publish it in a scholarly journal, or send it via email to your immediate supervisor. The distribution method depends on who will peruse the report. Regardless of the format of your report, your objective is to produce a coherent and informative document that will guide decision-makers. Critical to the writing process, proofreading is examining a written document by native English speakers to identify and correct grammar, punctuation, spelling, and vocabulary errors. Proofreading is fundamental to this process, as good writing always requires modification and revision.
FAQs
What are the qualities of a good report?
The perfect sample report should be clear, concise, accurate, and well-organized section headings. Simple for the audience to comprehend. Presentation is a crucial component of effective report writing. Formatting, amending, and proofreading are vital steps in the writing process. A report provides comprehensive, factual, and up-to-date information about a topic or issue. The report contains well-organized information that can be used for future planning and decision-making.
Why are reports important to management?
It enables managers to recognize tendencies. This allows them to make more informed business decisions. The reports aid senior decision-makers in understanding KPIs and establishing performance objectives. Managers can assess the business’s overall healing using the information in the reports.
Why is a research report important?
A typical research report is a firsthand account of the investigation process and is regarded as a reliable source of information. A well-written research report will provide you with a summary report of the research process that details the significant aspects of the research process.
Reports also aid in monitoring expenses and sales budget, allowing for more efficient budgeting and resource conservation. You can use these reports appropriately to generate new, enhanced, applicable strategies for achieving company objectives. By writing a report, you construct an expanding timeline of your research. Also, you can retain statistical data and strategic patterns for future development.
