Test Report Samples
-
Test Coverage Report
download now -

Test Incident Report
download now -

Drug Test Report
download now -
Dengue Test Report
download now -

Pressure Test Report Certificate Template
download now -

Free Web Usability Test Report Template
download now -

Free User Acceptance Test Report Template
download now -

Software Test Report Template
download now -

Free Agile Test Report Template
download now -

Weekly Test Report Template
download now -

Concrete Cube Test Report Template
download now -

Test Report Template
download now -

Report – Test Summary Template
download now -

Test Tracking Report Template
download now -

Free Test Results Report Template
download now -

Test Summary Report Template
download now -

Test Case Report Template
download now -

Test Result Evaluation Report Template
download now -
Quality Test Report
download now -
Sample Vision Test Report
download now -
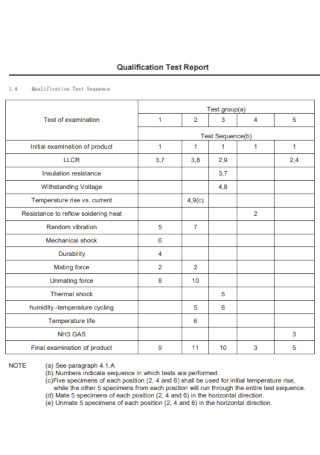
Qualification Lab Test Report
download now -

System Testing Report
download now -
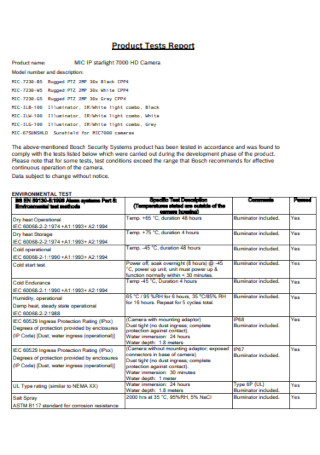
Product Test Report
download now -
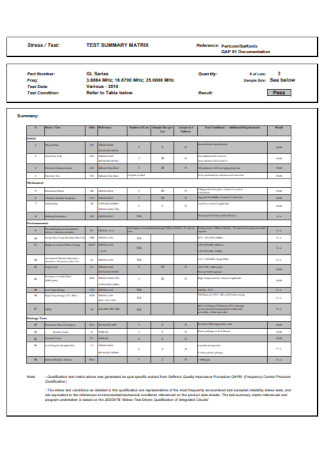
Material Test Report
download now -

Test Summary Report
download now -
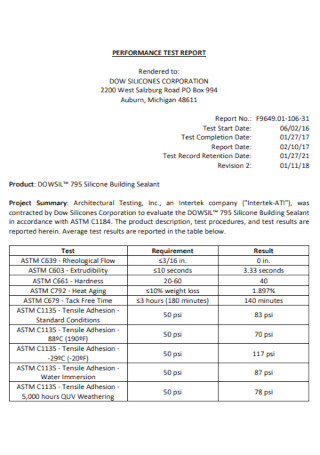
Medical Test Report
download now -
Cancer Test Report
download now -

Sample Urine Test Report
download now -
Patient Test Report
download now -
Positive Test Report
download now -
Hospital Test Report
download now -
Test Report Analysis
download now -
Typhoid Test Report
download now -

Test Report Certificate
download now -
Application Test Plan
download now -

Test Report Number
download now -

Certification Test Report
download now -

Formal Test Report
download now -
Sample Alcohol Test Report
download now -
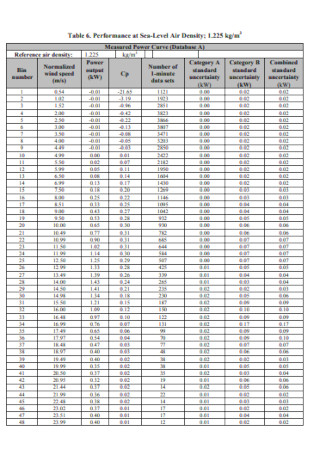
Power Performance Test Report
download now -
Riding Test Report
download now -
Elevator Test Report
download now -

Simple Test Report
download now -
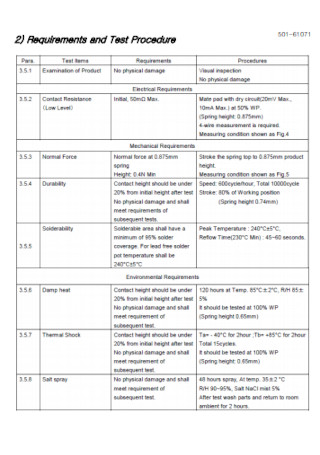
Validation Test Report
download now -
Cable Commissioning Test Report
download now -

Laboratory Test Report
download now -
Firewall Test Report
download now -
Backflow Prevention Device Test Report
download now -
Sample Annual Test Report
download now -

Environmental Test Plan
download now -
Printable Test Report
download now -
Project Test Report
download now -
Historical of Test Report
download now -

Metal Roof Test Report
download now -
Sample Initial Test Report
download now -
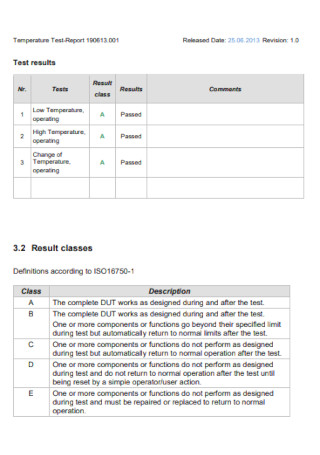
Temperature Test-Report
download now -
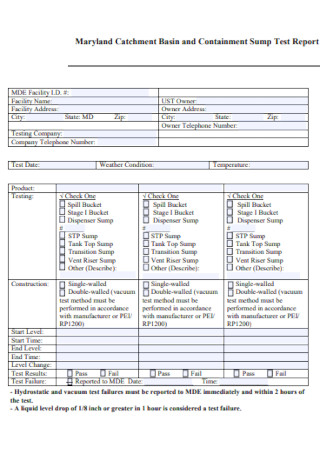
Containment Sump Test Report
download now -

Test Plan and Report
download now -
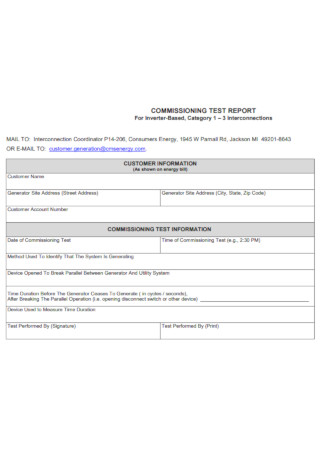
Sample Commissioning Test Report
download now -
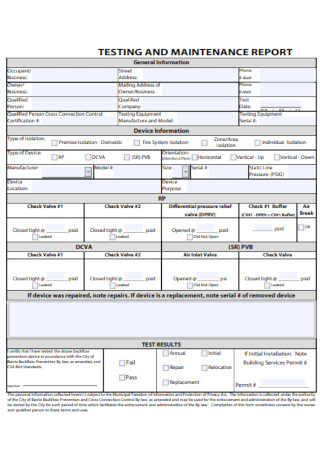
Testing and Maintenance Report
download now -
Food Test Report
download now -

Functional Test Report
download now -

Water Test Report
download now -

Hydrostatic Test Report
download now -
Sample Reliability Test Report
download now -

Simple Performance Test Report
download now -
Packaging Test Report
download now
FREE Test Report s to Download
Test Report Format
Test Report Samples
Test Report: What Is It?
The Big Four: Elements of a Test Report
How to Write an Effective Test Report
FAQs
When should test reports be made?
What are other documents to prepare aside from test reports?
What is a test status report?
What is the difference between a summary and a detailed test report?
How can a test report help with compliance and audits?
How do you classify issues or defects in a test report?

Test Report Format
1. Title Page
- Title of the Report: Clearly mention “Test Report” along with the project or system name.
- Date of Report: The date on which the report is prepared.
- Prepared by: The name(s) and designation(s) of the person(s) preparing the report.
- Reviewed by: The name(s) and designation(s) of the person(s) reviewing the report.
- Approved by: The name(s) and designation(s) of the person(s) approving the report.
2. Table of Contents
- List all the sections and sub-sections with their respective page numbers.
3. Introduction
- Objective: The purpose and objectives of the test report.
- Scope: Define the scope of the testing process, including what is covered and what is not.
- Test Items: The list of items, modules, or features that were tested.
- Audience: Specify who the intended readers of the report are.
- References: List any references like documents, test cases, or design specifications used.
4. Test Summary
- Overview: A brief overview of the entire testing process and its outcome.
- Test Environment: Details of the environment where the tests were conducted, such as hardware, software, network configurations, etc.
- Test Schedule: Mention the testing start and end dates, deadlines, and important milestones.
- Test Coverage: The percentage of the system, features, or modules tested.
- Summary of Results: Overall results (e.g., pass/fail rate, total test cases executed, total defects found, etc.).
- Assumptions and Constraints: Any assumptions, constraints, or limitations that affected the testing process.
5. Test Design and Approach
- Test Methodology: The testing approach used (e.g., manual, automated, black-box, white-box, etc.).
- Test Levels: Types of testing conducted (e.g., unit, integration, system, acceptance, etc.).
- Test Strategy: Details of how the testing was planned and executed.
- Entry and Exit Criteria: Conditions to start and end the testing process.
6. Test Execution Details
- Test Cases Executed: Number of test cases executed, with details.
- Test Case Status: List of test cases categorized as Pass, Fail, Blocked, or Not Run.
- Test Data: Sample test data used during testing.
- Defects Found: Summary of the number of defects found, including their severity and priority.
- Re-testing and Regression Testing: Details on re-testing and regression testing activities.
7. Test Results
- Defect Report:
- Defect ID
- Description of the defect
- Severity (Critical, High, Medium, Low)
- Priority (High, Medium, Low)
- Status (Open, In Progress, Closed, Deferred)
- Assigned To (Person or team responsible for resolving the issue)
- Test Case Results:
- Test Case ID
- Description
- Expected Results
- Actual Results
- Status (Pass, Fail, Blocked)
- Comments
8. Defect Analysis
- Root Cause Analysis: Analyze the reasons for defects.
- Defect Distribution: Identify defects by type (e.g., functional, UI, security, performance, etc.).
- Severity and Priority Distribution: Details of how many defects are in each severity and priority category.
9. Test Metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Total Test Cases: The total number of test cases created.
- Test Case Execution Status: Pass, Fail, Blocked, Not Run (percentage or count).
- Defect Density: Number of defects per unit of testing.
- Defect Rejection Rate: Number of rejected defects.
- Test Effectiveness: Percentage of test cases that found defects.
- Test Efficiency: The number of defects found per unit of time.
10. Risks and Mitigation
- Identified Risks: List of risks encountered during testing.
- Impact: The potential impact of these risks.
- Mitigation Strategies: How the risks were mitigated or managed.
11. Issues and Challenges
- Highlight issues and challenges faced during testing.
- Possible resolutions or improvements.
12. Recommendations
- Recommendations for future testing.
- Process improvement suggestions.
13. Conclusion
- Summary of key findings and overall test results.
- Final status of the system or product (Ready for Release, Needs Further Testing, etc.).
- Next steps or follow-up actions.
14. Appendices
- Glossary: Definitions of key terms, abbreviations, or acronyms used in the report.
- References: Any relevant documents, links, or materials referred to during testing.
- Supporting Documents: Screenshots, test logs, or attachments to support the test results.
Test Report: What Is It?
A test is a reliable medium used for measuring efficiency, quality, and more, particularly in evaluation reports and assessments. And when various tests are conducted for any project, a test report follows. This official document or report summarizes every test activity involved and outlines the tests’ final results. In short, test reports assess how effective the testing procedures performed were. Meanwhile, the test report’s content will be studied and evaluated by stakeholders to check if the quality and total package of projects are worth releasing or not.

Did you know that in 2017, 34% of respondents from the global manufacturing industry spent around 30 hours or more conducting plant maintenance?
Meanwhile, Statista’s 2019 survey confirmed that a panel of senior technology experts and CIOs allocated around 23% of their yearly IT budget plan for quality assurance (QA) and testing.
On another note, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) reported that electrical engineers’ median yearly wage reached $98,530 in 2019.
The Big Four: Elements of a Test Report
Are you curious about what a test report contains? There are many details to incorporate inside, but you can expect that the info is divided into four major elements. And such aspects make a complete and excellent test report. In this section, we outlined the four elements of a test report.
How to Write an Effective Test Report

Without a test report, do you think clients and stakeholders would just sit and not care about whatever is going on with testing projects for a particular period? Hence, test reports solve this problem to inform every manager, client, stakeholder, and more about how tests went. But, the report might not be of any help if poorly made. You can also see more on Performance Reports. Be sure to create a well-thought-out report instead. To do that, kindly follow these six easy steps in writing an effective test report:
Step 1: Know Your Purpose
Why do you need a test report in the first place? Answer that question first to recognize your purpose. This step helps you determine the objective and description of your document. For example, are you preparing a test report to see if every material and resource used for manufacturing items help the business be more profitable? In fact, around 34% of respondents from the worldwide manufacturing industry spent nearly 30 hours or even more to conduct plant maintenance. That is, according to Statista. And for your application, clarify the purpose, or the whole output would go wrong.
Step 2: Determine the Scope and Metrics
The next step involves the section specifically explaining the modules for in scope, out of scope, and items not tested. A tip is to conduct a SWOT analysis or needs analysis to specify the needed tests and metrics to measure every test afterward. For the metrics, you will slowly understand why results are good or bad. It can help you stay up to date with the test cases or defects. But, be sure to set the appropriate metrics that are relevant to your application. And you can provide visuals with the help of graphs or charts. Go for the best format and content, no matter what.
Step 3: Identify the Testing Methods Performed
Now for the main dish, specify the types of testing methods performed. You will also write the location or test environment, what tools and equipment are needed, etc. Maybe you want to assess the customer feedback form, and you can run through tests like doing a survey for customers to fill out or interviewing them personally. Whatever the tests are, they should be managed carefully. Maybe you fail to gather the right data when you handle the process poorly. Record the important details in the report.
Step 4: Gather the Results and Insights
Next, jot down the results of every test conducted. This step is where you should study the results because they can bring you insights and lessons worth interpreting afterward. For example, what were some issues noticed from the various tests? And what solutions led you to fix such problems? Please write it down. Be sure to collect the results of data analysis because you would have nothing to analyze or study later on.
Step 5: Interpret the Data
Data interpretation cannot be forgotten. This section requires you to analyze the results and write your realizations from them. This step may help you identify the strengths of the series of steps conducted and even the problems that could have been fixed next time. Data analysts would even regard the findings crucial since the interpretation also serves as your report’s meat. Do not just show the results because you need to explain it further.
Step 6: Note Your Recommendations
For future tests that may come up next time, note your recommendations too. Maybe the previous tests were too much of a hassle, and after the data interpretation, you can make better suggestions and solutions to smoothen the process. Focus on providing best practices so no one else would have to continue those flawed tests but rather a more well-developed one already. And don’t forget to state your conclusion as a way of signing off the sample report.
FAQs
When should test reports be made?
Test reports are generally prepared after the series of test plans. Because how else can you summarize or interpret data if the testing process isn’t finished yet?
What are other documents to prepare aside from test reports?
Besides test reports, you may need to make test strategies, test plans, configuration management plans, and risk management plans. And what other reports or documents to add would also depend on your purpose.
What is a test status report?
The test status report is similar to a general test report that uses data gathered from performing various testing procedures. However, the report relies more on the test’s status, not exactly the total package of the test report.
What is the difference between a summary and a detailed test report?
A summary test report offers an overview of testing activities, key metrics, and major findings. It is concise and used for high-level decision-making. A detailed test report provides a comprehensive view of all test cases, metrics, issues, and solutions. It is used by QA teams and technical stakeholders for a deeper analysis of the testing process.
How can a test report help with compliance and audits?
Test reports act as formal evidence of testing activities, which is essential for compliance with industry regulations like ISO, GDPR, or HIPAA. They document testing methodologies, issue resolution processes, and overall test coverage, which auditors and regulatory bodies require during inspections or audits. You can also see more on Medical Report.
How do you classify issues or defects in a test report?
Issues are classified based on severity and impact. Critical issues are high-priority errors that block functionality, while major issues significantly affect performance. Minor issues are low-priority bugs that have minimal impact on the system. Classifying issues allows developers to prioritize fixes and reduce delays.
