50+ Atomic Structure Worksheet (Periodic Table, Chemisty, Physical Science, High School, Middle School, 7th Grade, 9th Grade, 10th Grade)
-

Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet with Answer key
download now -

8th Grade Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
High School Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Grade 9 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

7th Grade Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
Physical Science Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Grade 7 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
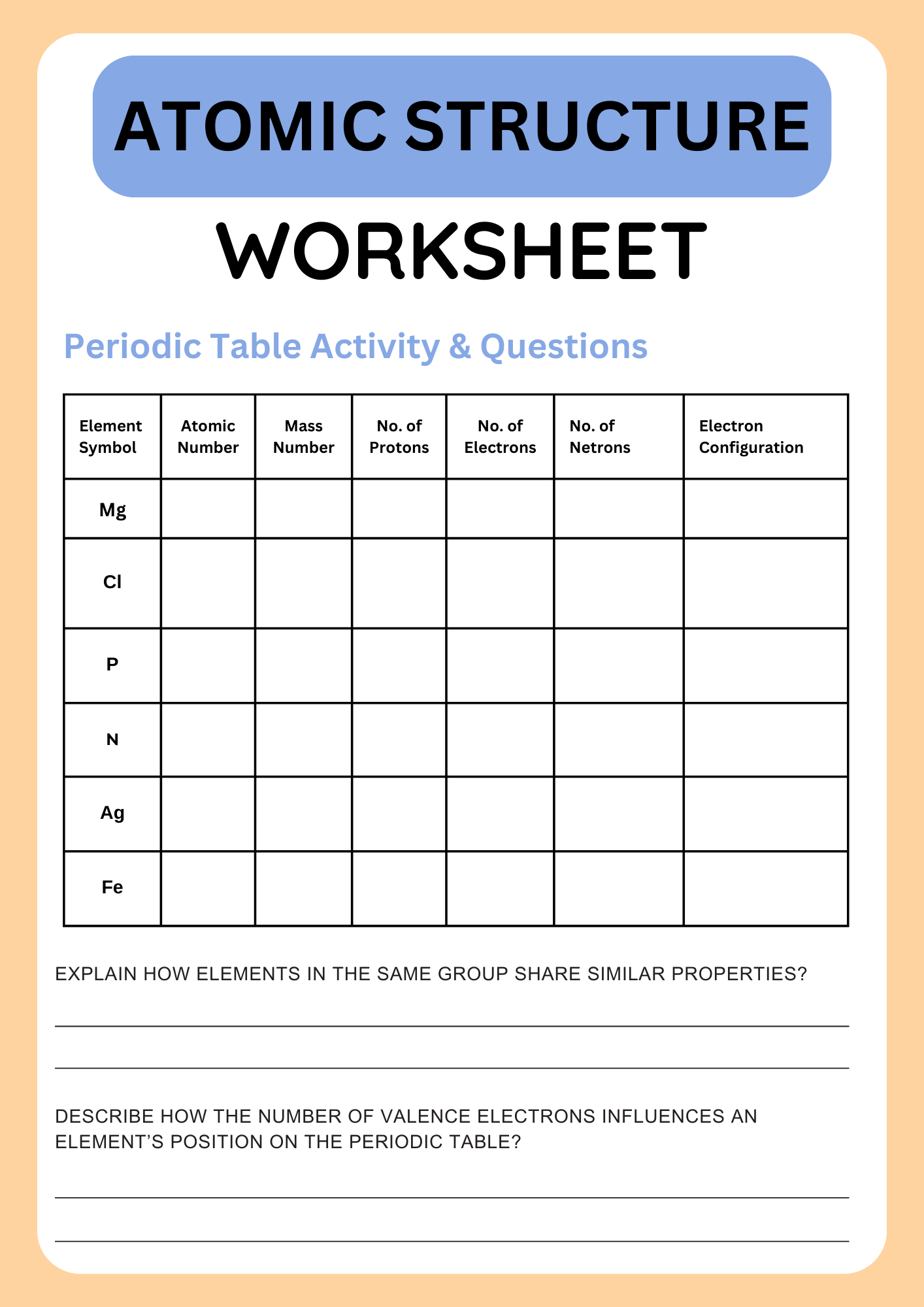
Atomic Structure Periodic Table Worksheets
download now -
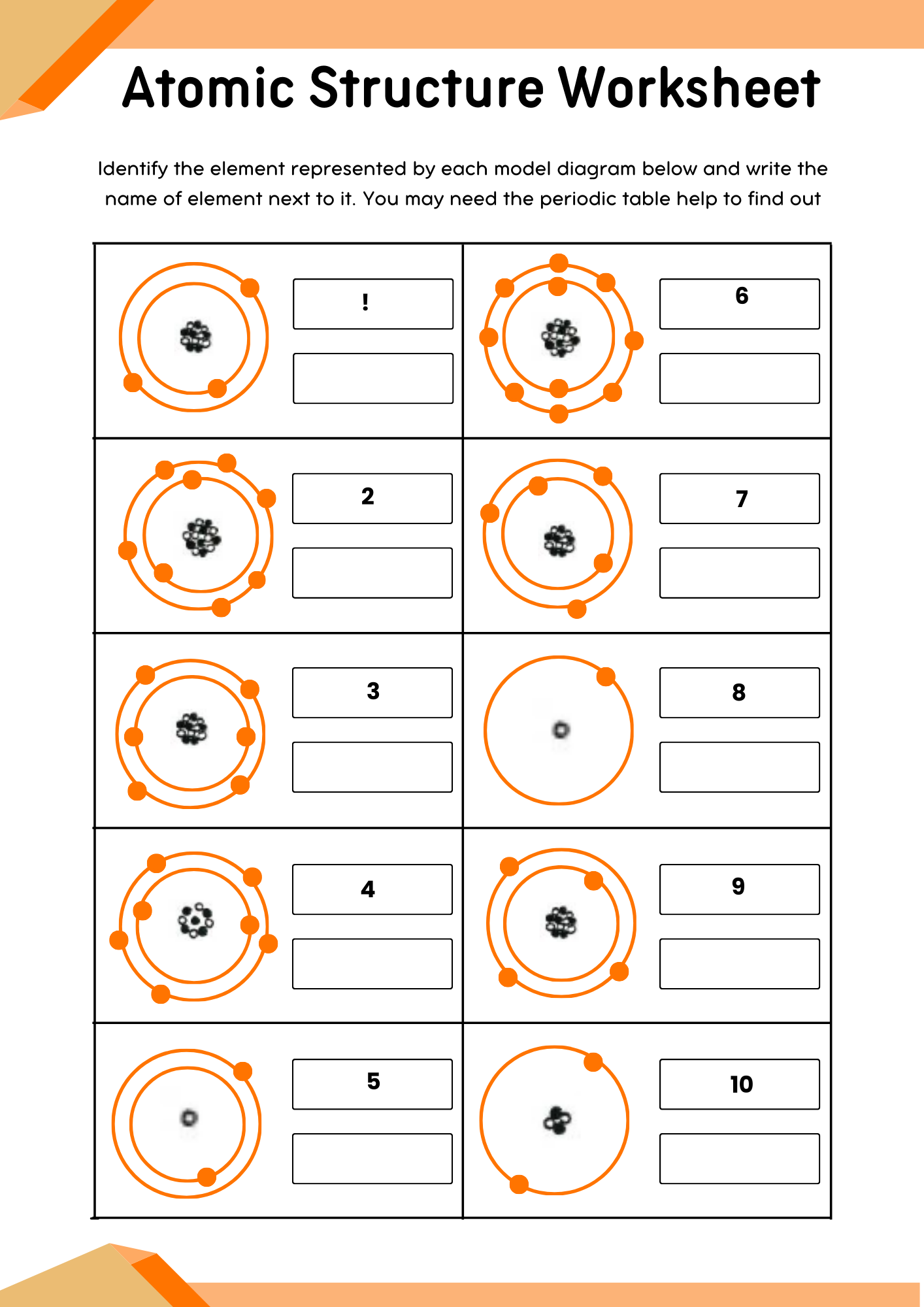
Middle School Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

6th Grade Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
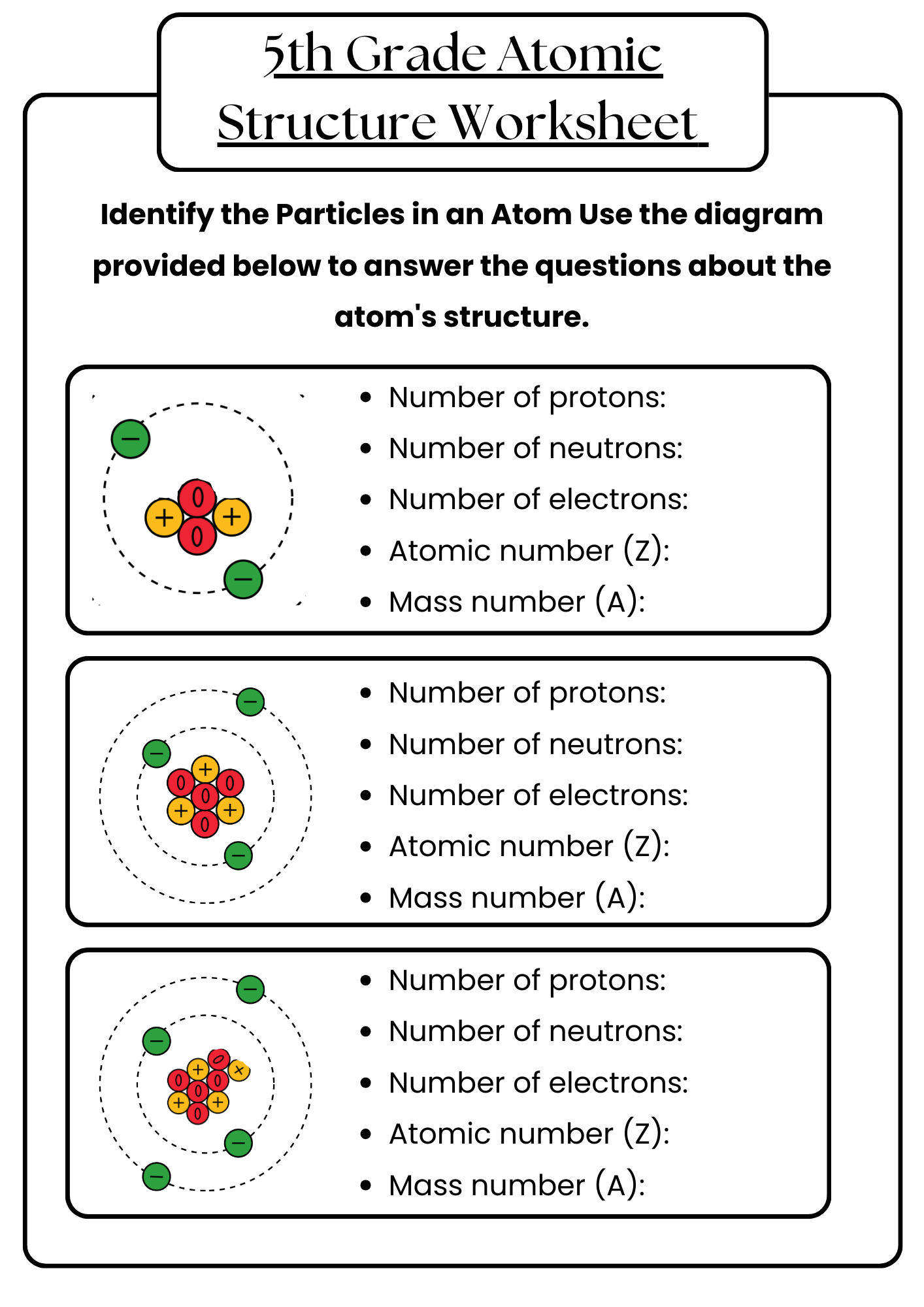
5th Grade Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet in PDF
download now -

9th Grade Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
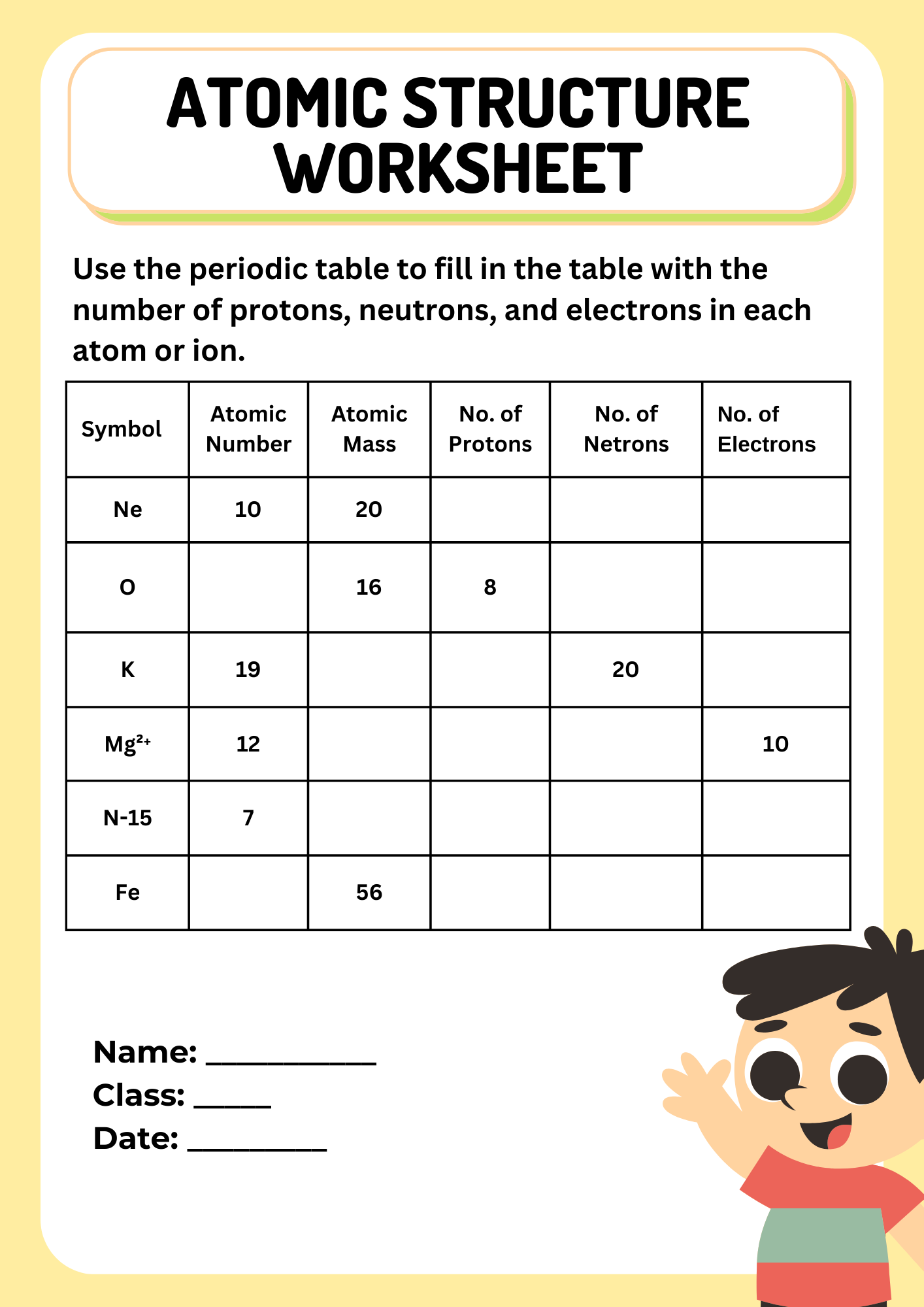
10th Grade Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet for Practice
download now -

Atomic Number Structure Worksheet
download now -
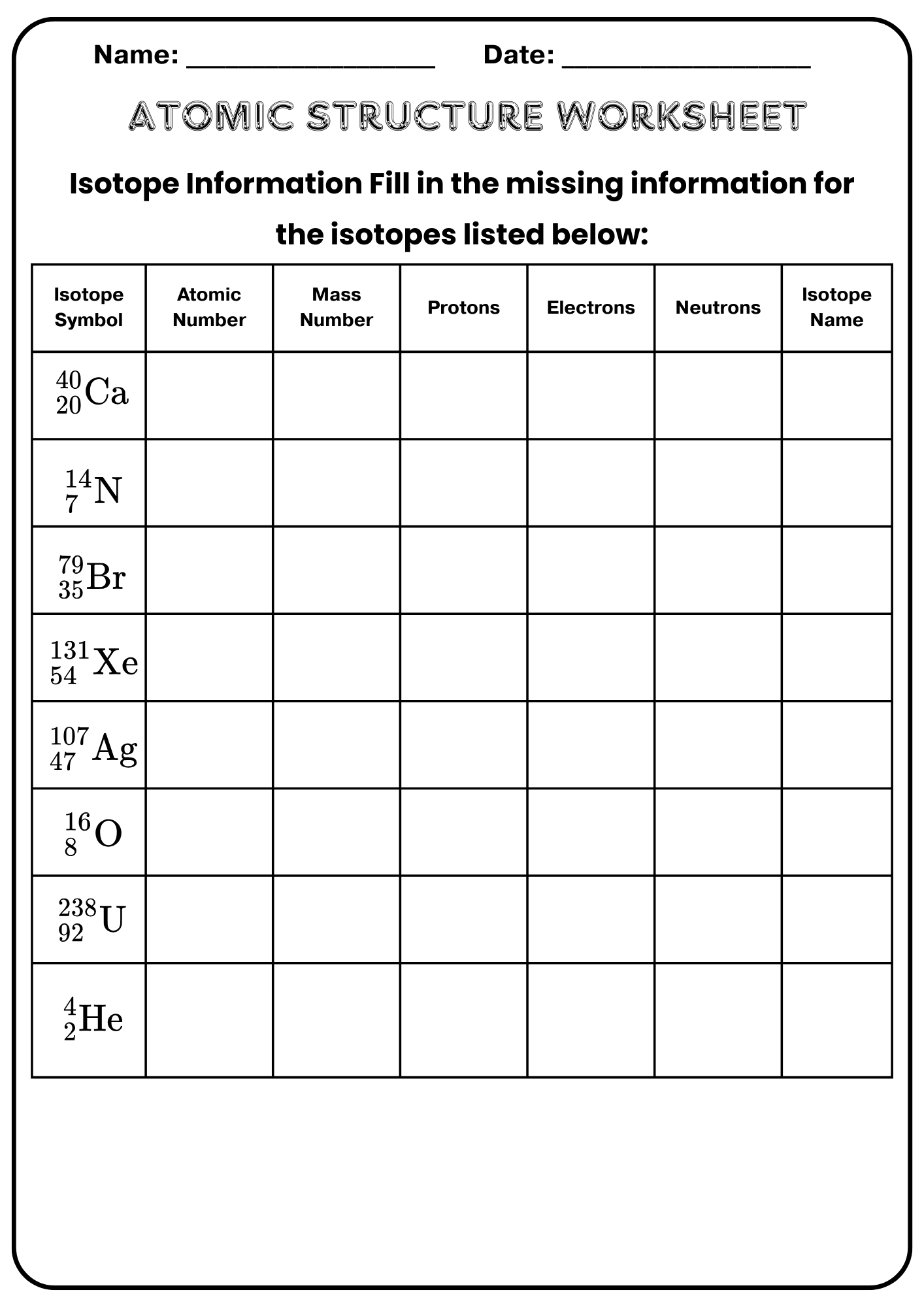
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Chapter 3 Worksheet
download now -
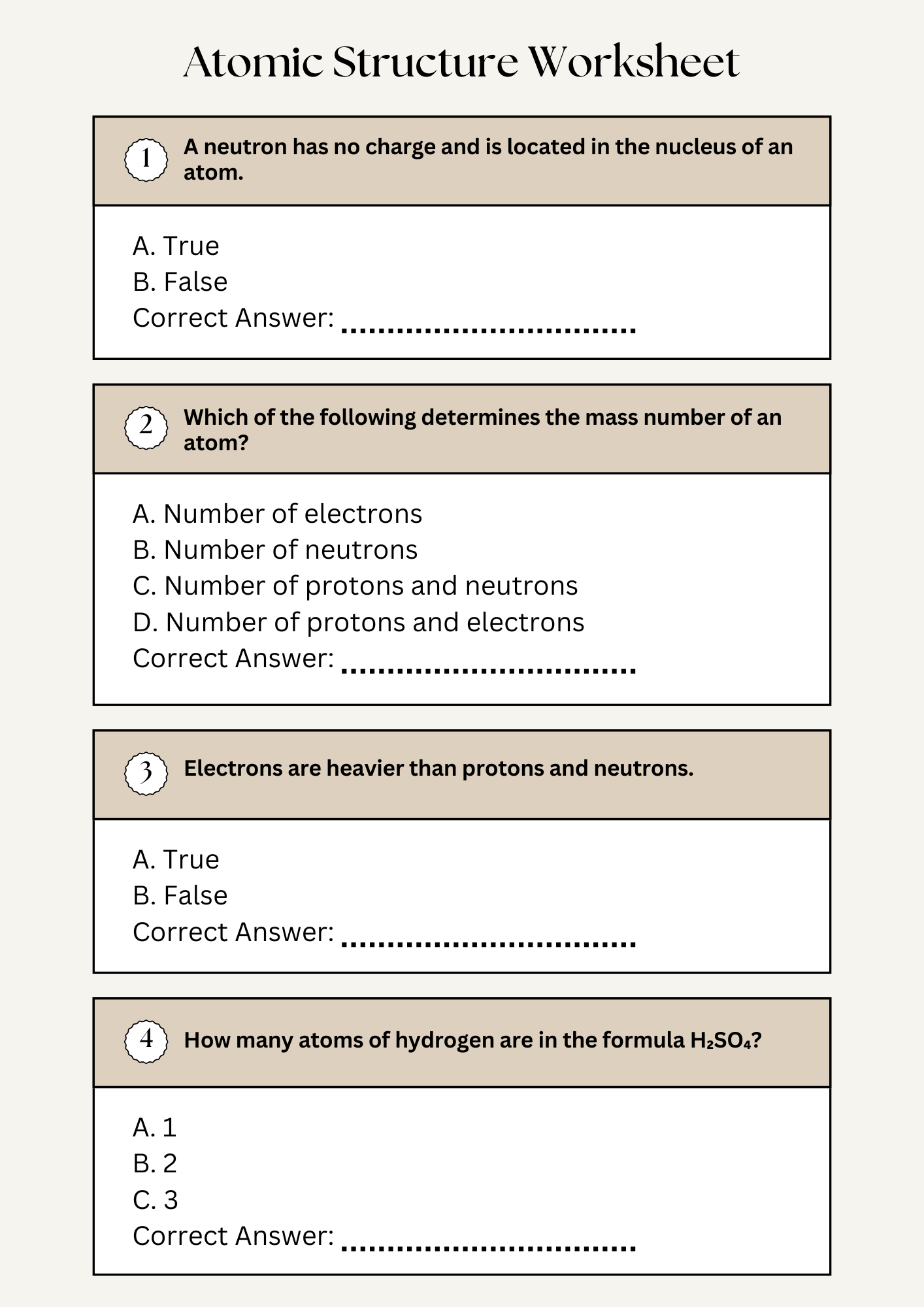
Atomic Structure Quiz Questions Worksheet
download now -
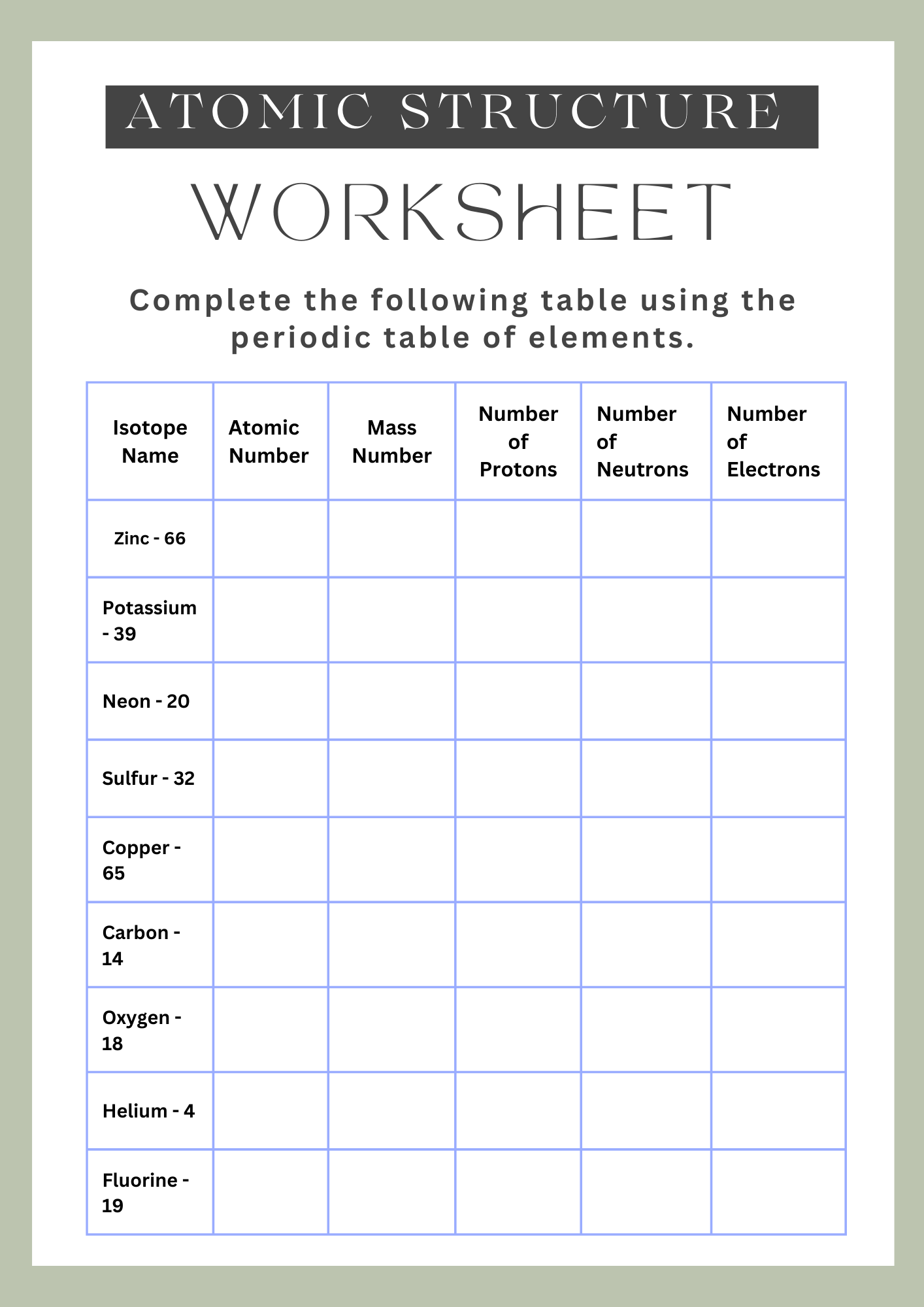
Atomic Structure Worksheet Chart
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet Ks3
download now -

Year 8 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Year 9 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Class 7 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Class 8 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Class 9 Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
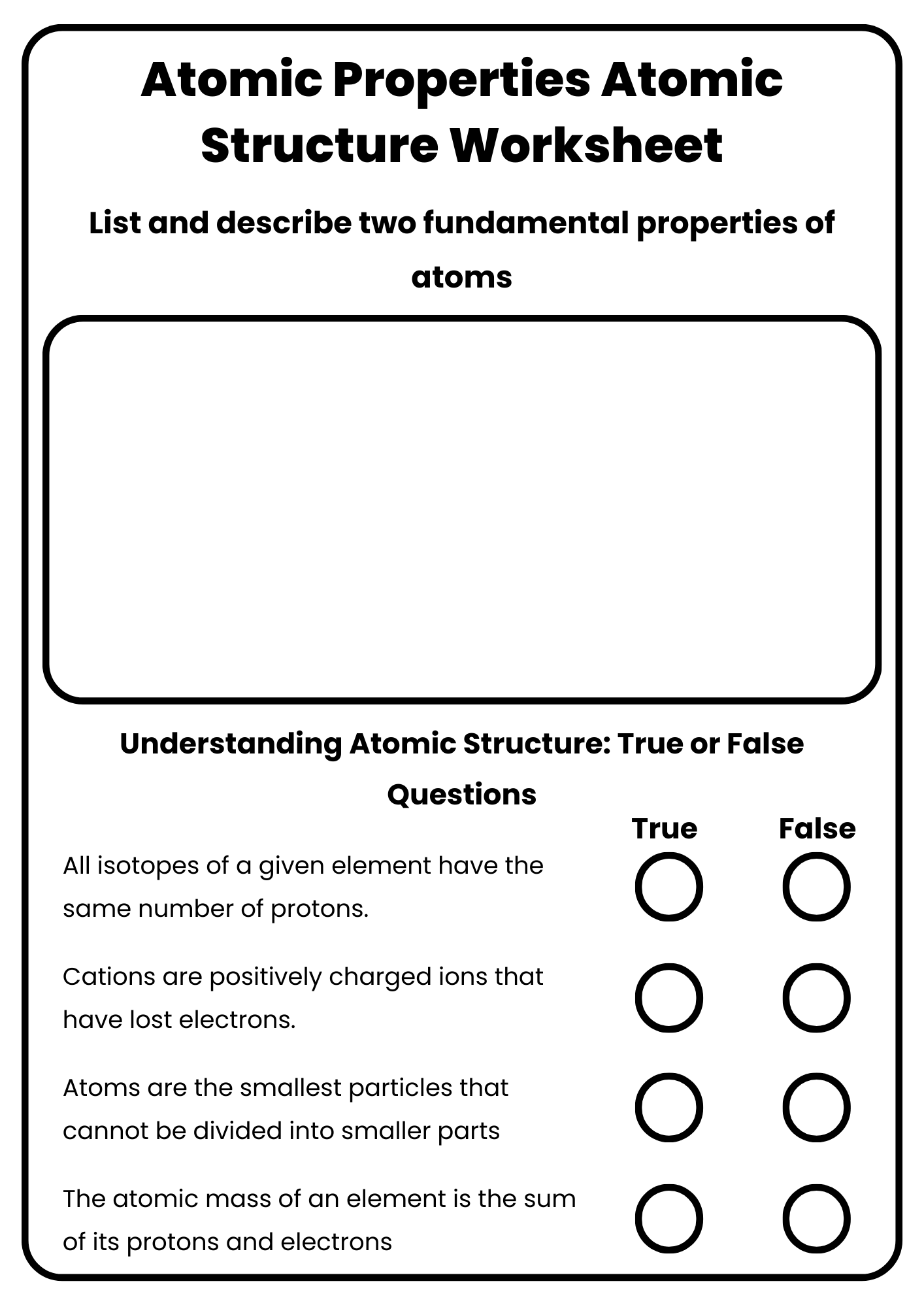
Atomic Properties Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Printable Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -
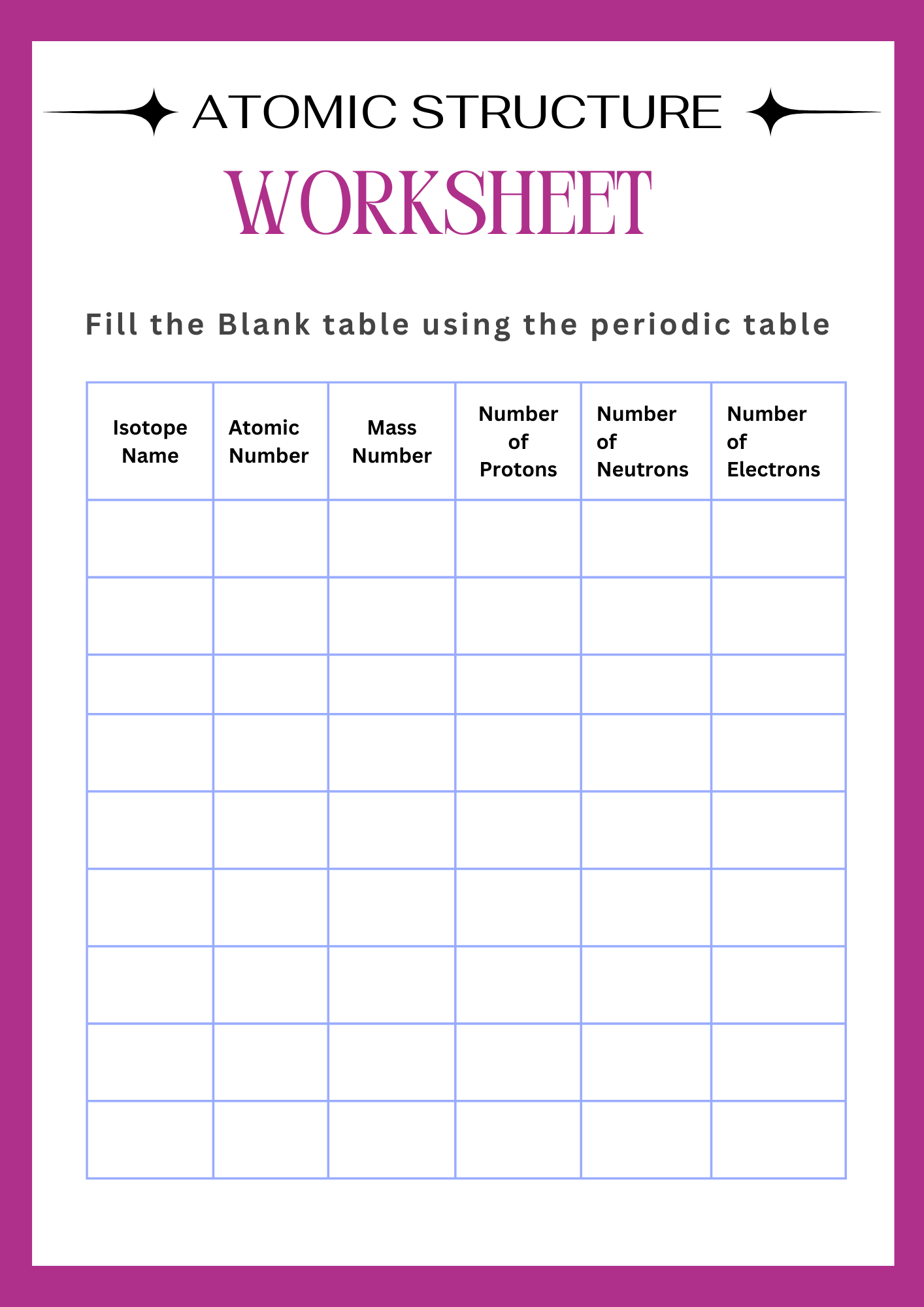
Blank Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

GCSE Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Subatomic Particles Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Isotope Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Review Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Properties Worksheet
download now -

Sub Atomic Structure Particles Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Compounds Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet with Answer Key
download now -
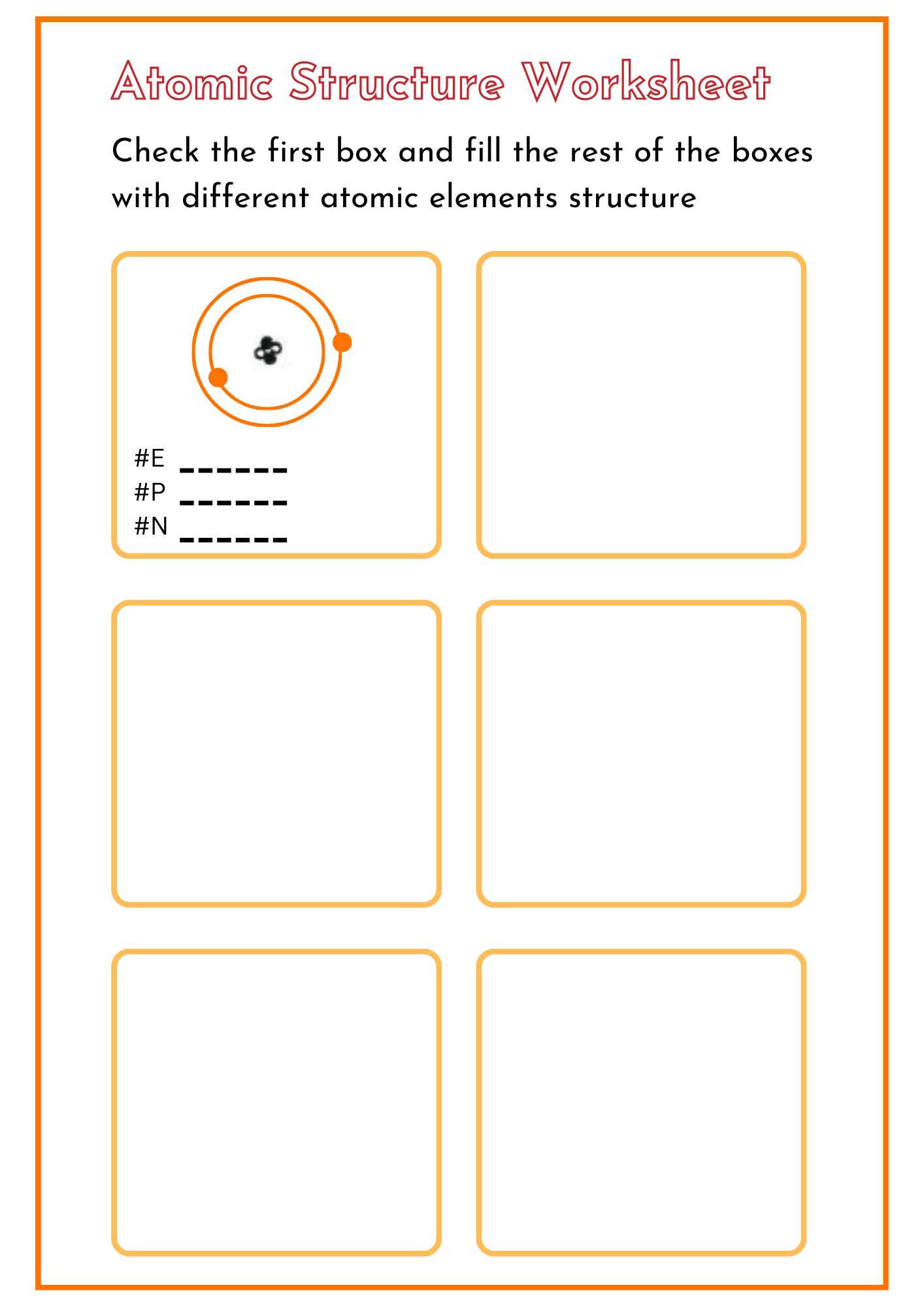
Atomic Structure Activity Worksheet
download now -
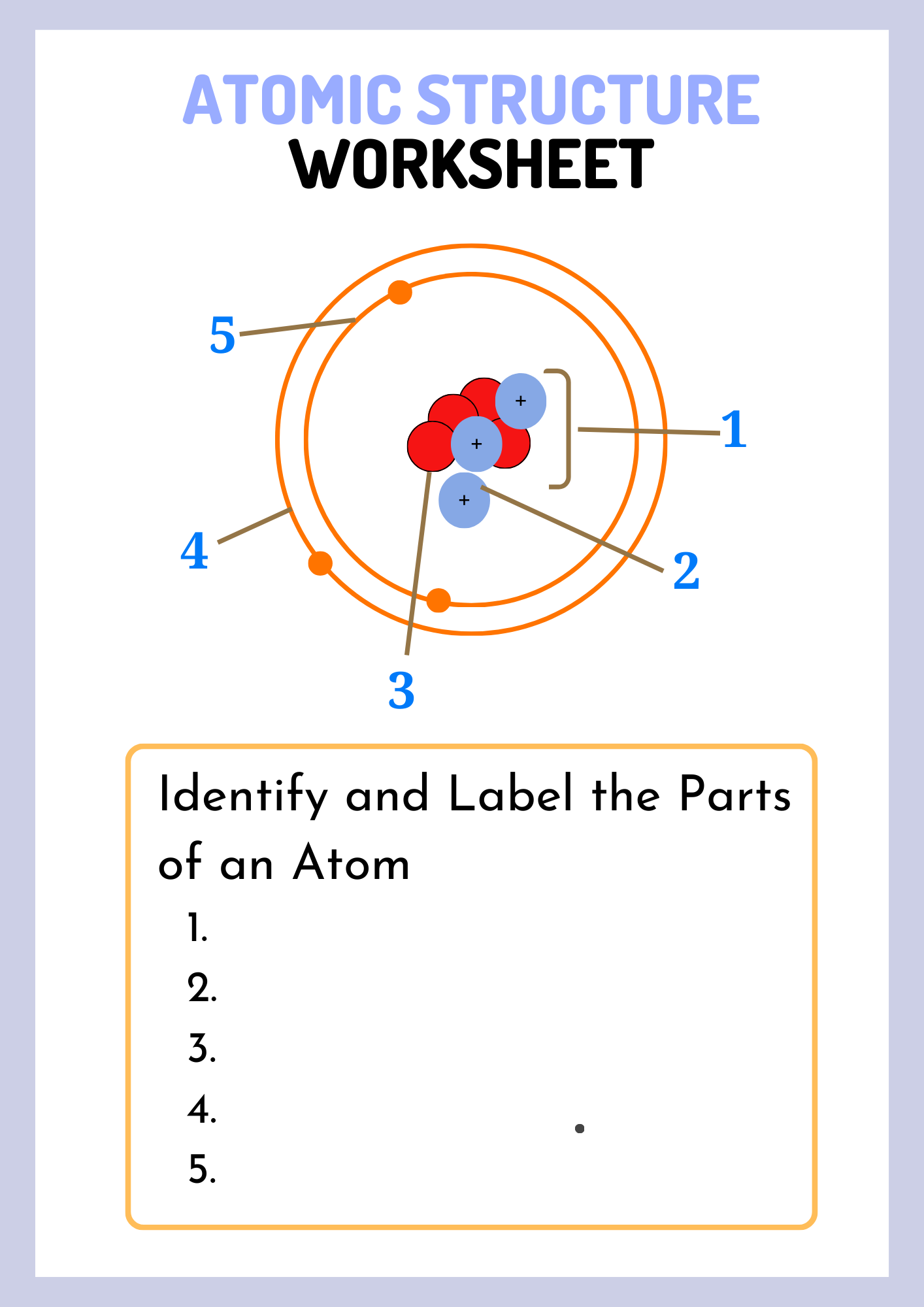
Atomic Structure Digital Interactive Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Lesson Worksheet
download now -

Simple Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Classroom Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Exercise Worksheet
download now -
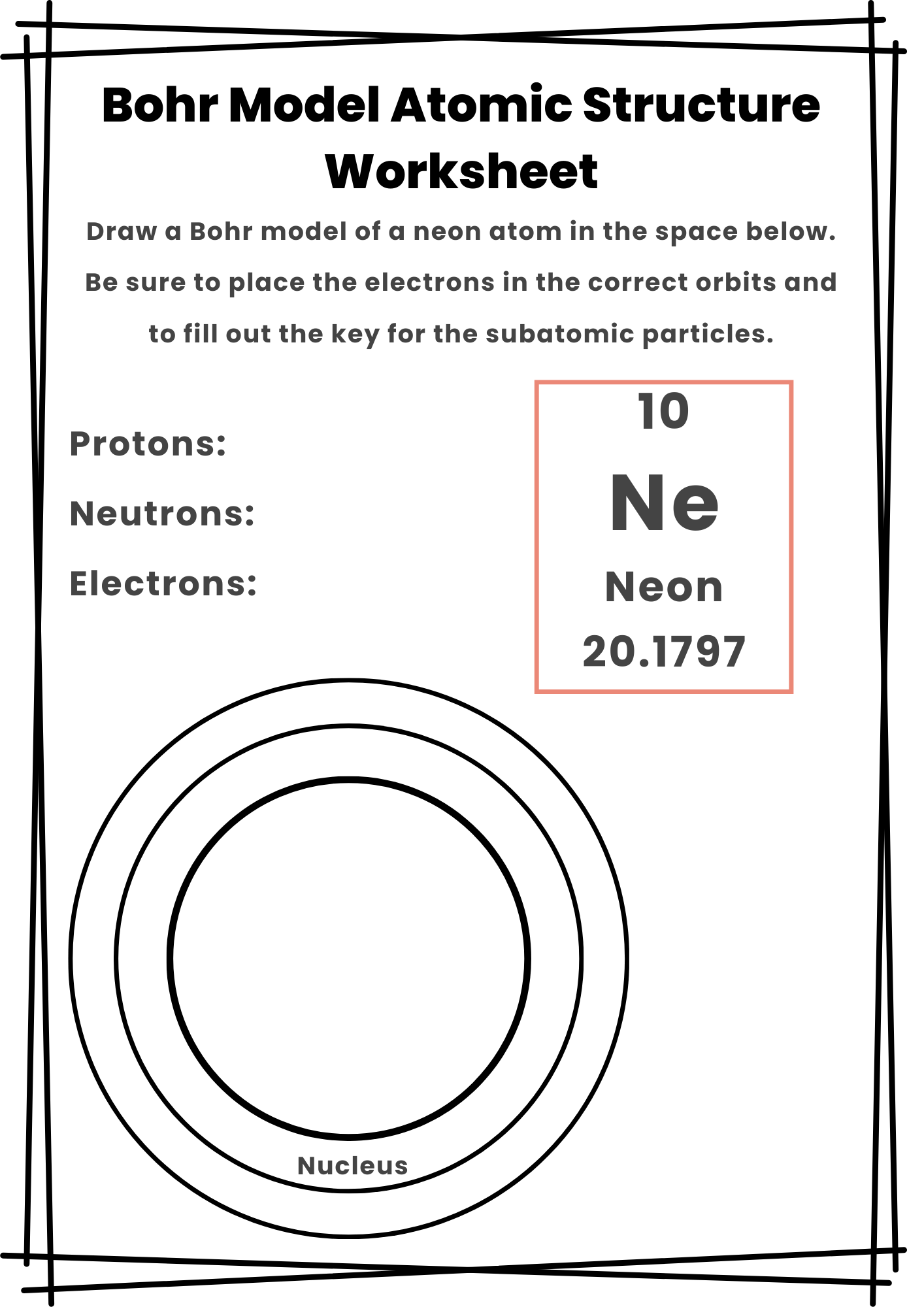
Bohr Model Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Model Worksheet
download now -
Atomic Structure Method Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Interactive Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Homework Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Group Work Worksheet
download now -
Atomic Structure Plan Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Function Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Elements Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Task Worksheet
download now -
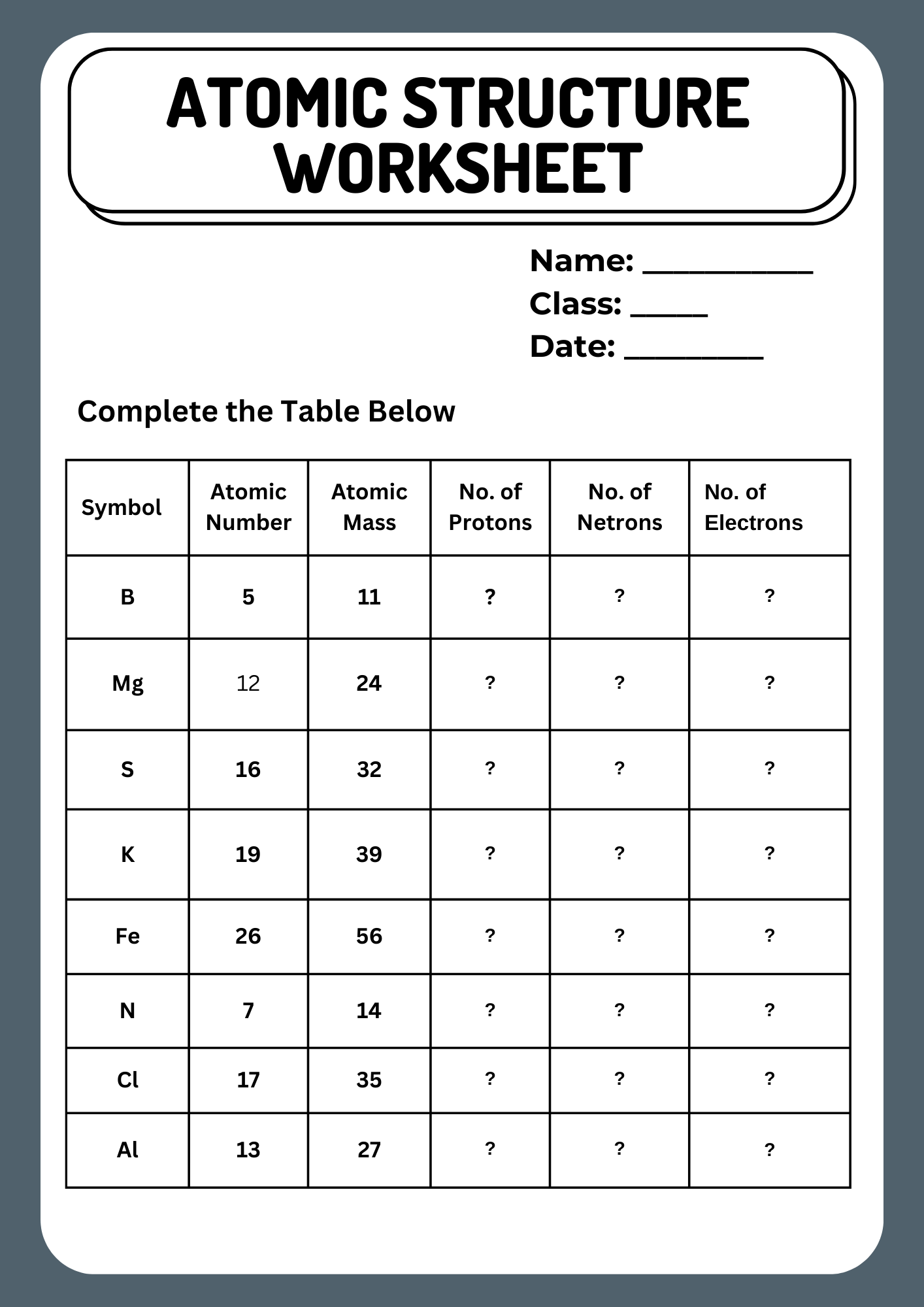
Editable Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet Activity
download now -
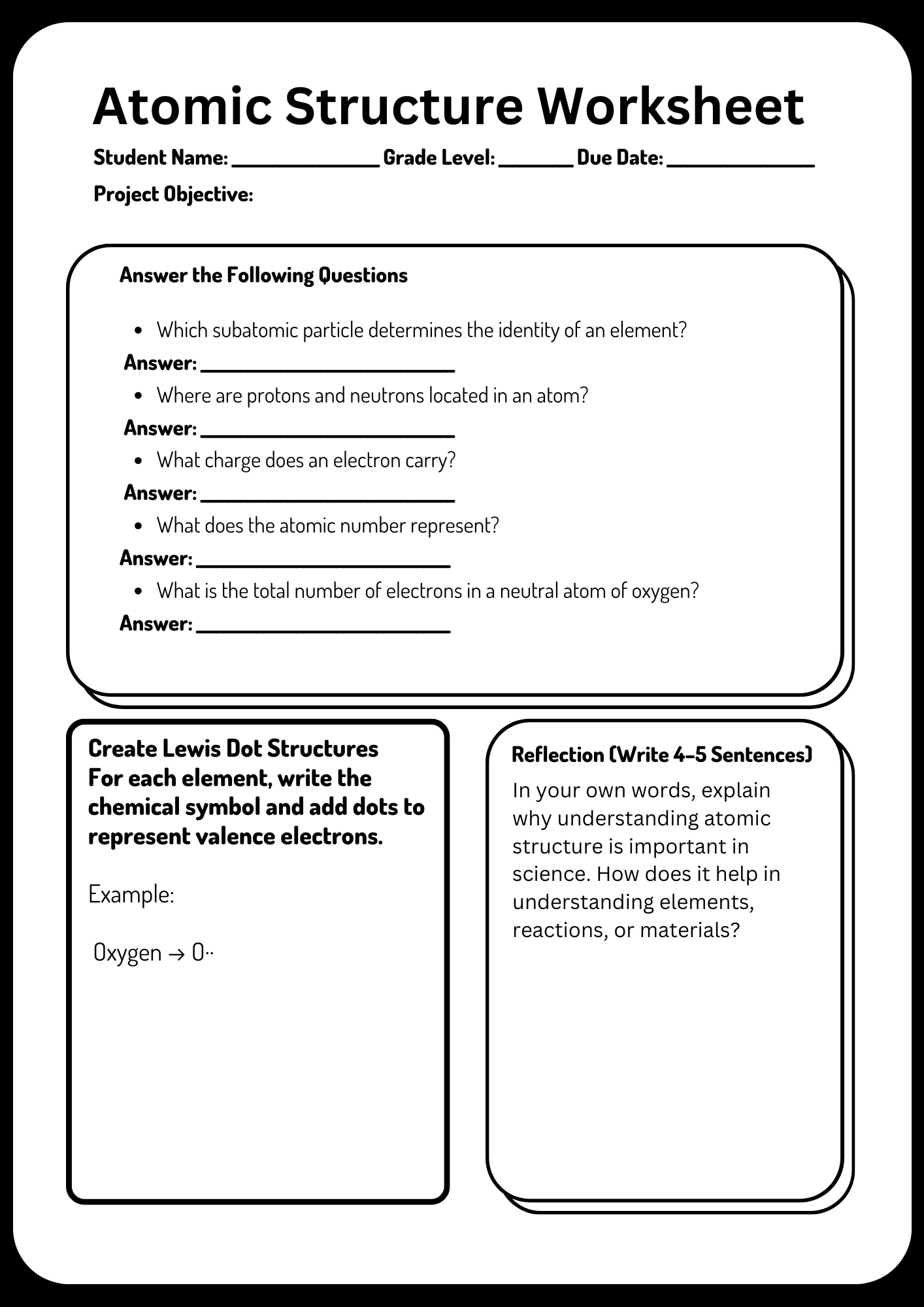
Atomic Structure Worksheet Project
download now -
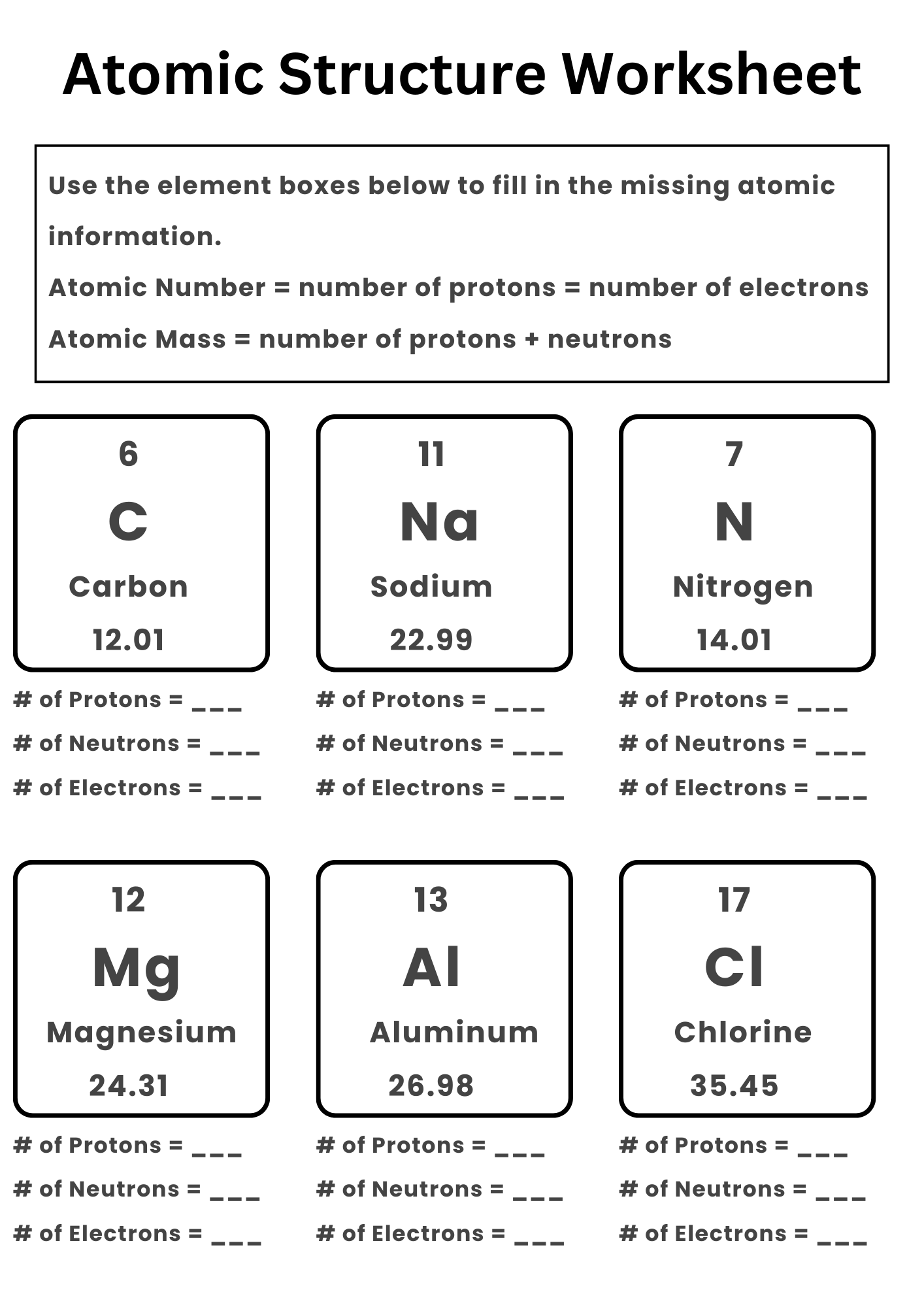
Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet Crack Case Answer Key
download now -

Atomic Structure Worksheet Quiz
download now -
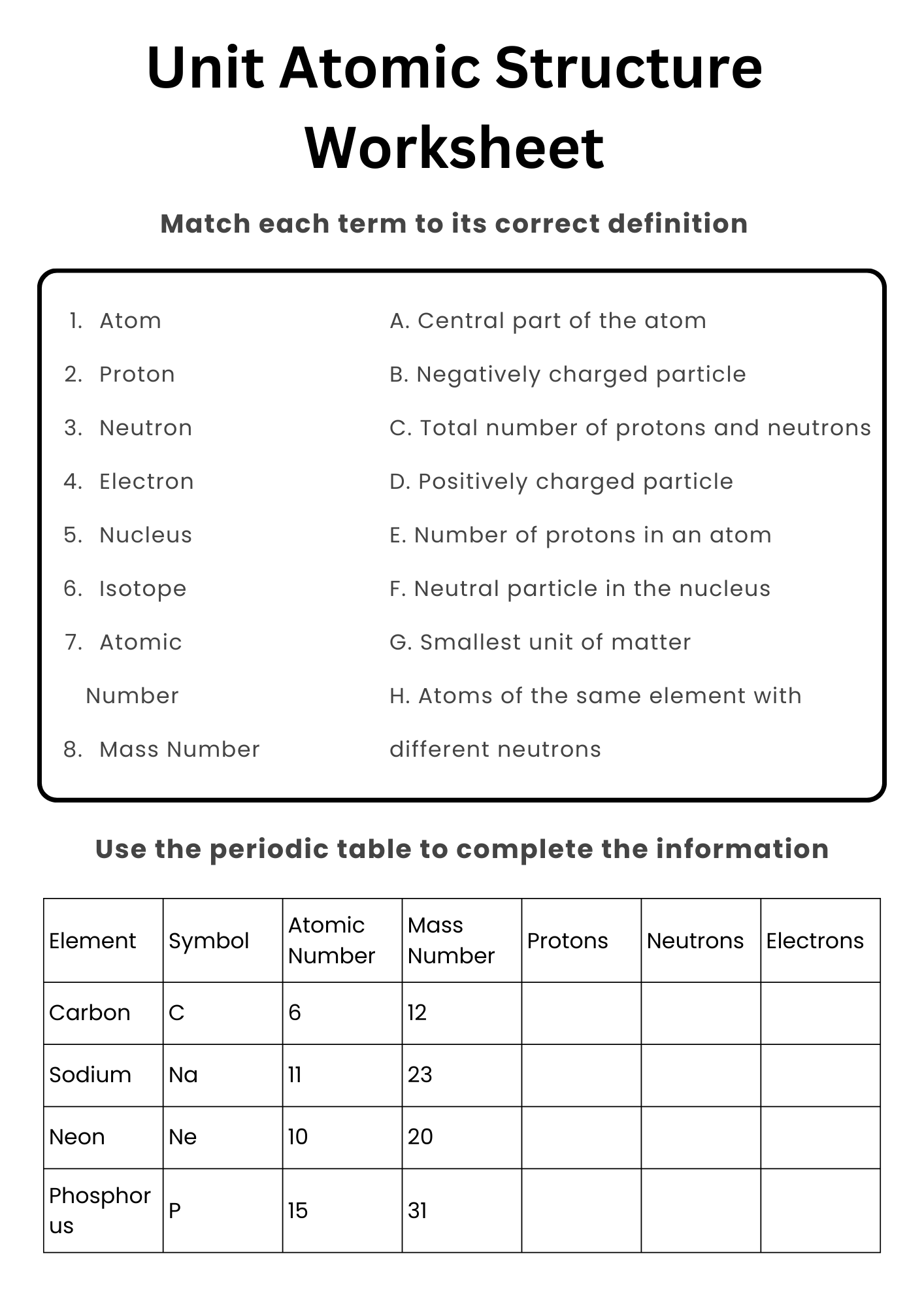
Unit Atomic Structure Worksheet
download now -

Atomic Structure Task Worksheet PDF
download now
Free Printable Atomic Structure Worksheet to Download
50+ Atomic Structure Worksheet (Periodic Table, Chemisty, Physical Science, High School, Middle School, 7th Grade, 9th Grade, 10th Grade)
What is Atomic Structure?
What is an Atomic Structure Worksheet?
Why is Atomic Structure Important?
Components of Atomic Structure Worksheet
How to Use an Atomic Structure Worksheet?
What Are the Types of Atomic Structure?
What is Atomic Structure?
Atomic structure is the arrangement of subatomic particles—protons, neutrons, and electrons—within an atom, where protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus and electrons orbit in energy levels around the nucleus.
What is an Atomic Structure Worksheet?
An Atomic Structure Worksheet is an educational tool designed to help students understand the fundamental components of an atom and their arrangement. These worksheets typically include exercises related to protons, neutrons, electrons, atomic number, mass number, isotopes, and electron configurations. By completing these activities, students reinforce their knowledge of atomic models, Bohr diagrams, Lewis structures, and periodic table trends. The worksheets often incorporate engaging questions on identifying elements, calculating subatomic particles, and predicting atomic behavior, making them essential for mastering the principles of atomic theory. This structured practice enhances critical thinking and provides a strong foundation in chemistry, preparing students for more advanced concepts in molecular interactions and chemical bonding.
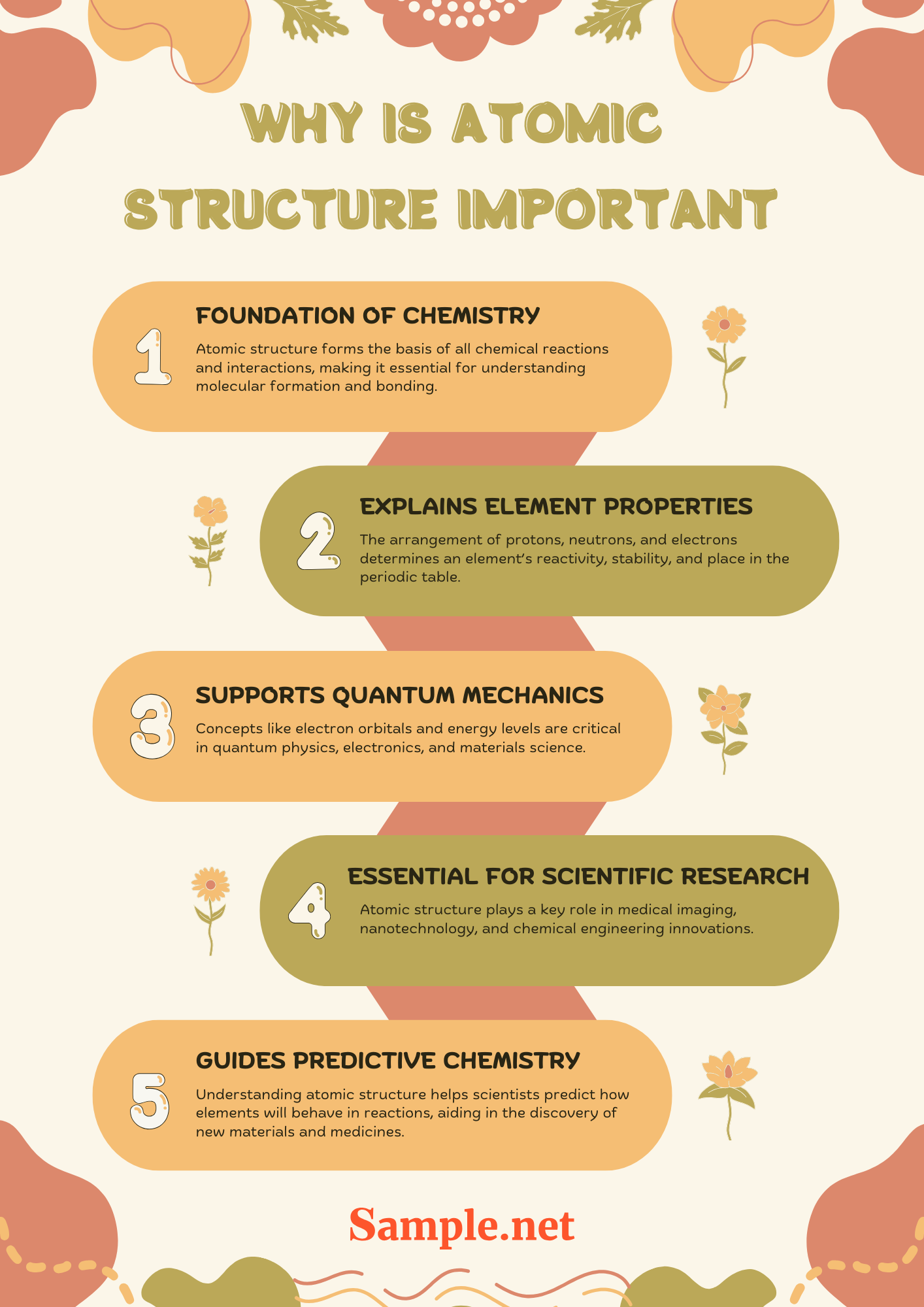
Why is Atomic Structure Important?
Understanding atomic structure is fundamental to mastering chemistry and physics. It explains the composition and behavior of matter at the most basic level. A deep knowledge of atomic structure helps in predicting chemical reactions, understanding the periodic table, and explaining the properties of different elements. Here’s why atomic structure is crucial:
✅ Foundation of Chemistry: Atomic structure forms the basis of all chemical reactions and interactions, making it essential for understanding molecular formation and bonding.
✅ Explains Element Properties: The arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons determines an element’s reactivity, stability, and place in the periodic table.
✅ Supports Quantum Mechanics: Concepts like electron orbitals and energy levels are critical in quantum physics, electronics, and materials science.
✅ Essential for Scientific Research: Atomic structure plays a key role in medical imaging, nanotechnology, and chemical engineering innovations.
✅ Guides Predictive Chemistry: Understanding atomic structure helps scientists predict how elements will behave in reactions, aiding in the discovery of new materials and medicines.
Components of Atomic Structure Worksheet
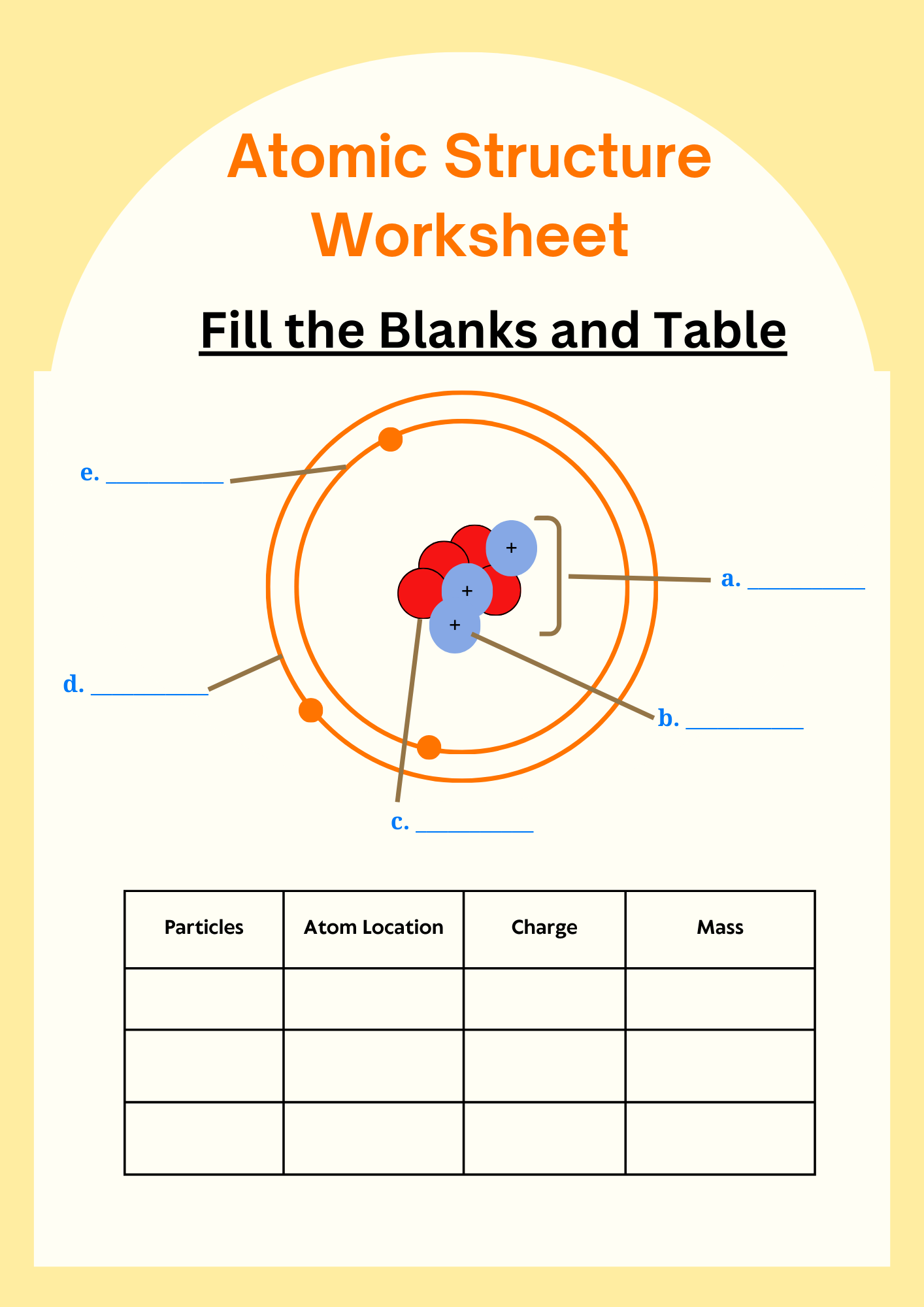
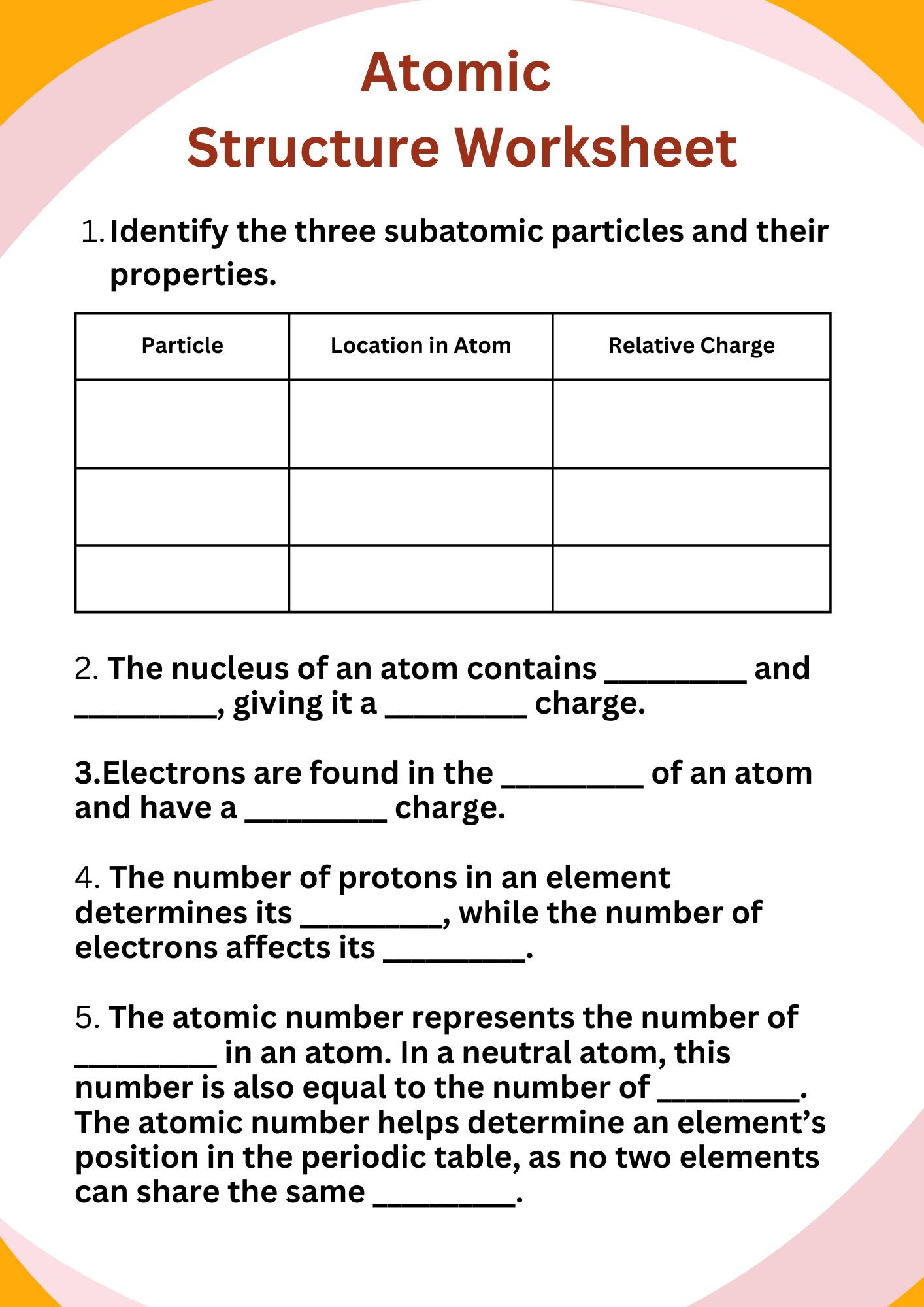
The atomic structure is made up of three primary subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of these particles plays a vital role in determining the atom’s identity, stability, and chemical behavior.
1. Protons
Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus (the dense center) of an atom. Each element is defined by the number of protons it has, known as the atomic number. For example, all hydrogen atoms have exactly one proton. The number of protons determines the element’s identity and its position on the periodic table.
2. Neutrons
Neutrons are neutral particles, meaning they carry no charge, and they are also located in the nucleus alongside protons. Neutrons add mass to the atom and help stabilize the nucleus. Atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. For example, Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon with 6 and 8 neutrons, respectively.
3. Electrons
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus in specific regions called energy levels or shells. They are much smaller in mass compared to protons and neutrons. The arrangement of electrons, especially in the outermost shell (called valence electrons), determines how an atom reacts chemically and forms bonds with other atoms.
How to Use an Atomic Structure Worksheet?
1️⃣ Understand Atomic Basics: Before starting, review key concepts such as protons, neutrons, electrons, atomic number, and mass number. A strong foundation in these topics is essential for accurately completing the worksheet.
2️⃣ Follow the Instructions Carefully: Each worksheet may have different tasks, such as identifying atomic components, drawing atomic models, or calculating isotopes. Read the instructions thoroughly to know what is expected.
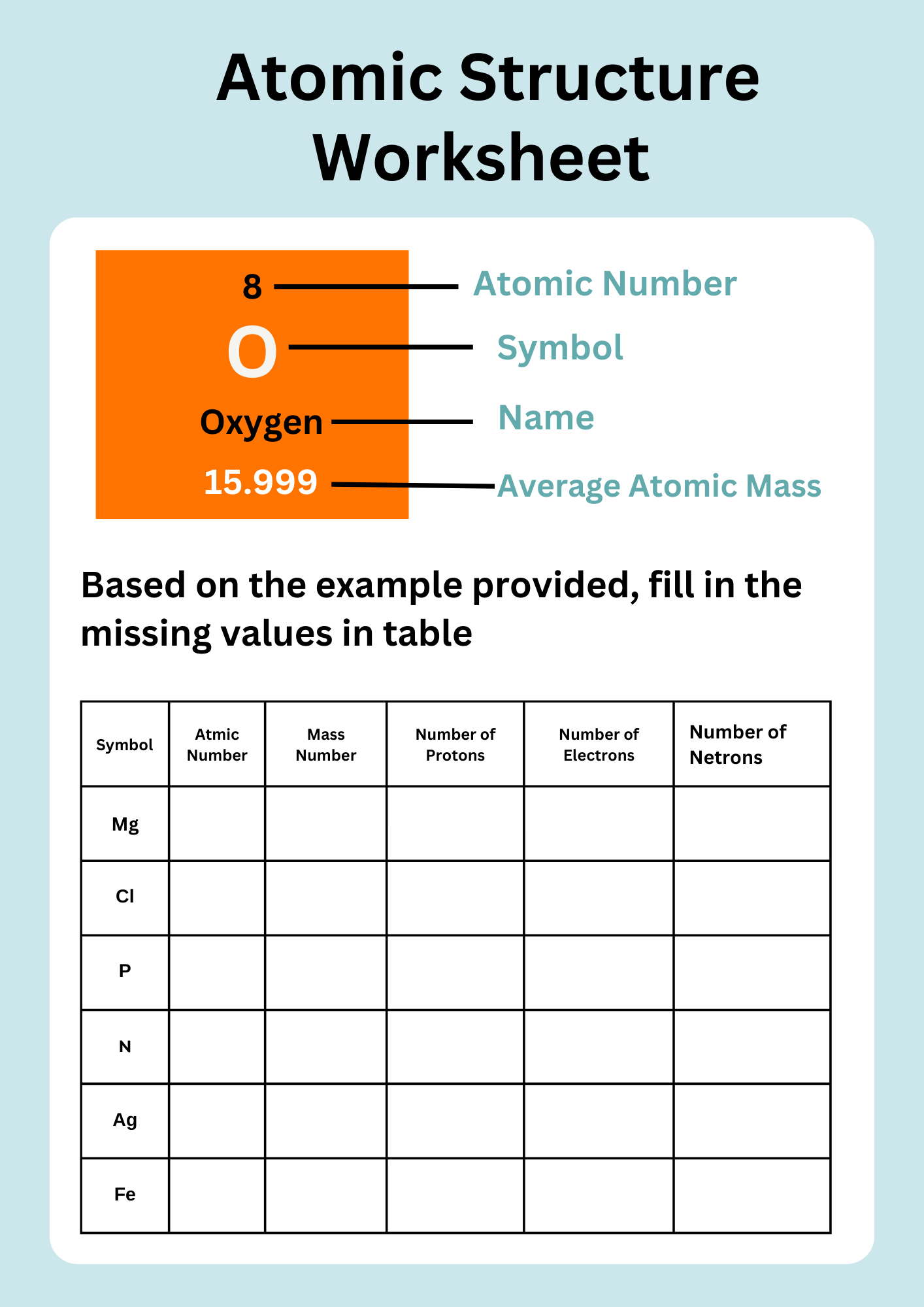
3️⃣ Determine Subatomic Particles: Use the periodic table to find the atomic number (protons) and mass number (protons + neutrons) for each element. Apply formulas like Neutrons = Mass Number – Atomic Number to fill in missing values.
4️⃣ Analyze Electron Configuration: Assign electrons to energy levels following the rule (2, 8, 18, 32) per shell. If required, draw Bohr diagrams or Lewis dot structures to visualize electron arrangement.
5️⃣ Compare Isotopes and Ions: Identify isotopes based on neutron variations and determine ion charges by checking electron gain or loss. This helps in understanding atomic behavior in reactions.
6️⃣ Review and Verify: After completing the worksheet, double-check calculations and diagrams to ensure accuracy. Seek feedback from a teacher or peer to correct mistakes and reinforce learning.
What Are the Types of Atomic Structure?
Atomic structure describes the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom. Over time, scientists have developed different models to explain atomic behavior and interactions. Here are the four main types of atomic structure:
✔️ Dalton’s Atomic Model: Dalton proposed that atoms are indivisible solid spheres that combine in fixed ratios to form compounds. This was the first scientific atomic model.
✔️ Thomson’s Atomic Model: J.J. Thomson discovered electrons and suggested that they are embedded in a positively charged sphere, resembling a “plum pudding.”
✔️ Rutherford’s Atomic Model: Rutherford’s gold foil experiment proved that atoms have a dense, positively charged nucleus, with electrons orbiting around it.
✔️ Bohr’s Atomic Model: Niels Bohr refined Rutherford’s model by introducing fixed electron orbits at specific energy levels, preventing electrons from collapsing into the nucleus.