40+ FREE Punnett Square Practice Worksheet (Middle School, Biology, High School, Dihybrid Cross, Genetics, Monohybrid Cross, Inheritance, 8th Grade)
-

Monohybrid Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
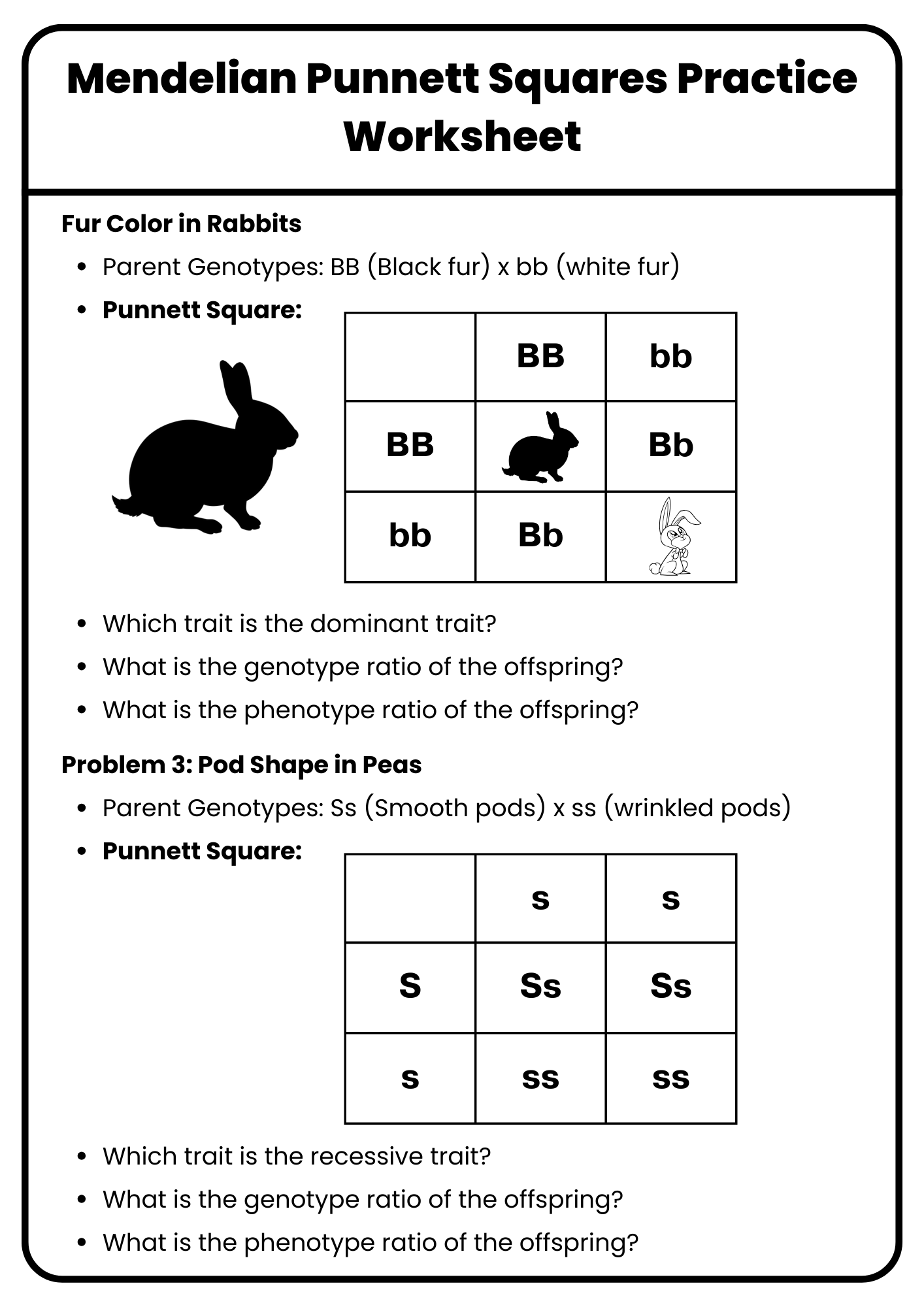
Mendelian Punnett Squares Practice Worksheet
download now -
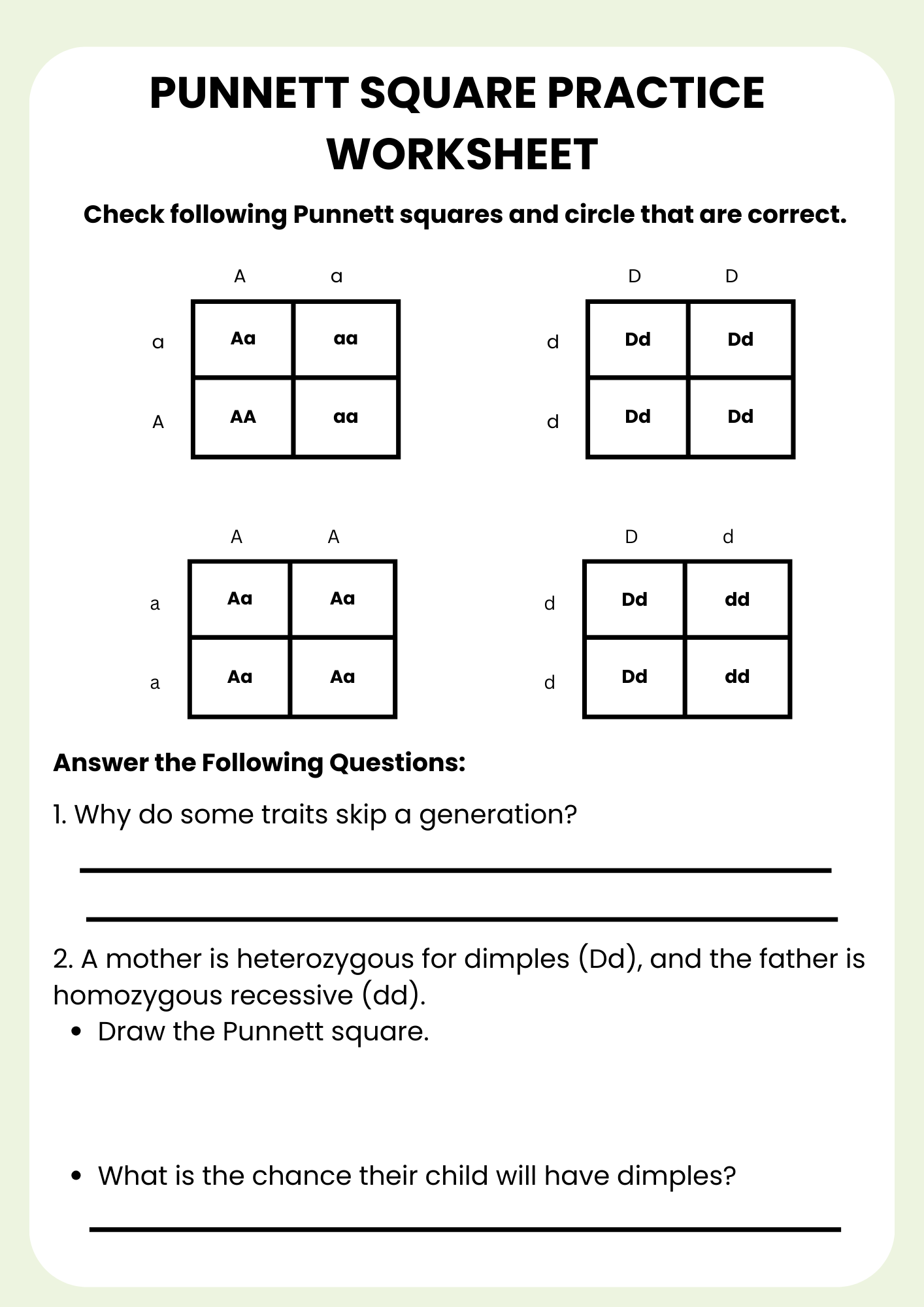
Middle School Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
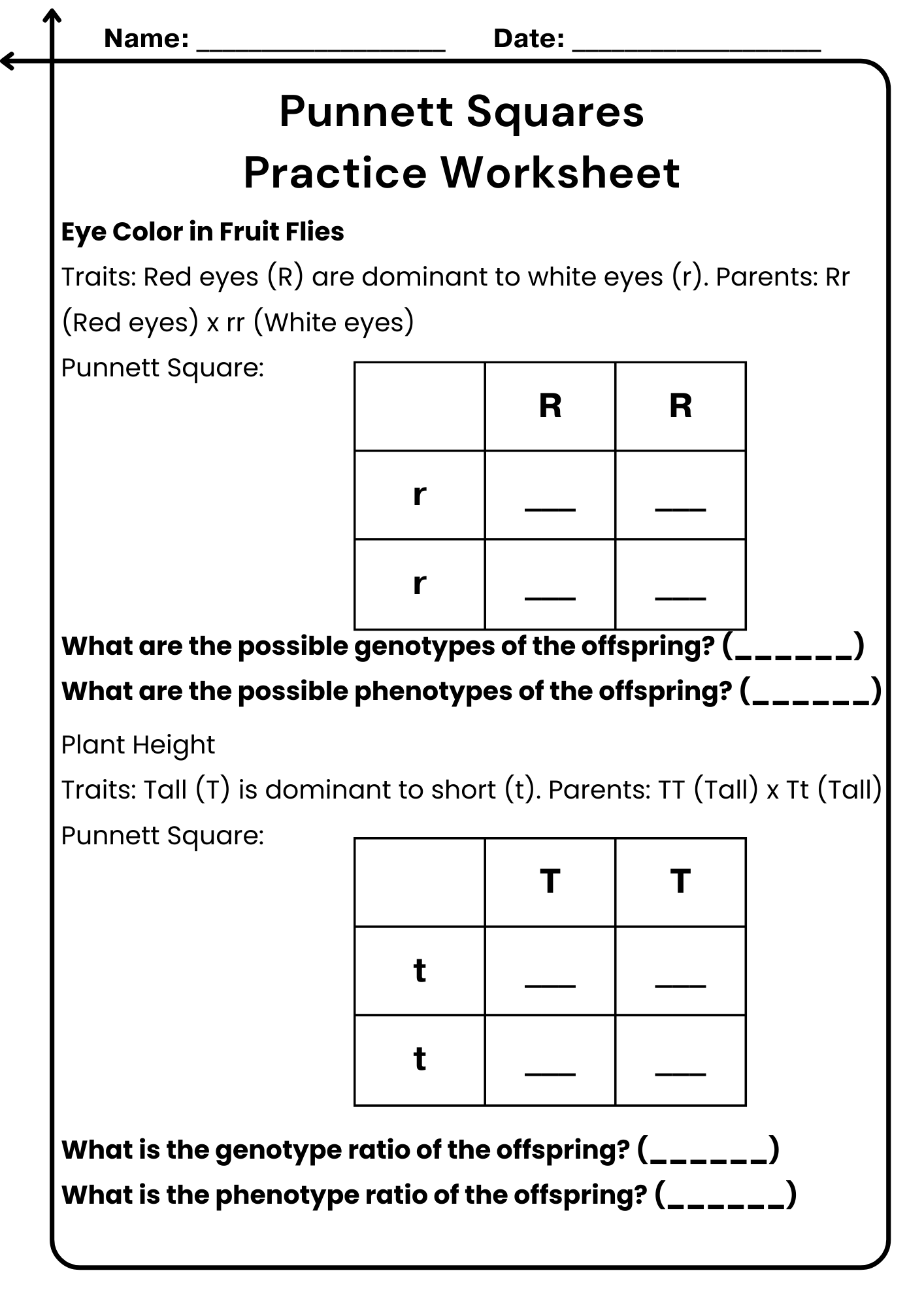
Punnett Squares Practice Worksheet
download now -
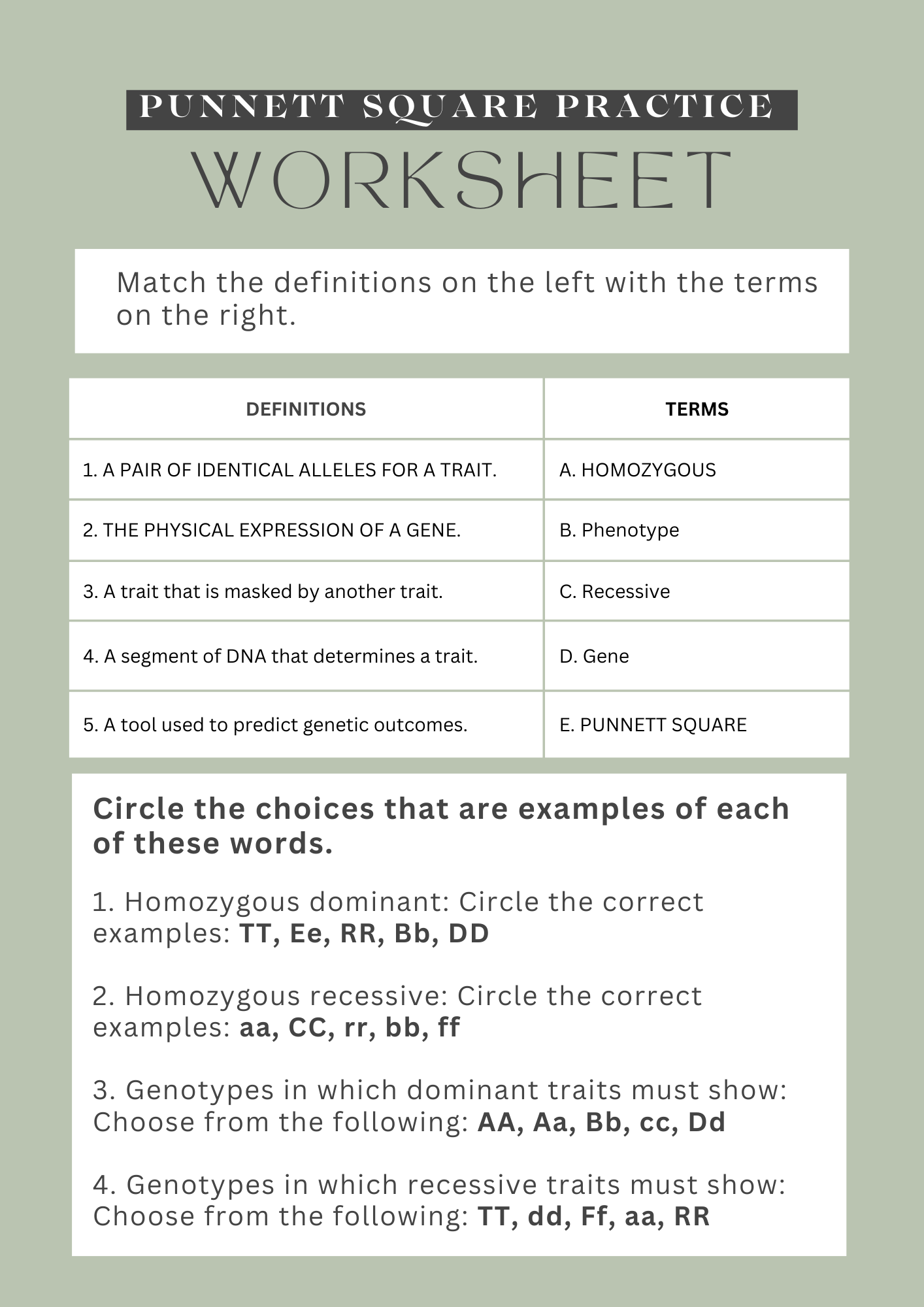
7th Grade Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
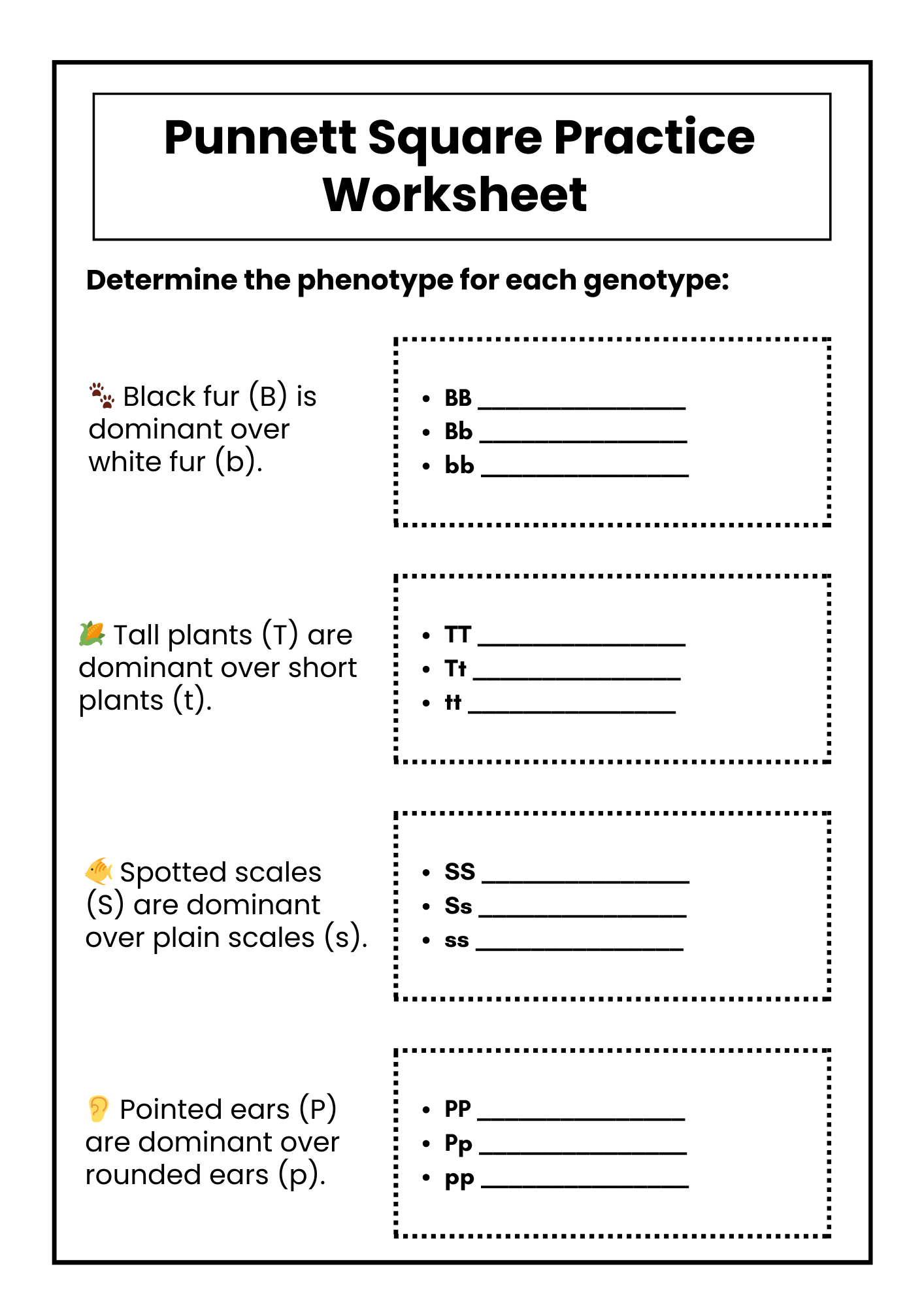
Biology Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
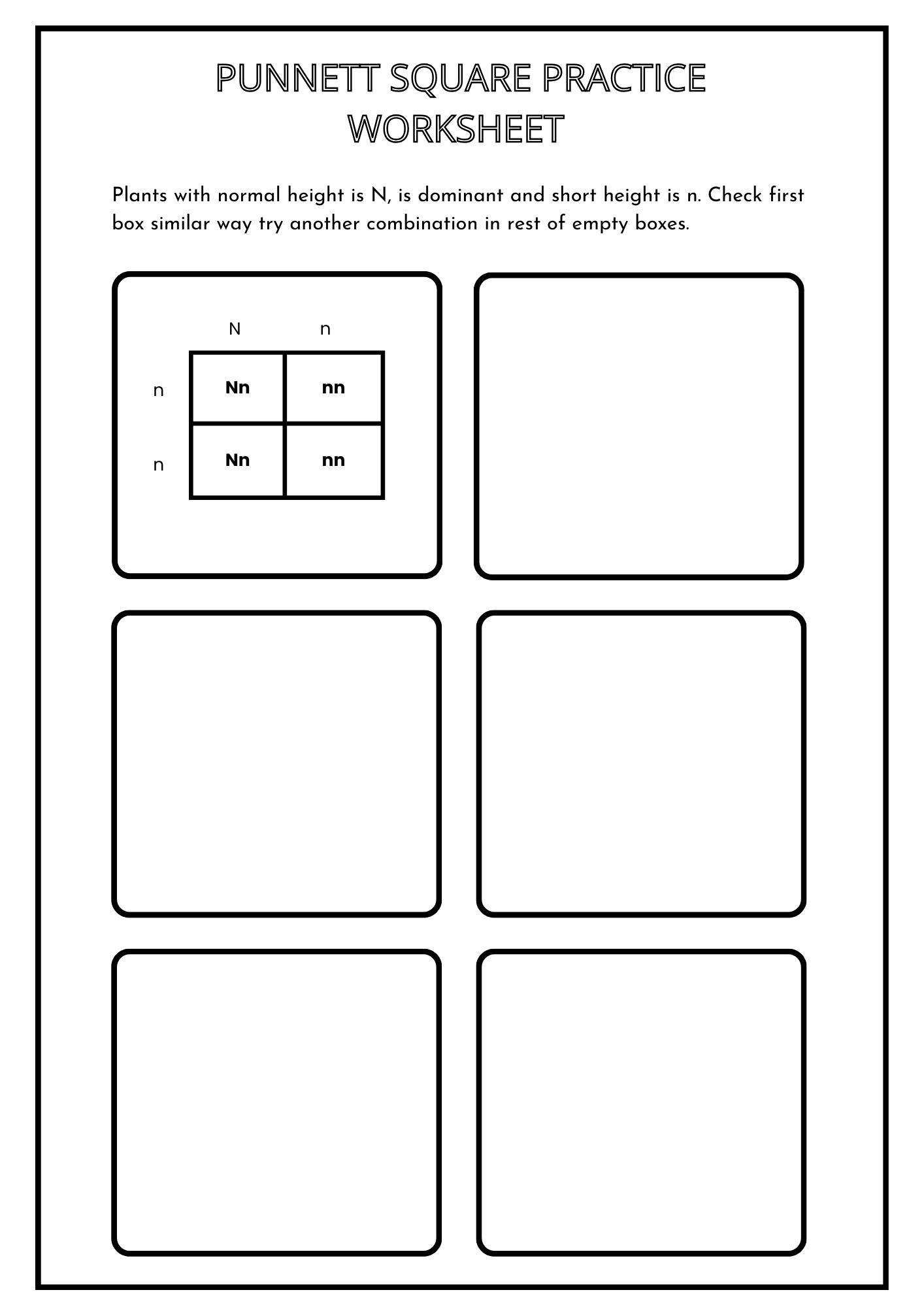
Printable Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

8th Grade Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
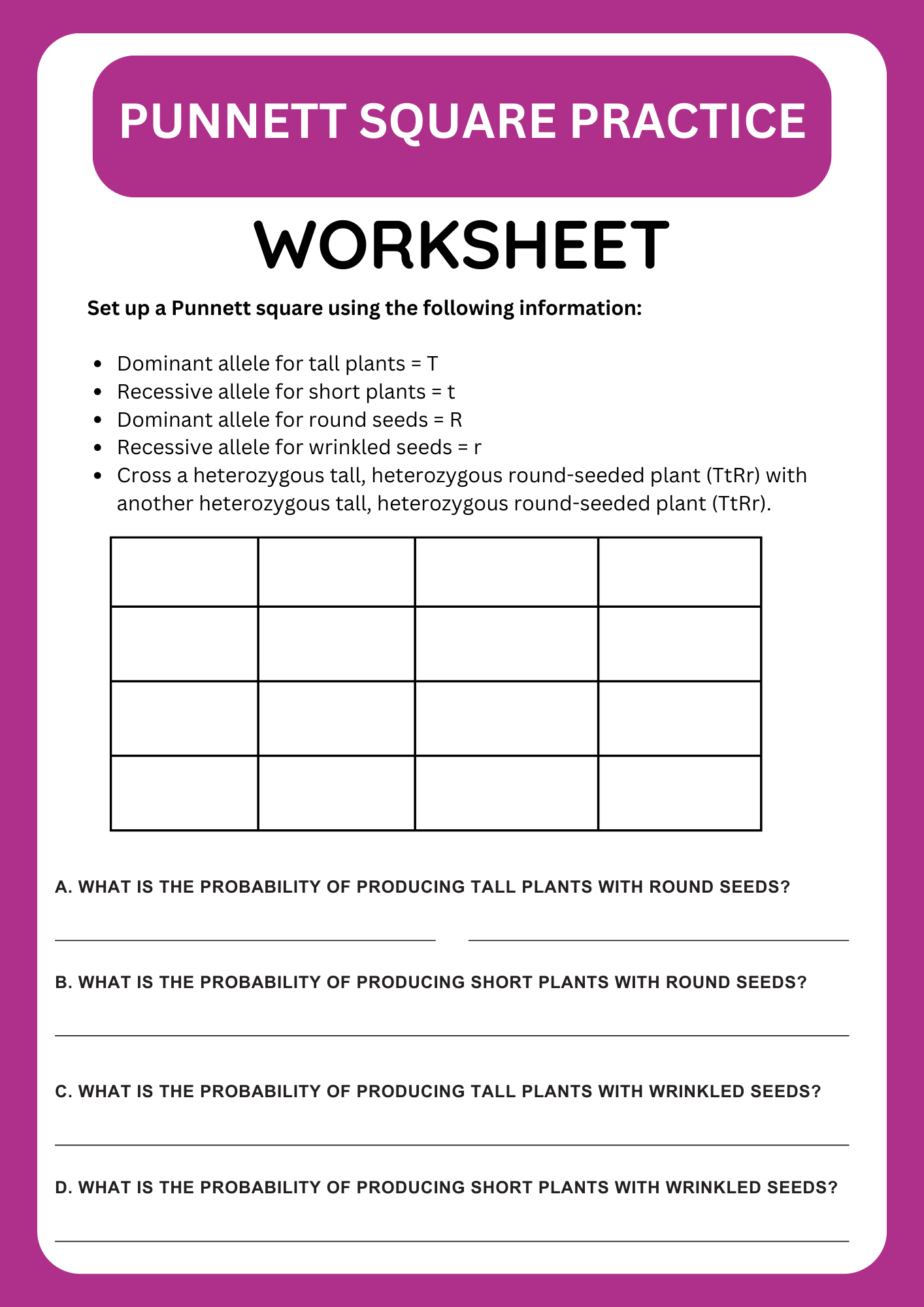
Dihybrid Cross Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
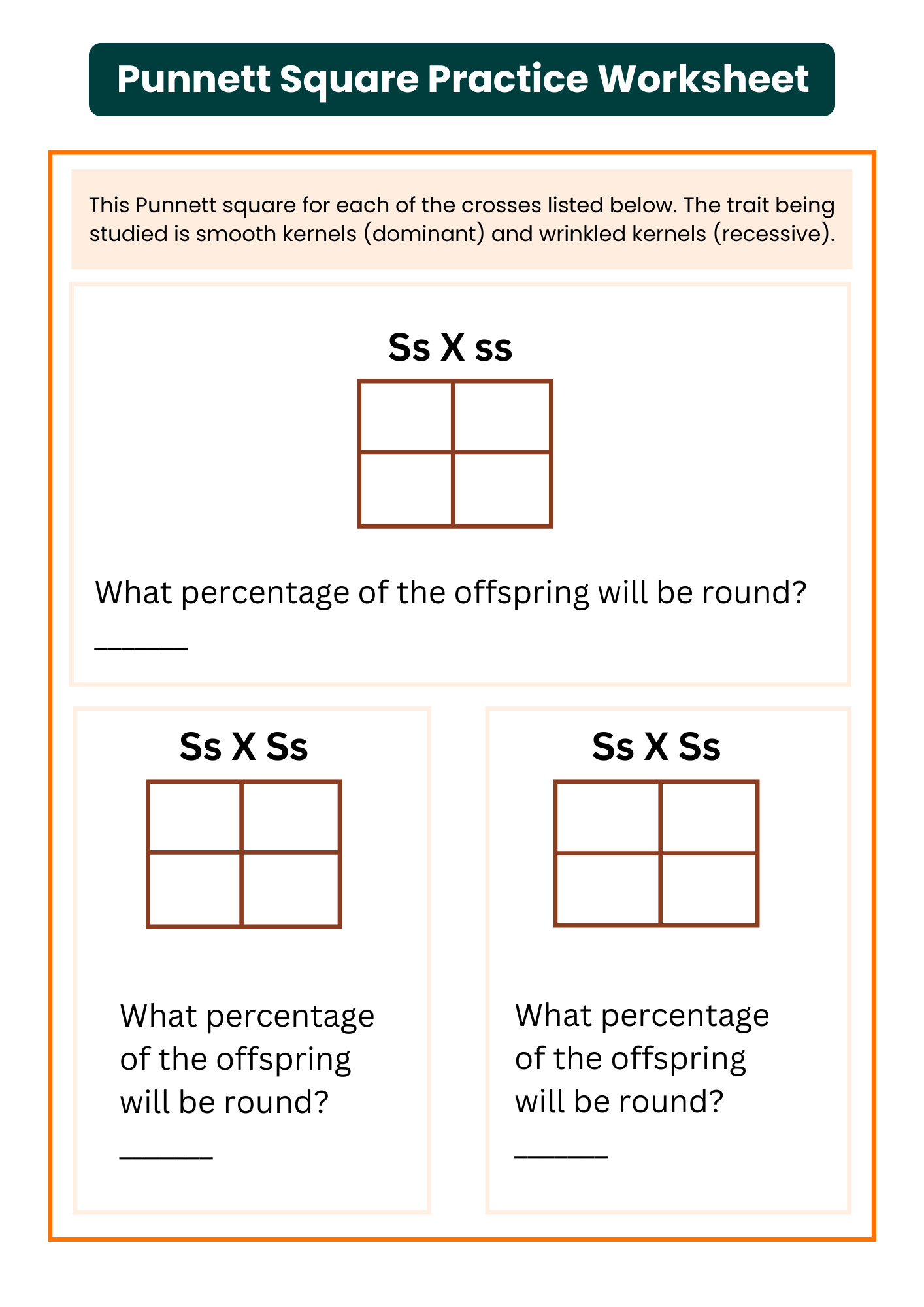
Genetic Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
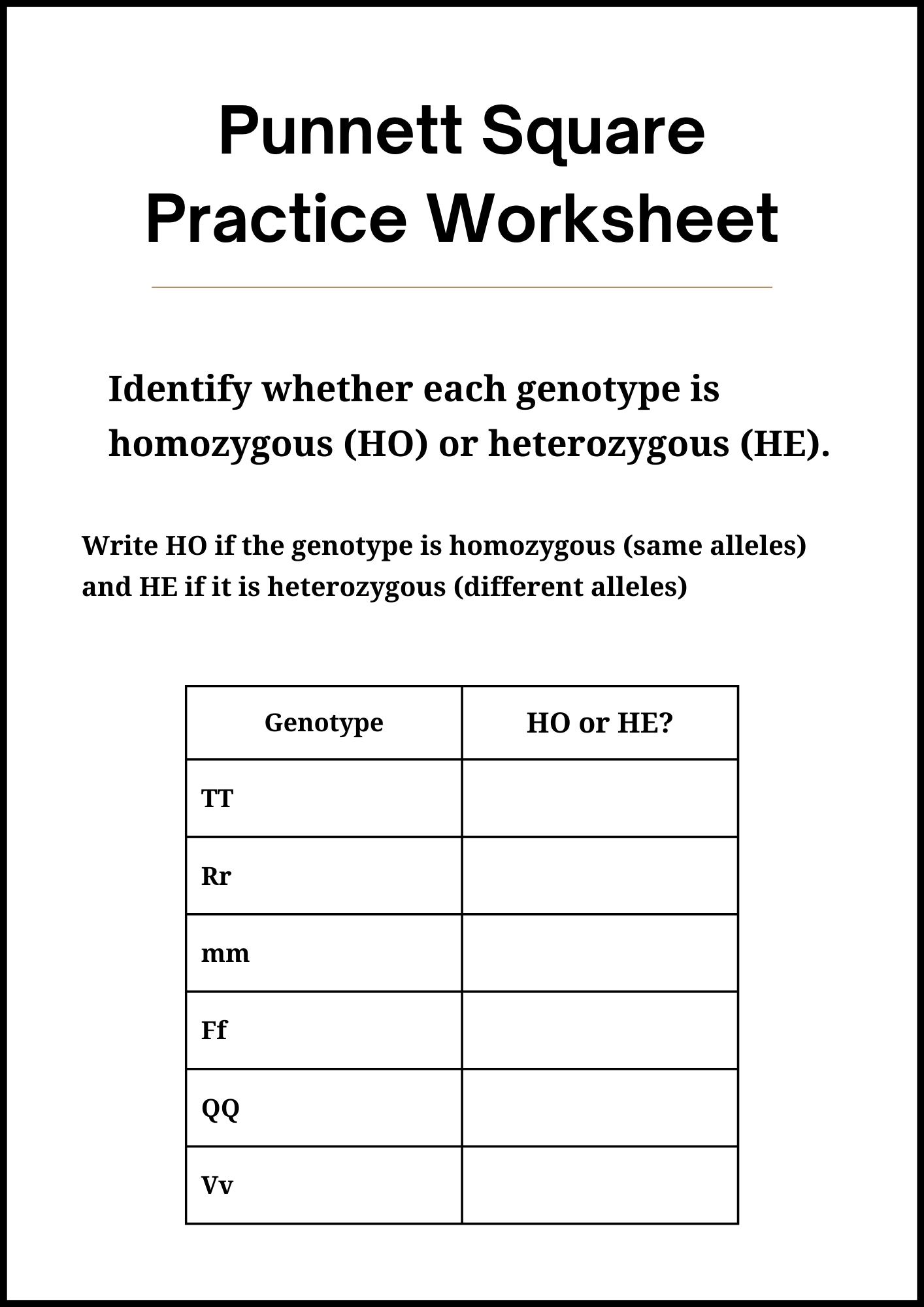
9th Grade Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Monohybrid Crosses Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Worksheet PDF
download now -
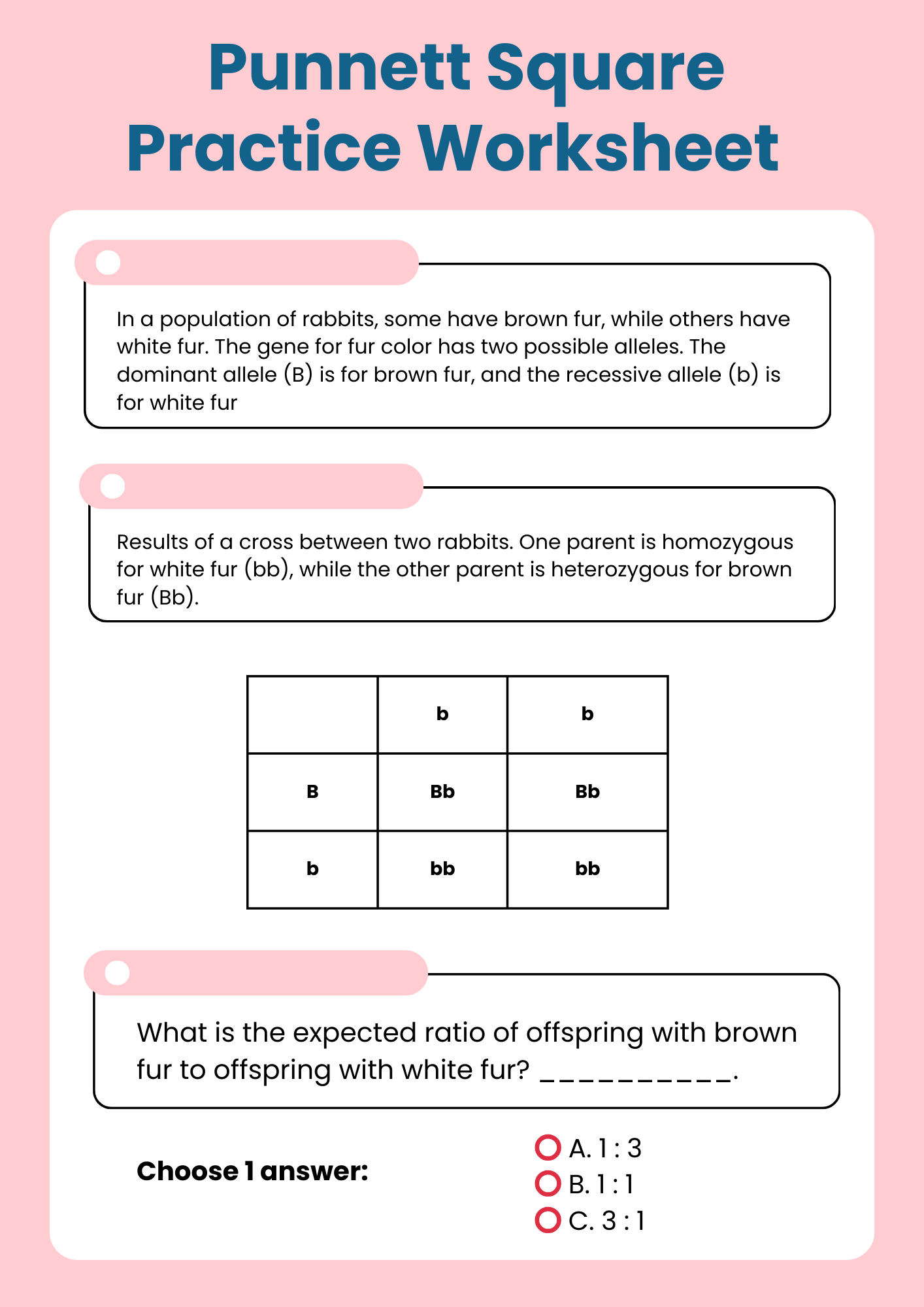
Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Vocabulary
download now -
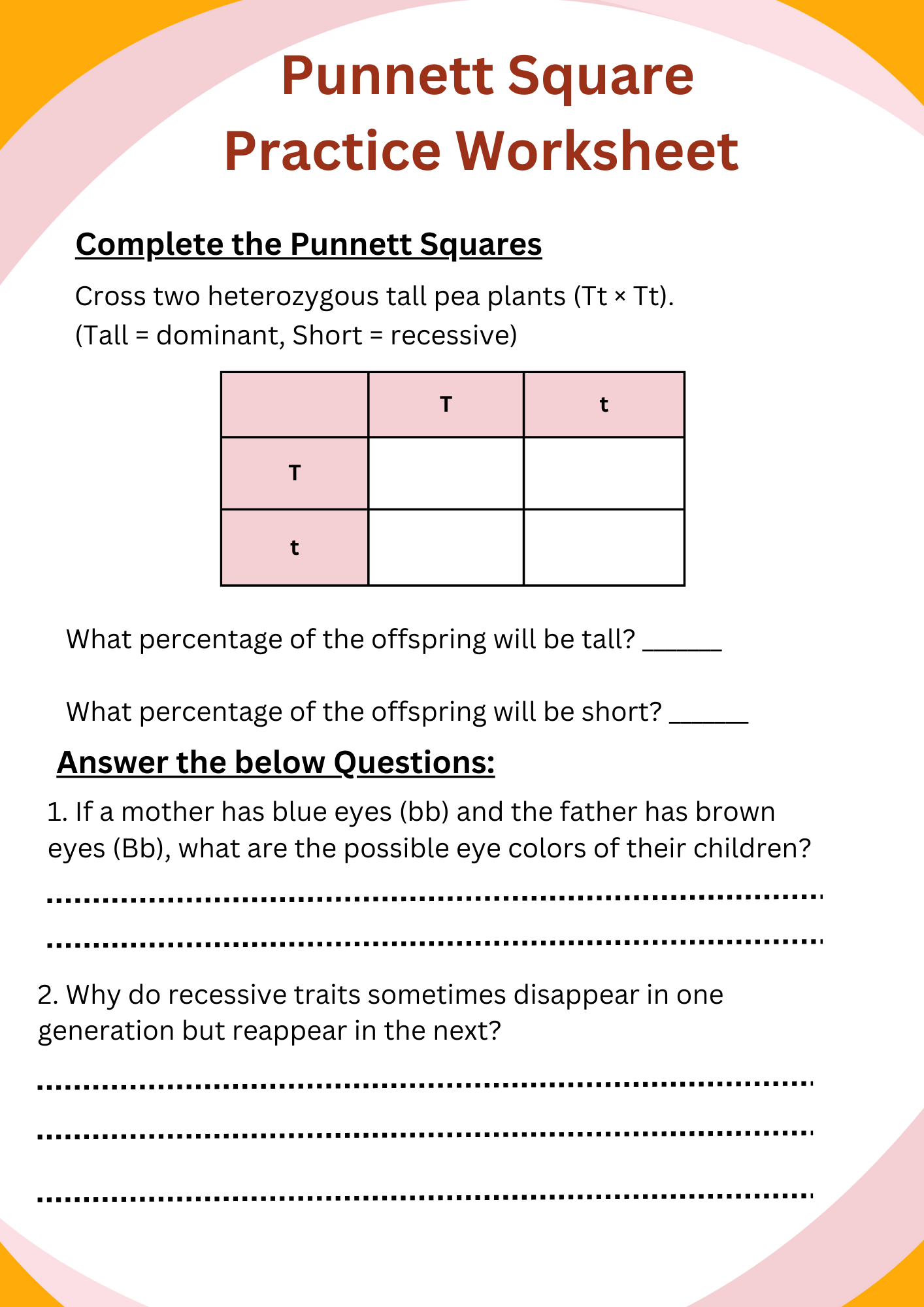
Basic Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
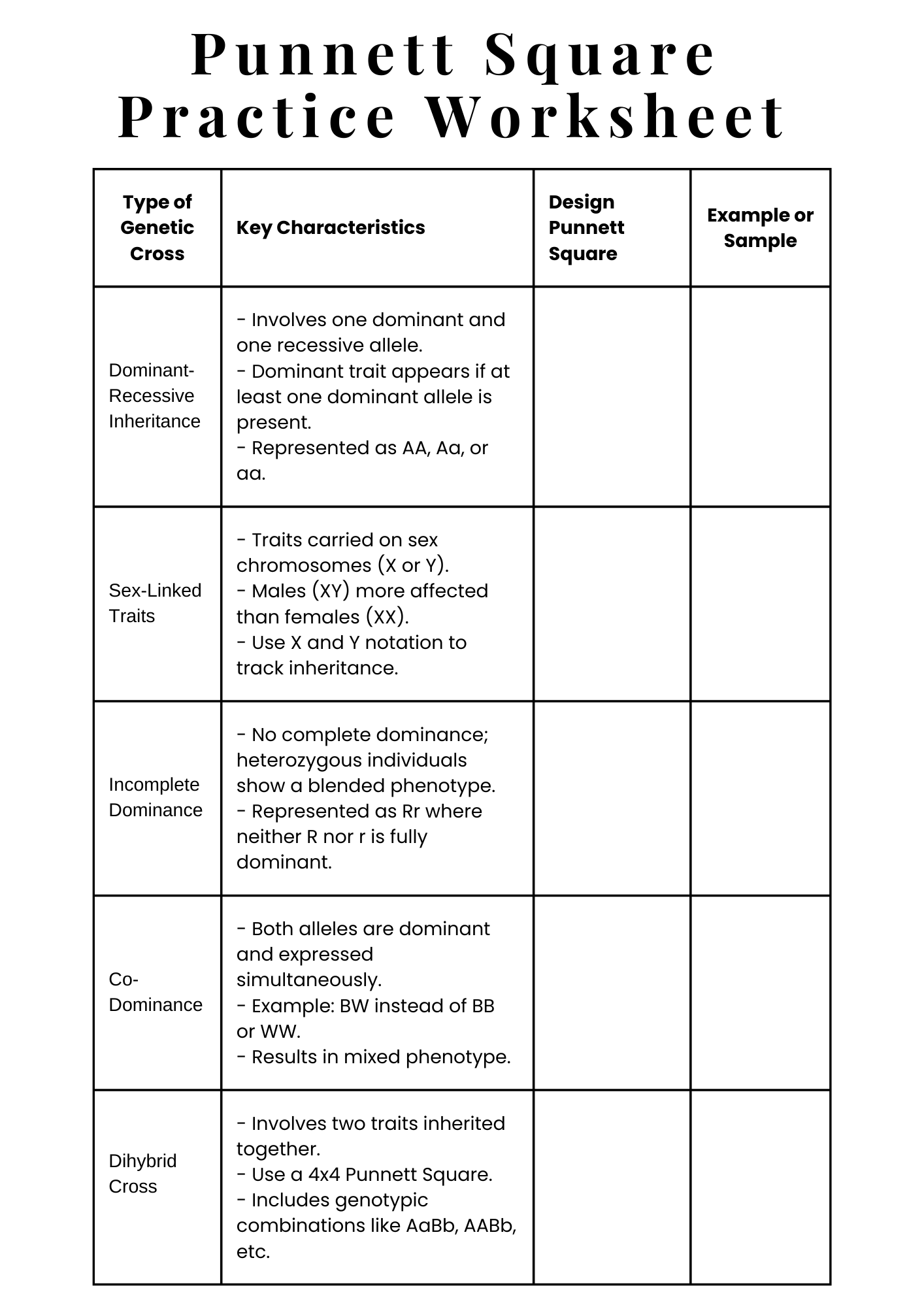
Punnett Square Cheat Sheet Practice Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Inheritance Practice Worksheet
download now -
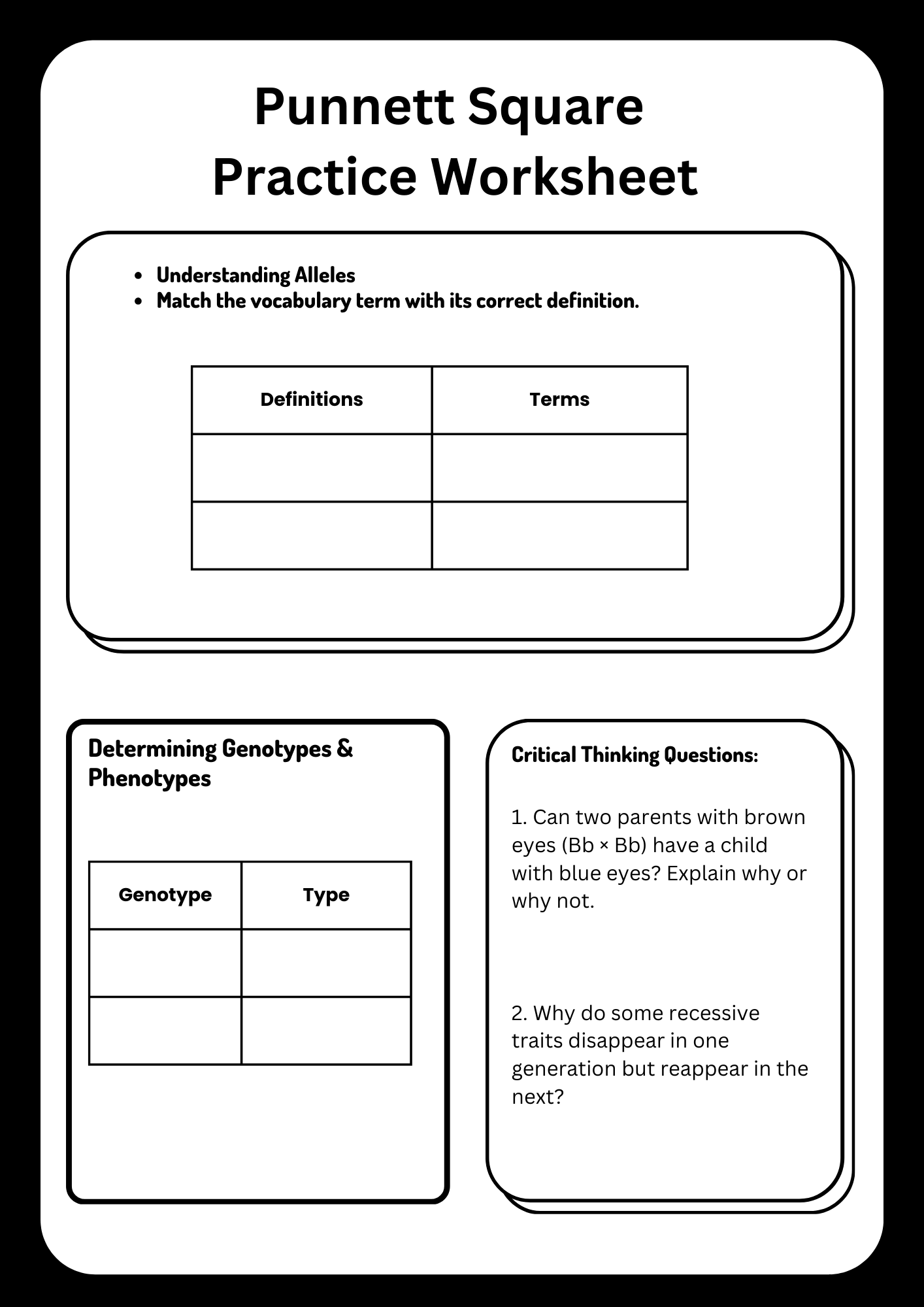
Allele Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Non-Mendelian Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
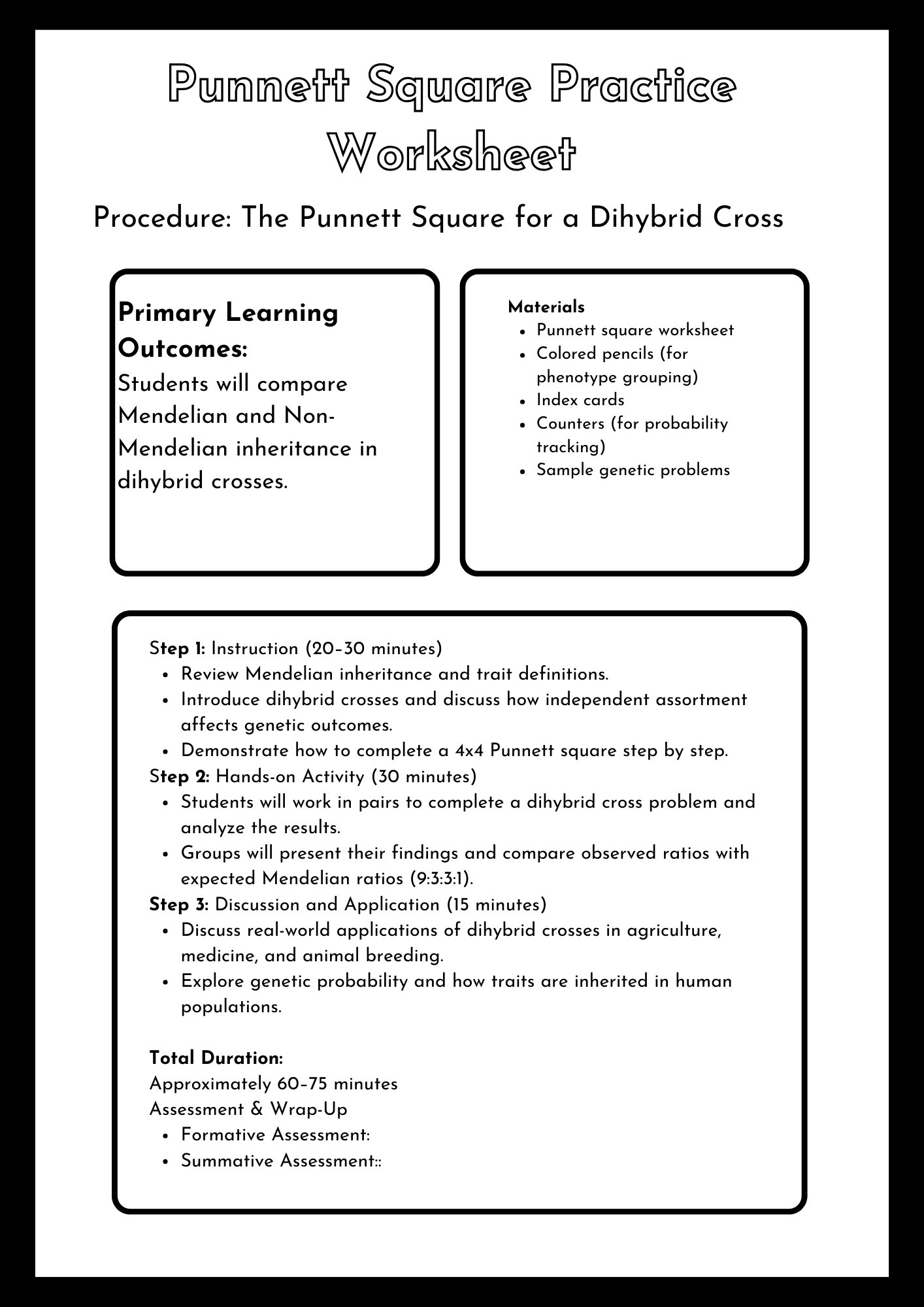
Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Lesson Plan
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Template
download now -

High School Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
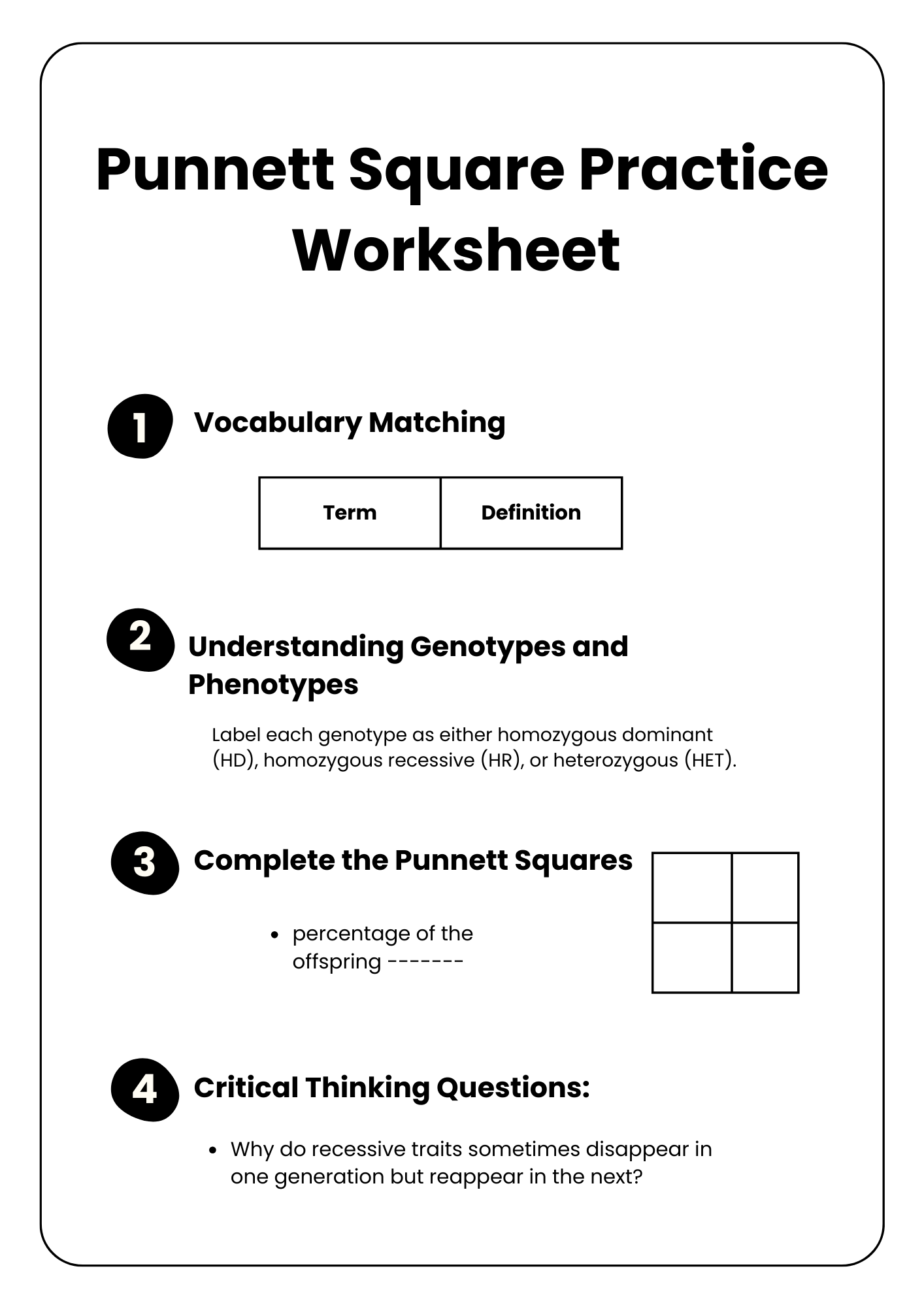
Punnett Square Practice Information Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Review
download now -
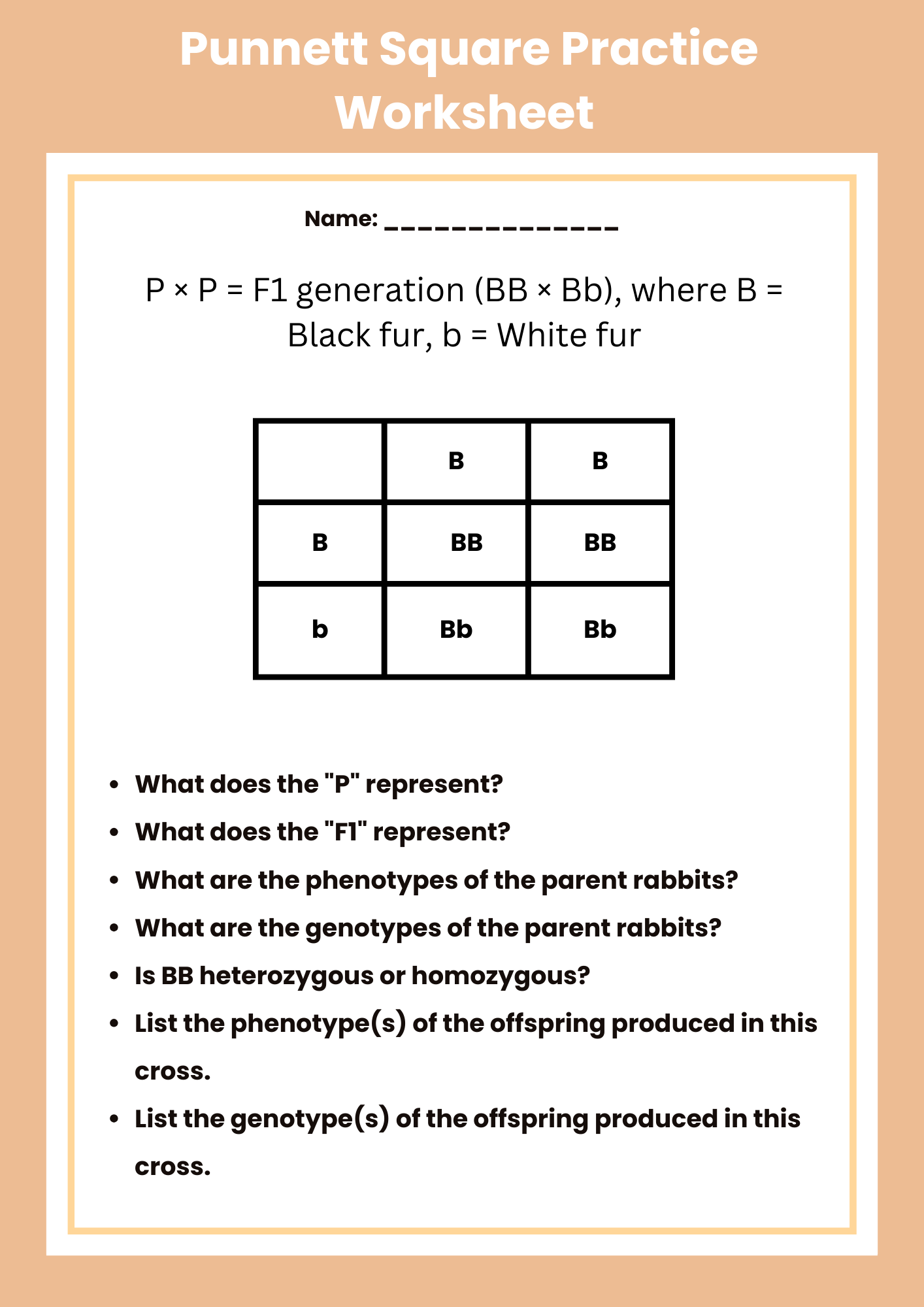
More Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Genotype Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
Punnett Square Practice Worksheet By laneylee
download now -
Pea Plant Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Dominant Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
Male Dog Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
Female Dog Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Black Fur Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Quiz
download now -
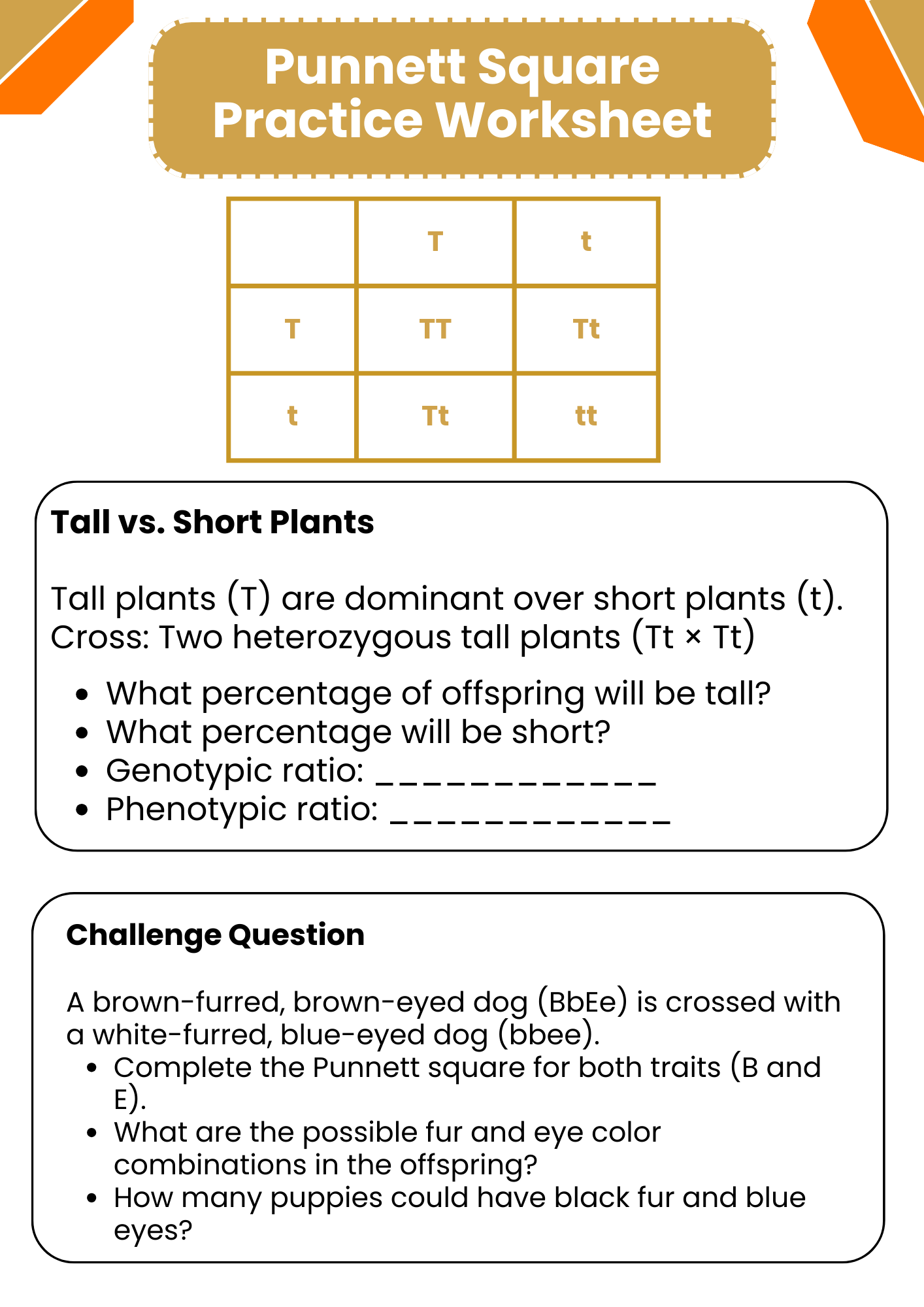
Simple Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Model
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Answer Key
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Activity Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Study Practice Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Plan Worksheet
download now -
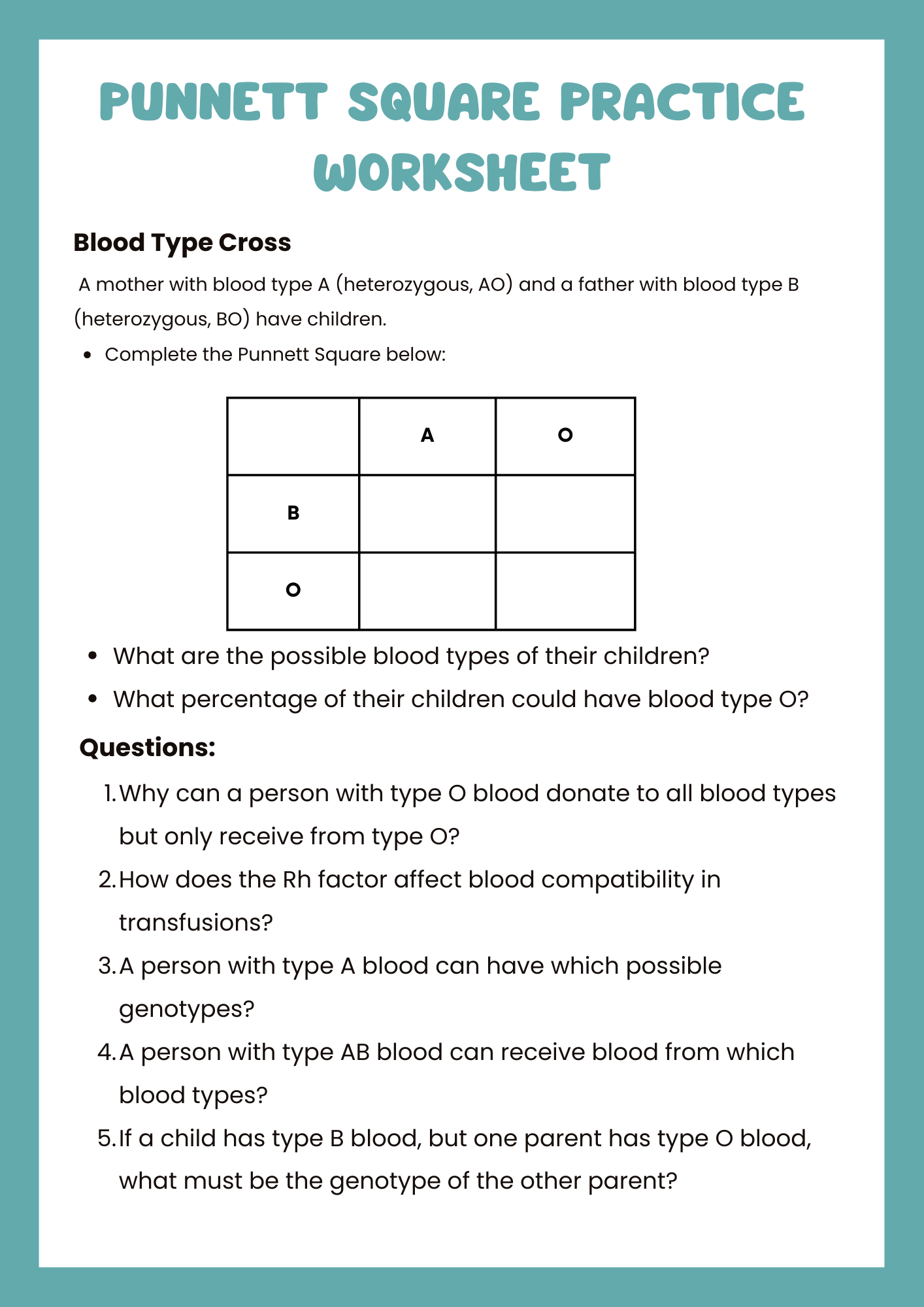
Blood Type Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -

Plant Based Punnett Square Practice Worksheet
download now -
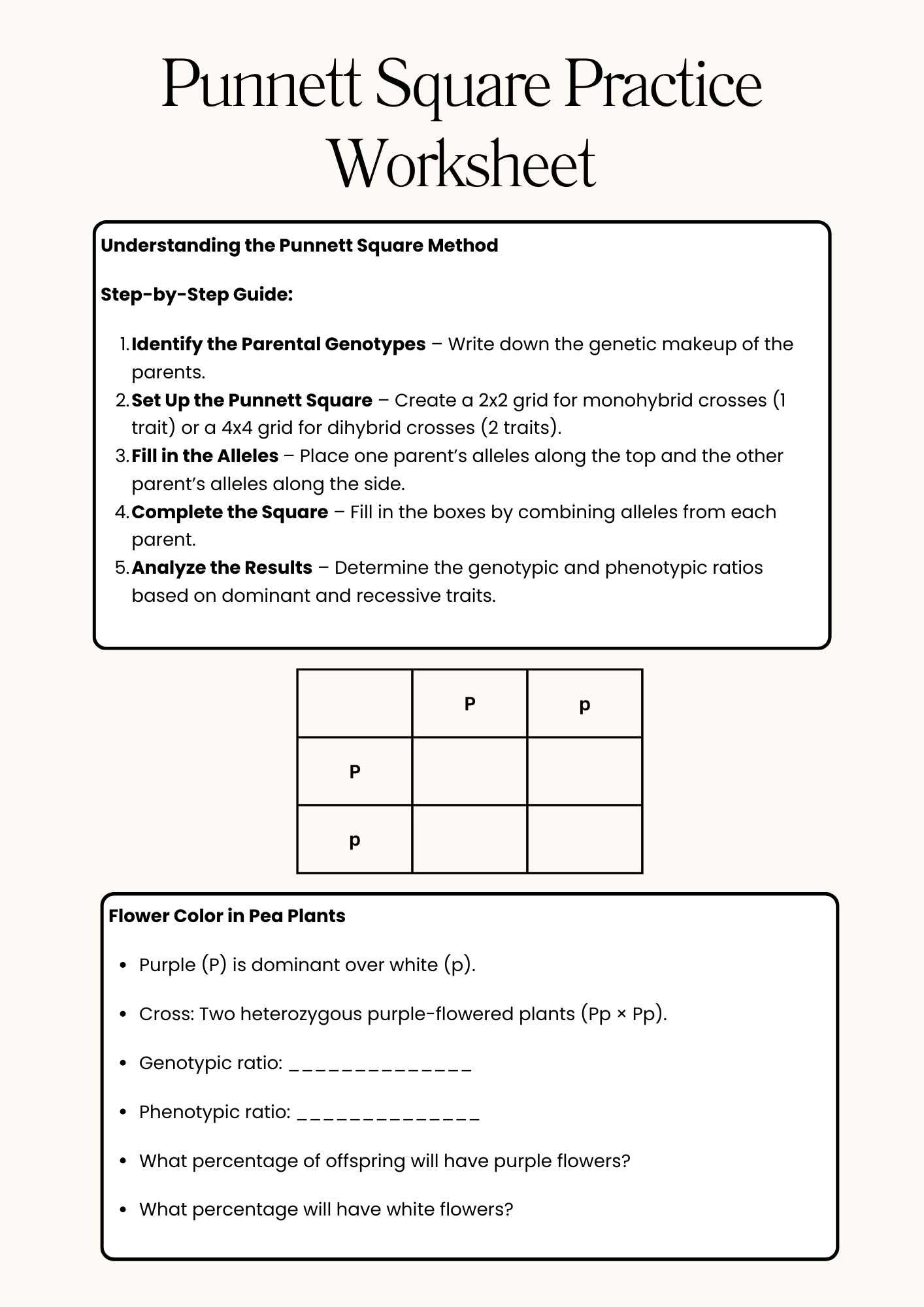
Punnett Square Practice Method Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Problems Worksheet
download now -

Punnett Square Practice Mutation Worksheet
download now
Free Printable Punnett Square Practice Worksheet To Download
40+ FREE Punnett Square Practice Worksheet (Middle School, Biology, High School, Dihybrid Cross, Genetics, Monohybrid Cross, Inheritance, 8th Grade)
What is a Punnett Square Practice Worksheet?
Why is Punnett Square Practice Important for Students?
How to Use a Punnett Square Practice Worksheet?
How to Do a Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Step by Step?
What is a Punnett Square Practice Worksheet?
A Punnett Square Practice Worksheet is an educational tool designed to help students understand the principles of genetic inheritance and how traits are passed from parents to offspring. These worksheets typically include exercises on dominant and recessive alleles, homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, monohybrid and dihybrid crosses, and probability calculations in genetics. By completing these activities, students reinforce their knowledge of Mendelian inheritance, genotype-phenotype relationships, and genetic variations. The worksheets often incorporate engaging problems involving predicting offspring traits, identifying genetic ratios, and analyzing inheritance patterns, making them essential for mastering the fundamentals of genetics. This structured practice enhances critical thinking and provides a strong foundation in biology, preparing students for more advanced concepts in heredity, evolution, and biotechnology
Why is Punnett Square Practice Important for Students?
Mastering Punnett squares is essential for students studying genetics, as it enhances their understanding of inheritance patterns and probability in biology. Practicing Punnett squares allows students to develop critical thinking skills and apply genetic principles to real-world scenarios. Here’s why Punnett square practice is particularly important for students:
✅ Builds a Strong Genetics Foundation: Understanding Punnett squares helps students grasp fundamental genetic concepts, including dominant and recessive traits, genotypes, and phenotypes.
✅ Improves Problem-Solving Skills: Working with Punnett squares encourages logical thinking by requiring students to analyze genetic crosses and predict trait inheritance in offspring.
✅ Prepares for Advanced Biology Topics: A solid grasp of Punnett squares sets the stage for more complex topics such as genetic mutations, biotechnology, and population genetics.
✅ Applies to Real-Life Genetics: Students learn how genetics influence characteristics in humans, animals, and plants, which is useful in medical science, agriculture, and breeding programs.
✅ Enhances Understanding of Probability: Punnett squares teach students the role of probability in genetics, helping them analyze the likelihood of certain traits appearing in future generations.
How to Use a Punnett Square Practice Worksheet?
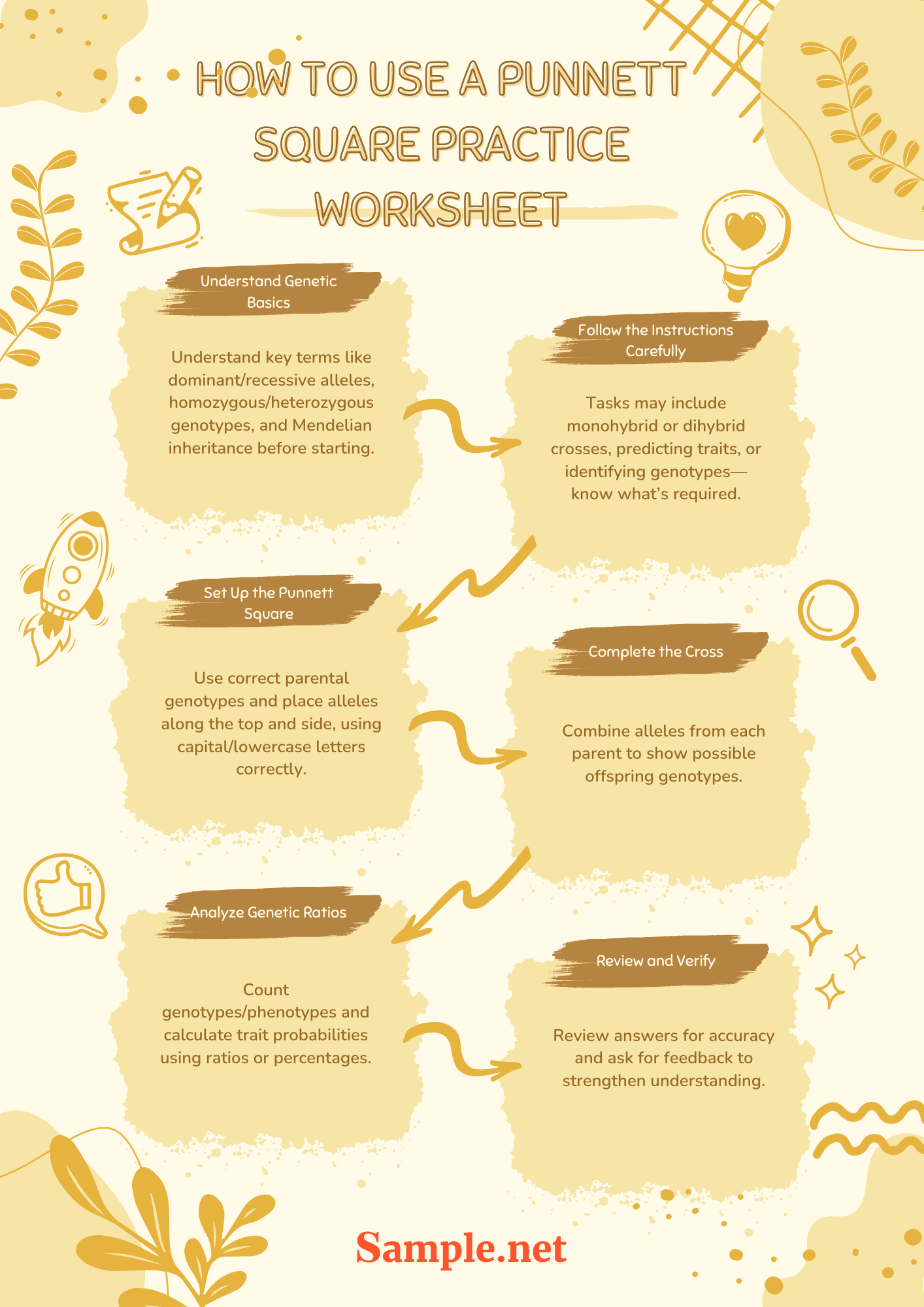
1️⃣ Understand Genetic Basics: Before starting, review key concepts such as dominant and recessive alleles, homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, and Mendelian inheritance. A strong foundation in these topics is essential for accurately completing the worksheet.
2️⃣ Follow the Instructions Carefully: Each worksheet may include different tasks, such as completing monohybrid or dihybrid crosses, predicting genetic ratios, or identifying genotypes and phenotypes. Read the instructions thoroughly to know what is expected.
3️⃣ Set Up the Punnett Square: Identify the parental genotypes and place them along the top and side of the square. Use proper notation (e.g., capital letters for dominant alleles and lowercase for recessive alleles) to ensure accuracy.
4️⃣ Complete the Cross: Fill in the Punnett square by combining alleles from each parent in the corresponding boxes. This helps visualize the possible genetic outcomes for the offspring.
5️⃣ Analyze Genetic Ratios: Count and record the number of different genotypes and phenotypes. Determine the probability of each trait appearing in the offspring using percentages or ratios.
6️⃣ Review and Verify: After completing the worksheet, double-check calculations and allele combinations to ensure accuracy. Seek feedback from a teacher or peer to correct mistakes and reinforce learning.
How to Do a Punnett Square Practice Worksheet Step by Step?
1️⃣ Understand the Genetic Cross: Before starting, identify whether the problem involves a monohybrid cross (one trait) or a dihybrid cross (two traits). Review key concepts like dominant and recessive alleles, homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, and Mendelian inheritance.
2️⃣ Identify Parental Genotypes: Determine the genetic makeup of both parents. Use capital letters for dominant alleles (e.g., T for tall) and lowercase letters for recessive alleles (e.g., t for short) to differentiate traits.
3️⃣ Set Up the Punnett Square:
- Draw a square grid (2×2 for monohybrid, 4×4 for dihybrid).
- Write one parent’s alleles across the top and the other parent’s alleles along the left side.
- Ensure correct letter placement to avoid mistakes in combinations.
4️⃣ Fill in the Punnett Square:
- Combine each allele from the top row with the corresponding allele from the side row.
- Each box represents a possible genetic combination for the offspring.
- Be mindful of dominant and recessive allele pairings.
5️⃣ Determine Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios:
- Genotypic Ratio: Count the number of homozygous dominant (AA), heterozygous (Aa), and homozygous recessive (aa) combinations.
- Phenotypic Ratio: Identify how many offspring will display the dominant or recessive traits.
6️⃣ Interpret the Results: Analyze the probabilities of each genotype and phenotype appearing in the offspring. Use percentages or ratios to express inheritance likelihood.
7️⃣ Review and Verify: Double-check allele combinations and calculations to ensure accuracy. If mistakes are found, redo the problem to strengthen understanding.
