50+ Unit Circle Worksheets (Trigonometric, Radians, Geometry, Degree, Interactive, Algebra 2, Math)
-
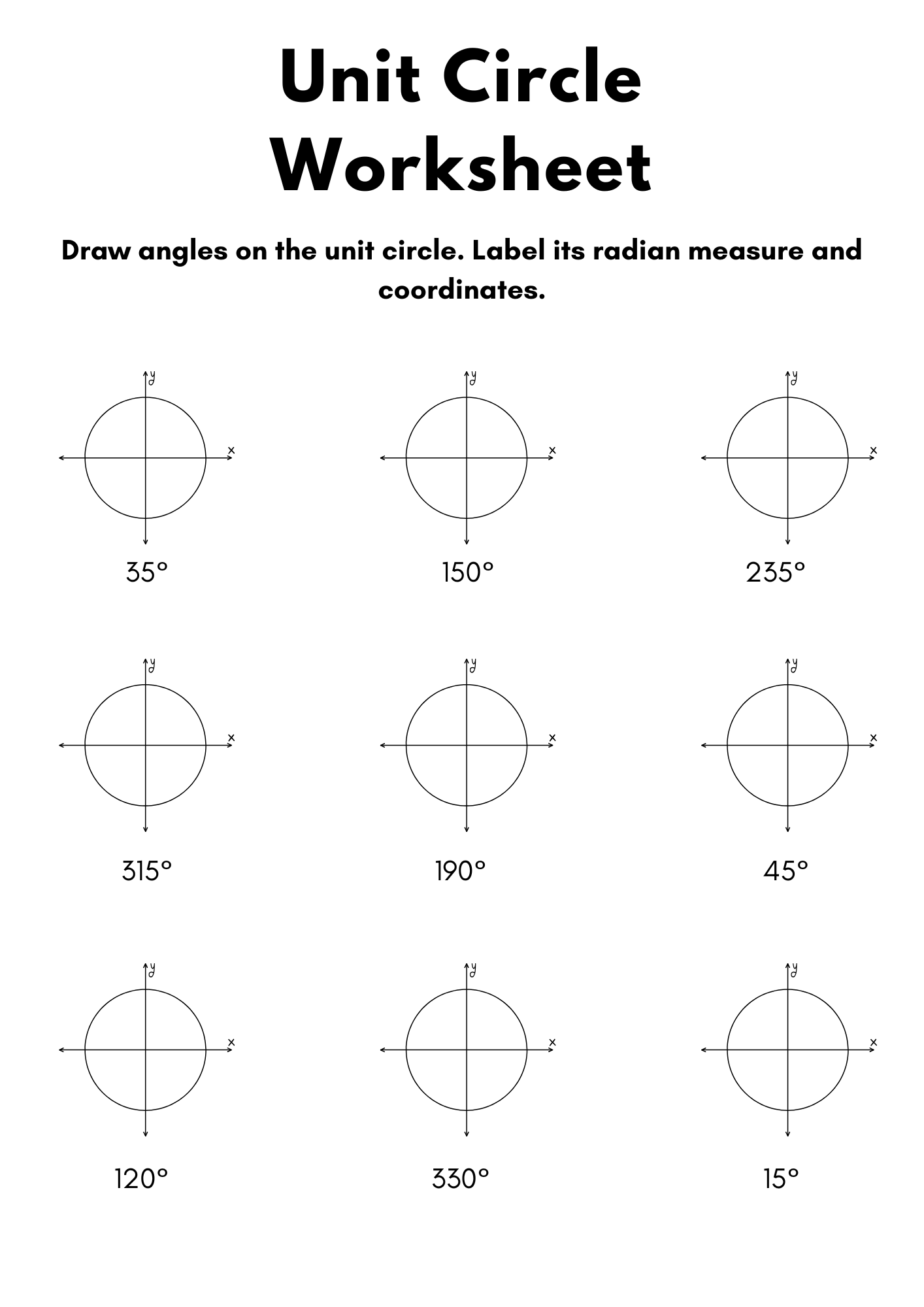
Labeled Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
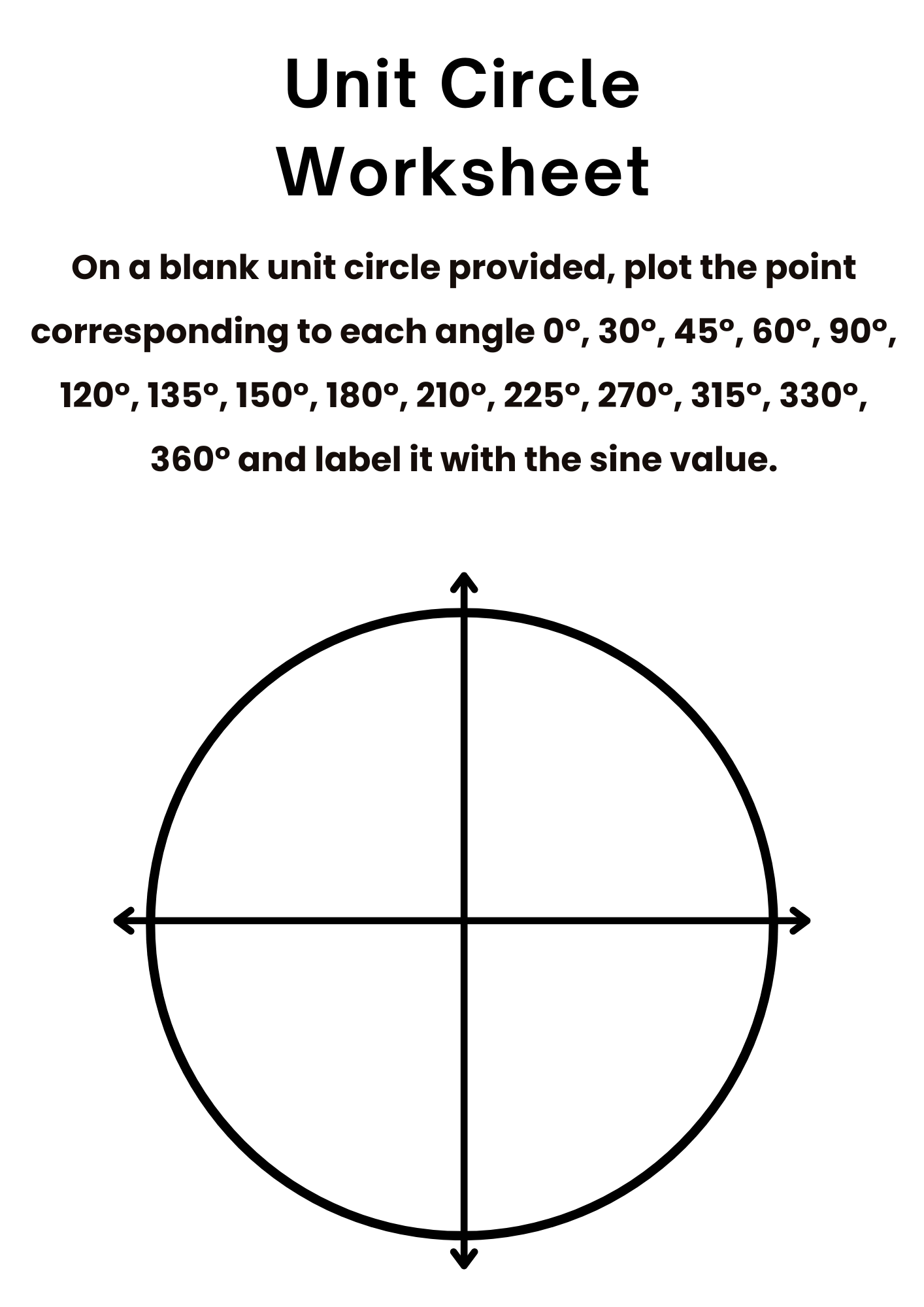
Unit Circle Worksheet for Students
download now -
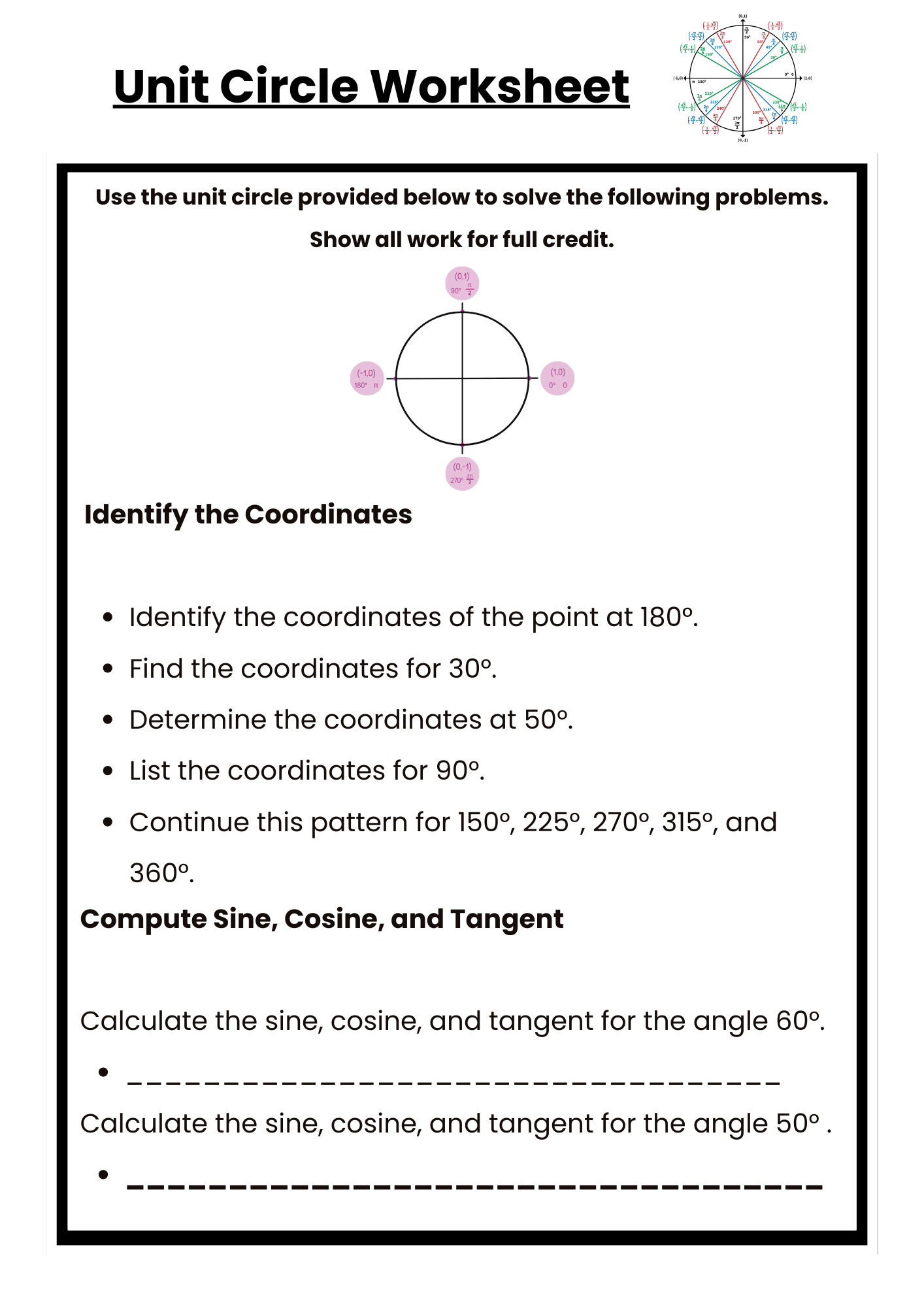
Unit Circle Worksheet for Trig Functions
download now -
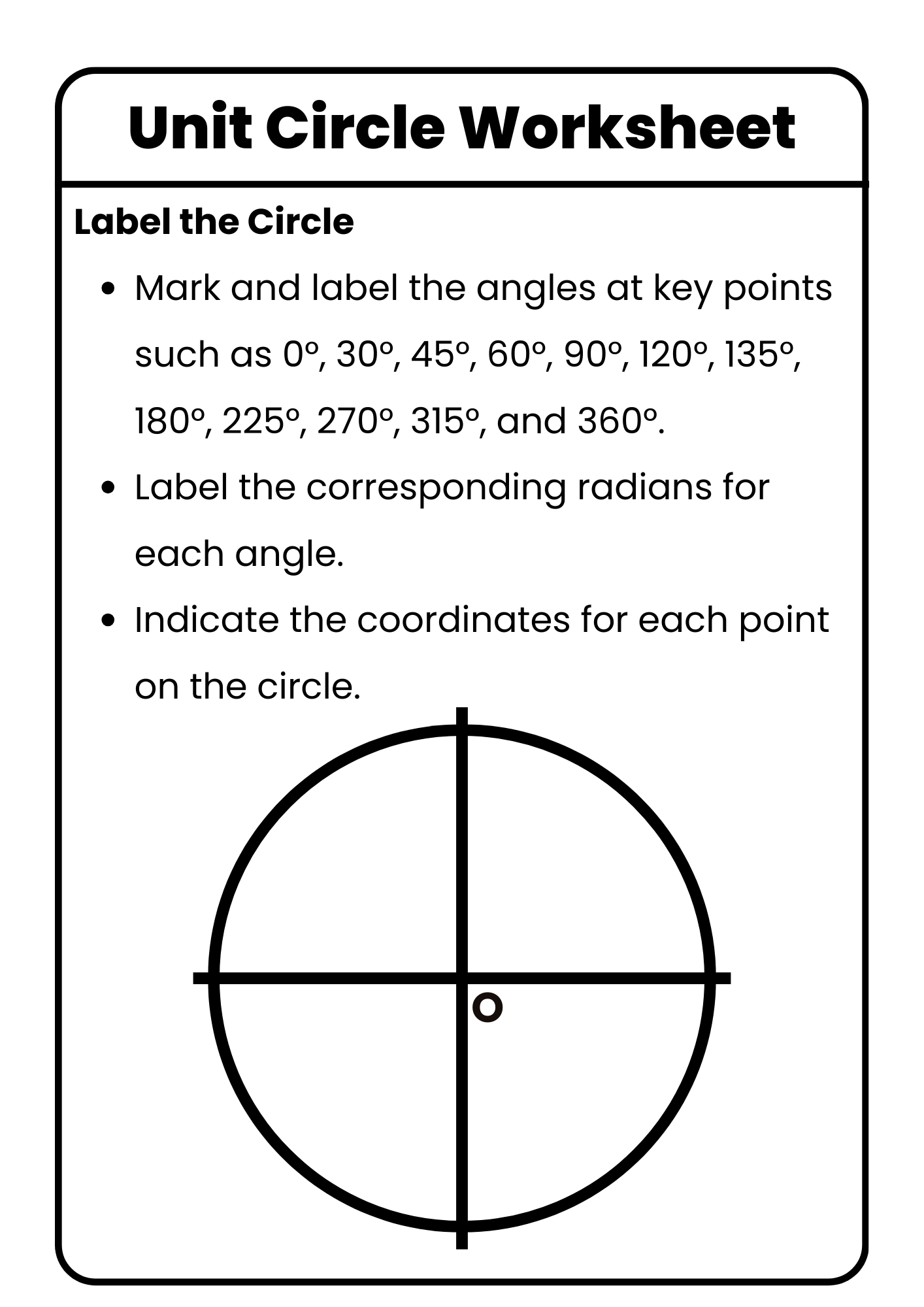
Unit Circle Worksheet Template
download now -
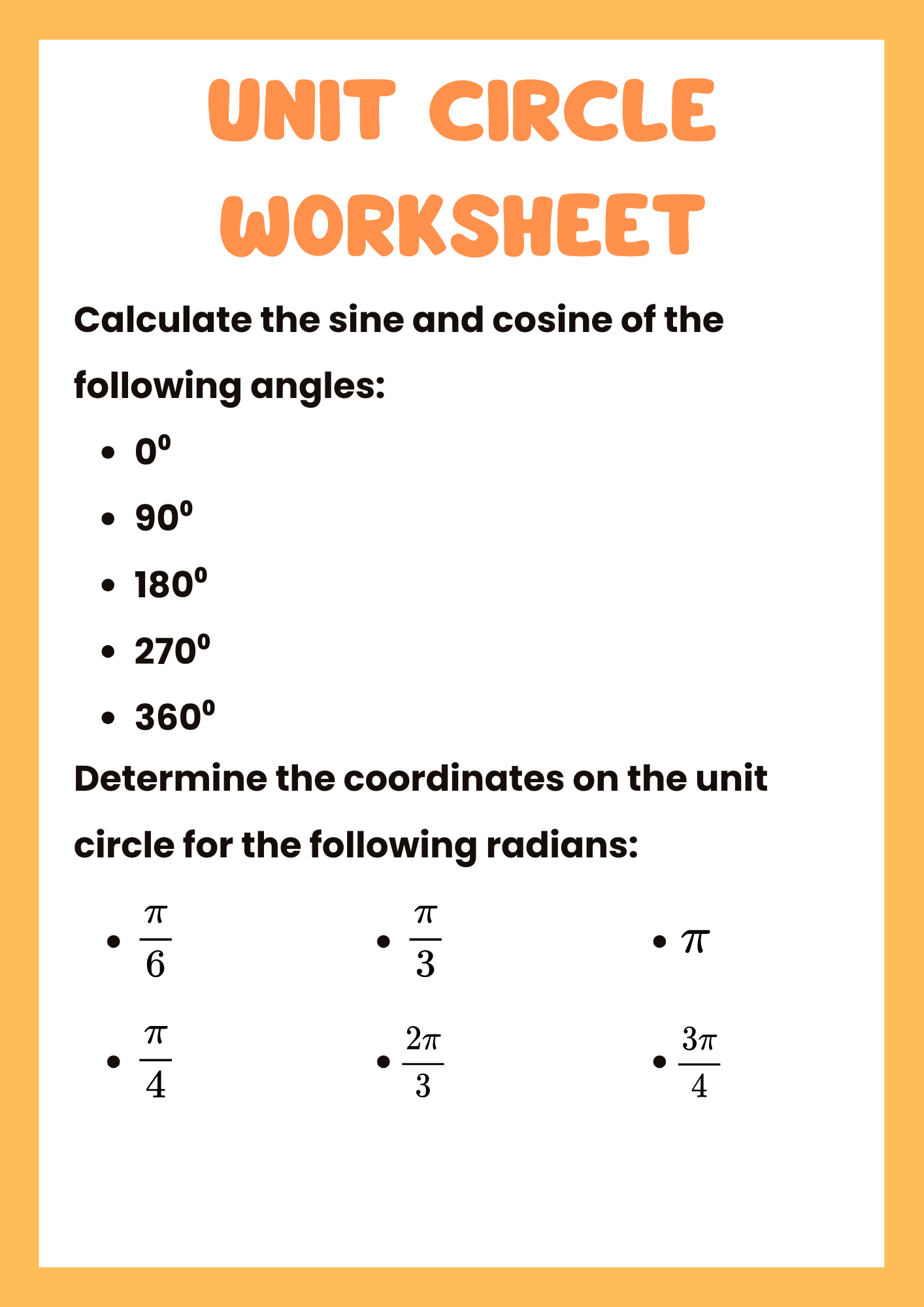
Practicing Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
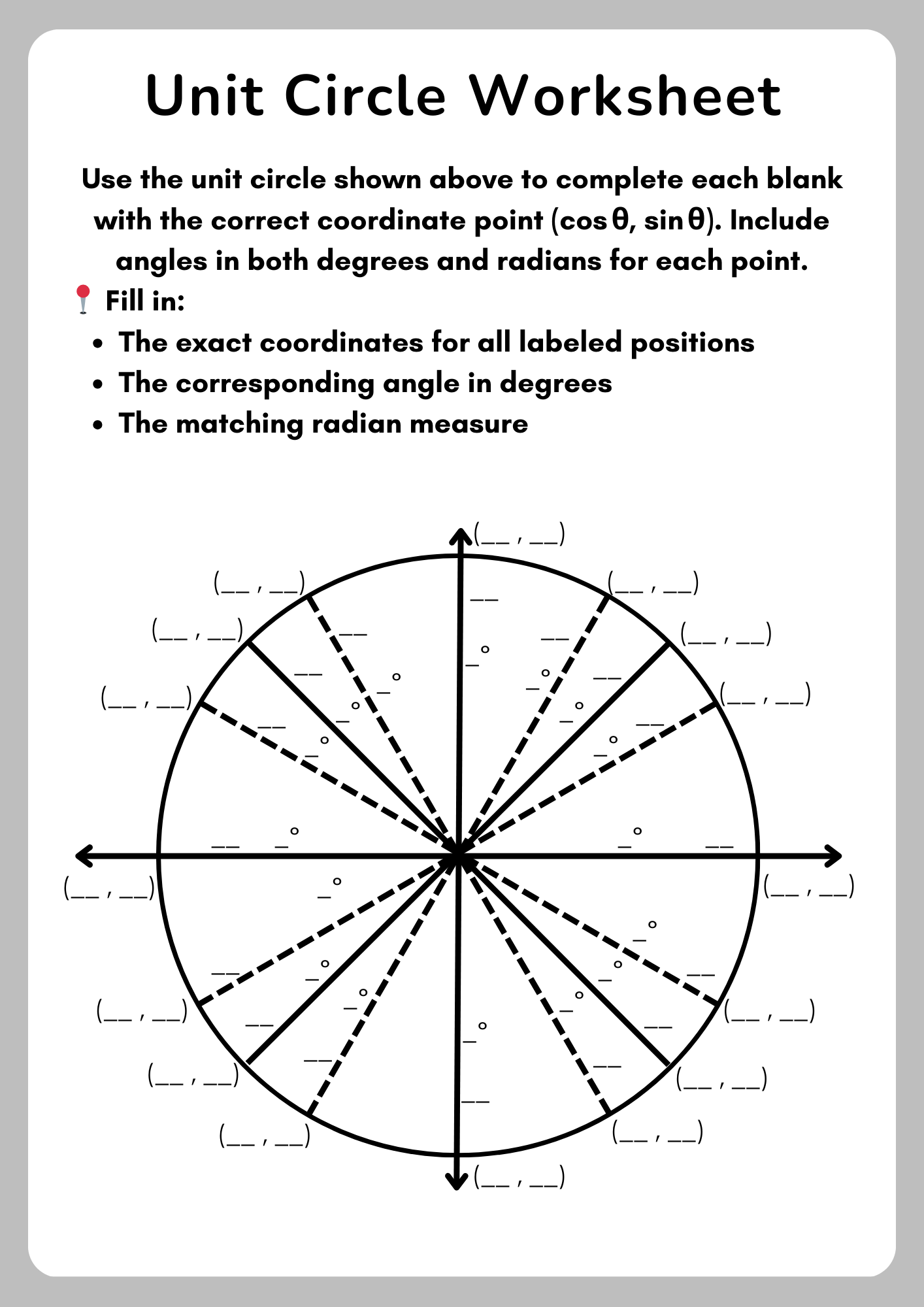
Finding Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Basic Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
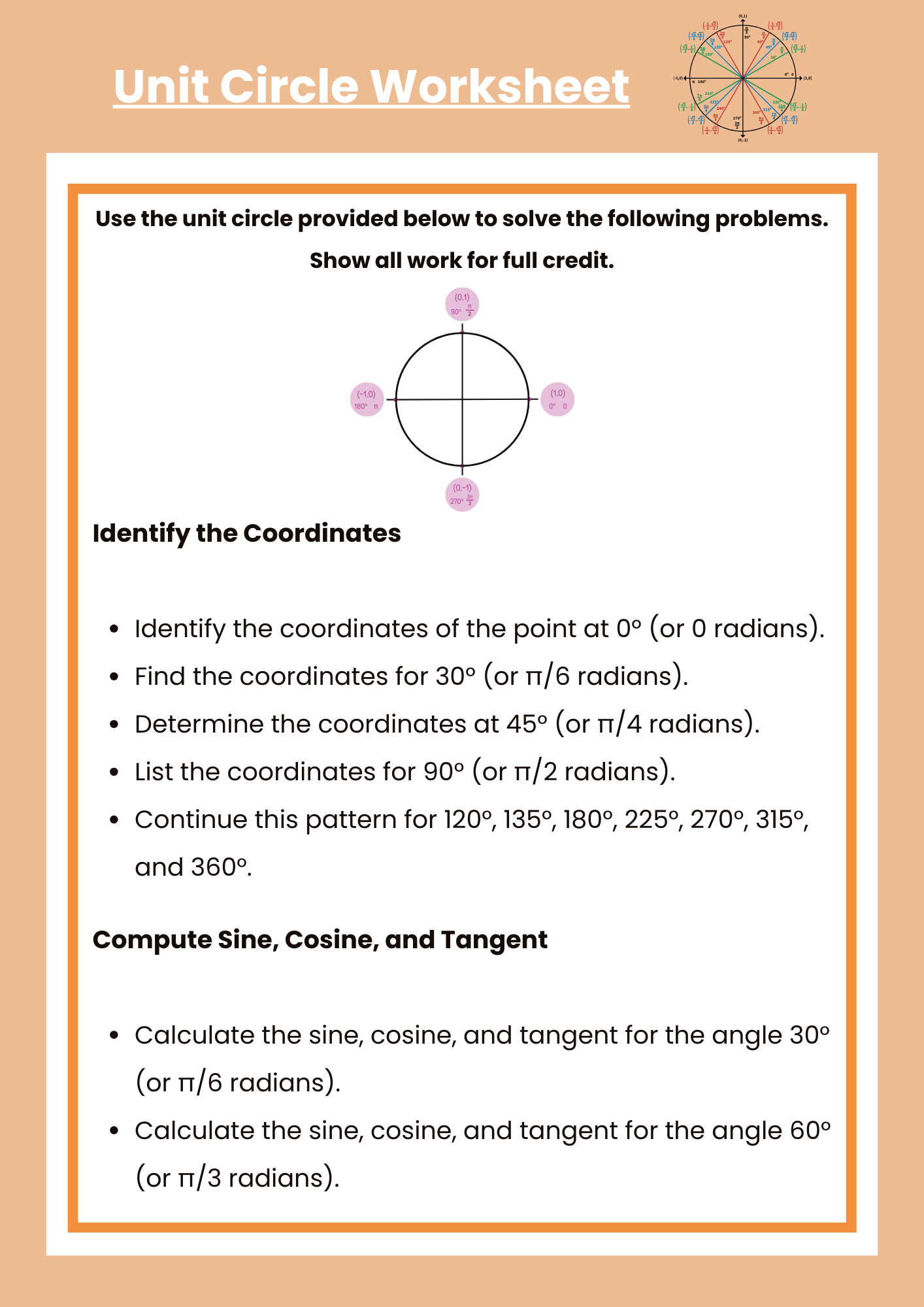
Trig Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
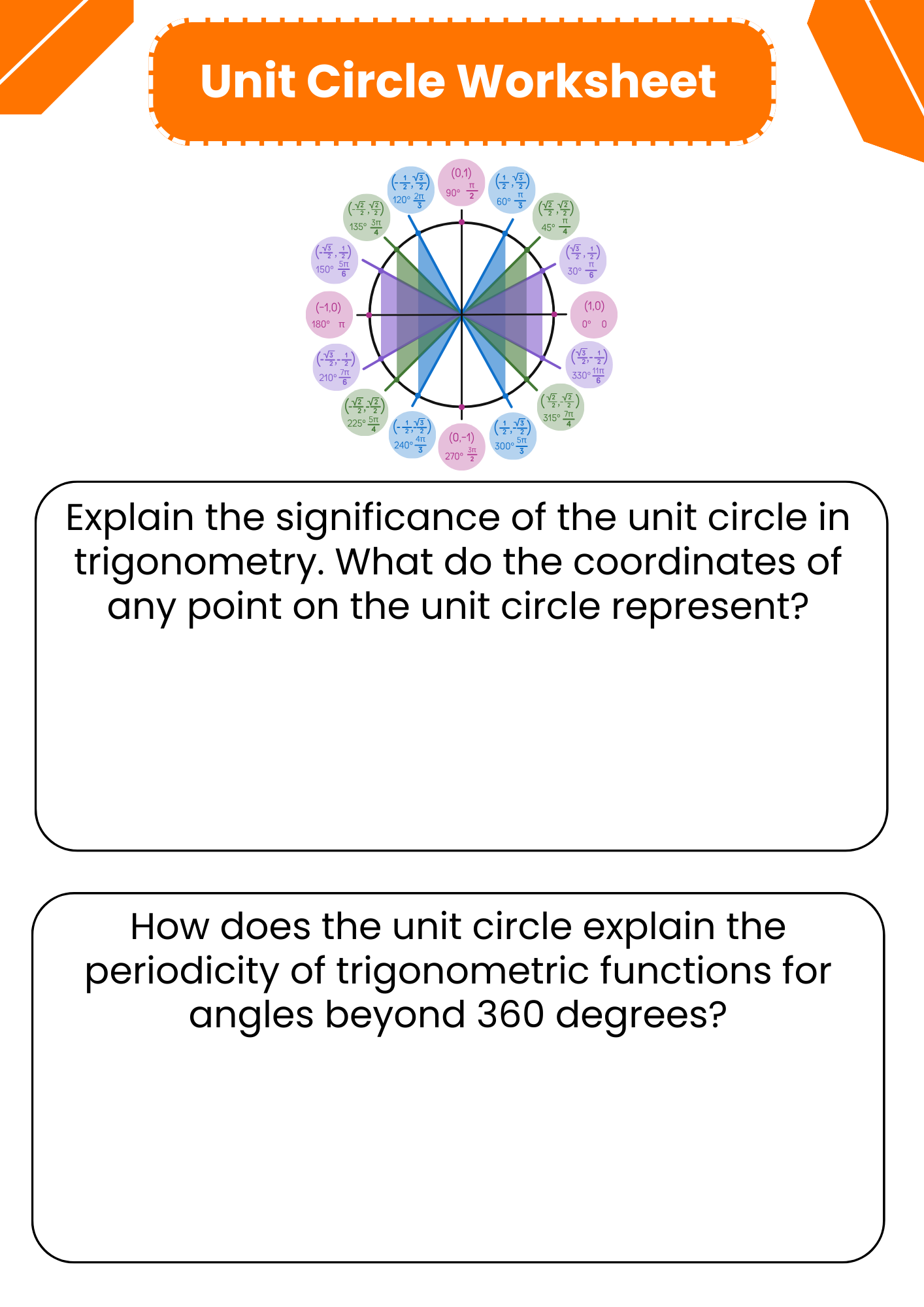
Simple Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
Unit Circle Worksheet for Classroom Test Preparation
download now -
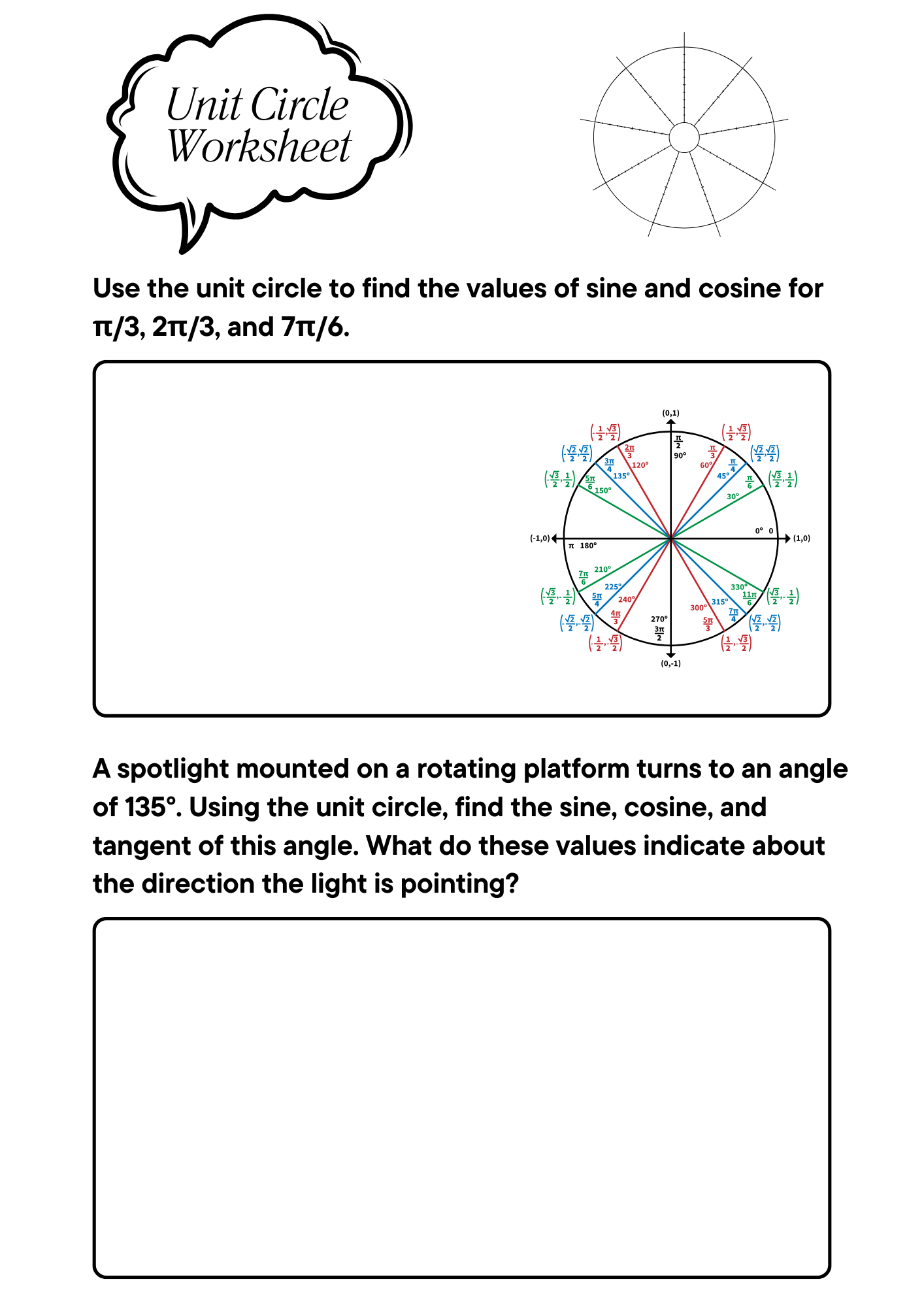
Visual Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Geometry Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Radians Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Worksheet Algebra 2
download now -
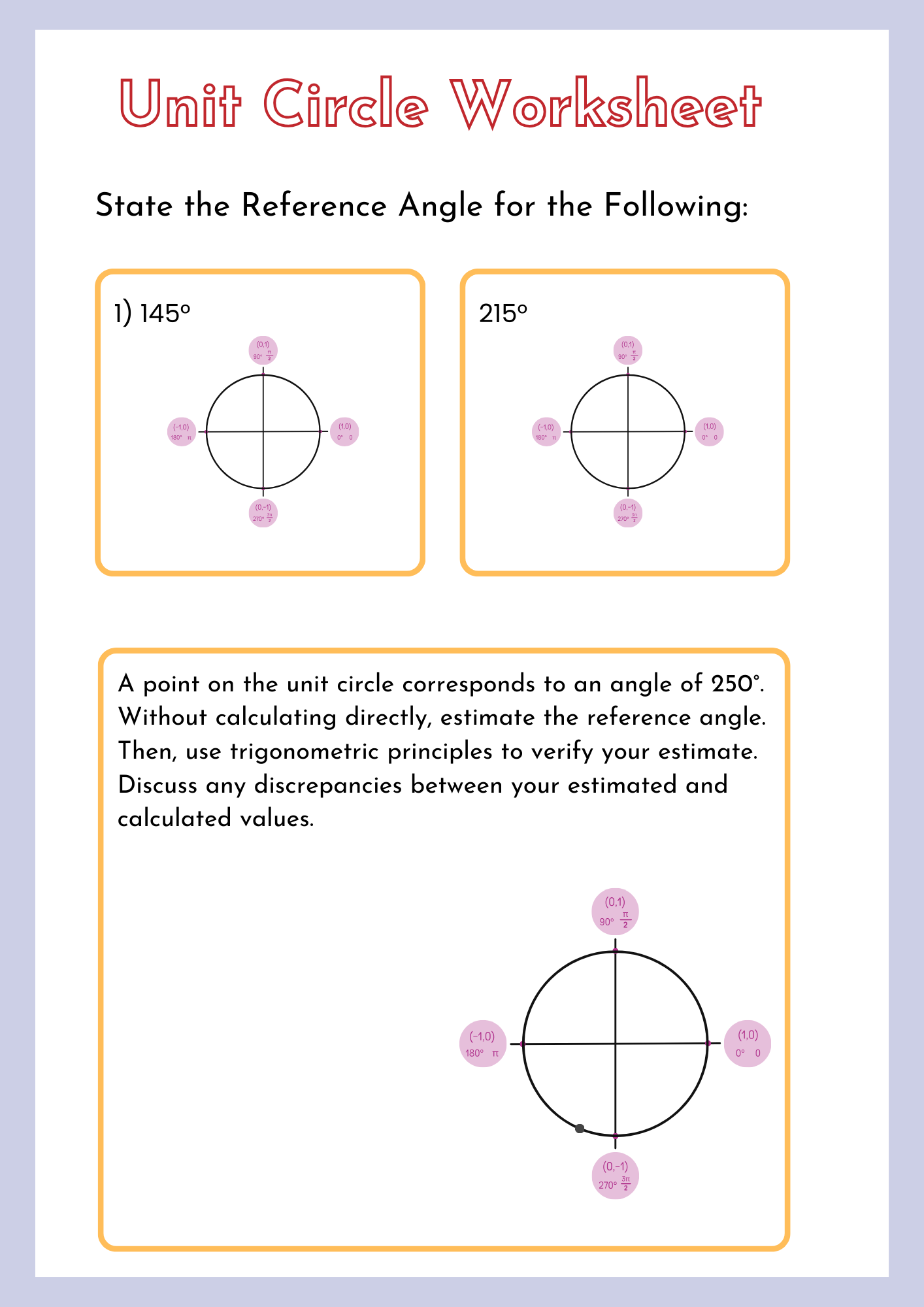
Reference Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
Interactive Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Inverse Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
Printable Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
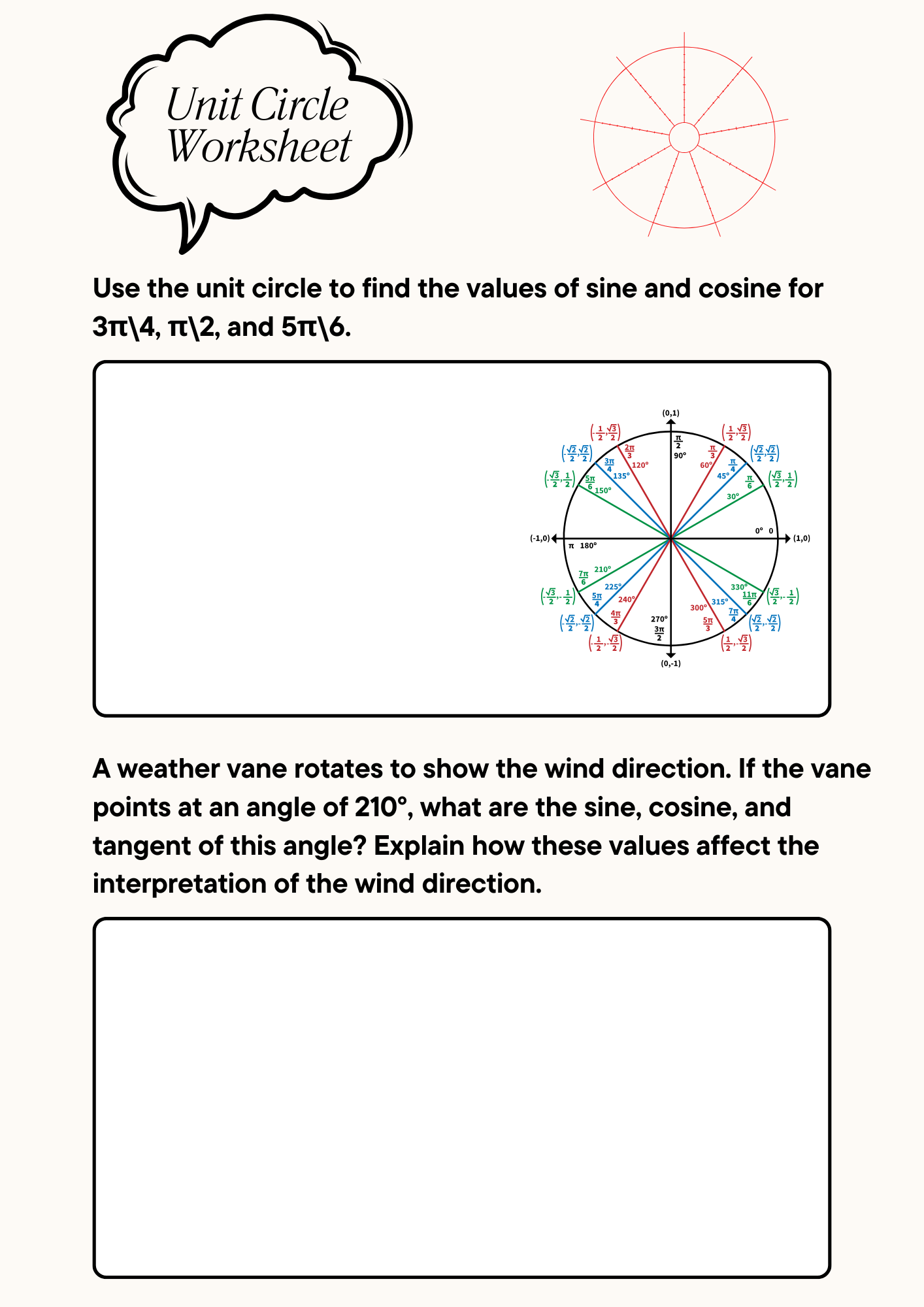
Math Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
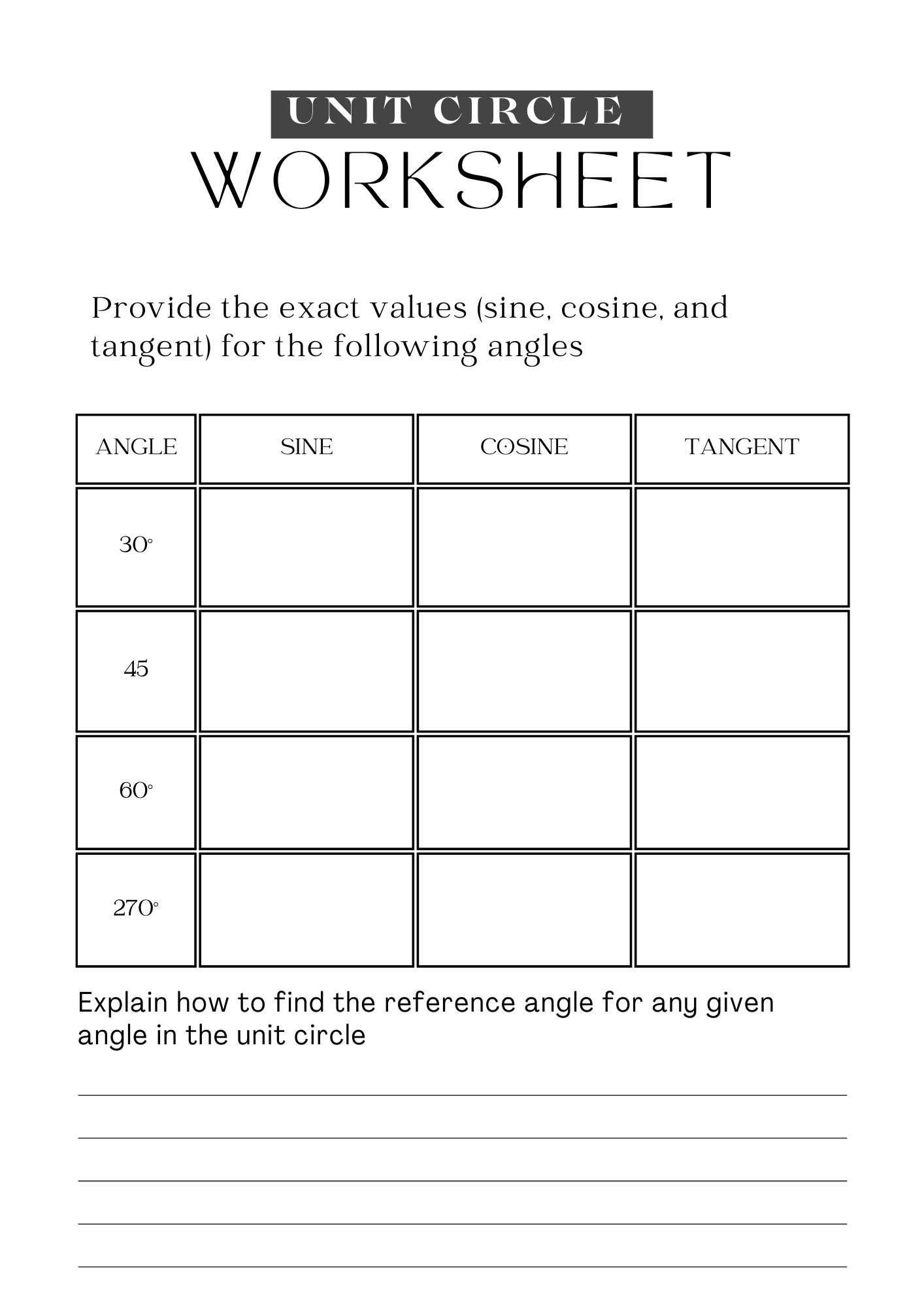
Pre-Calculus Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Angles Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Function Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Trigonometric Ratios Worksheet
download now -

Sin Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
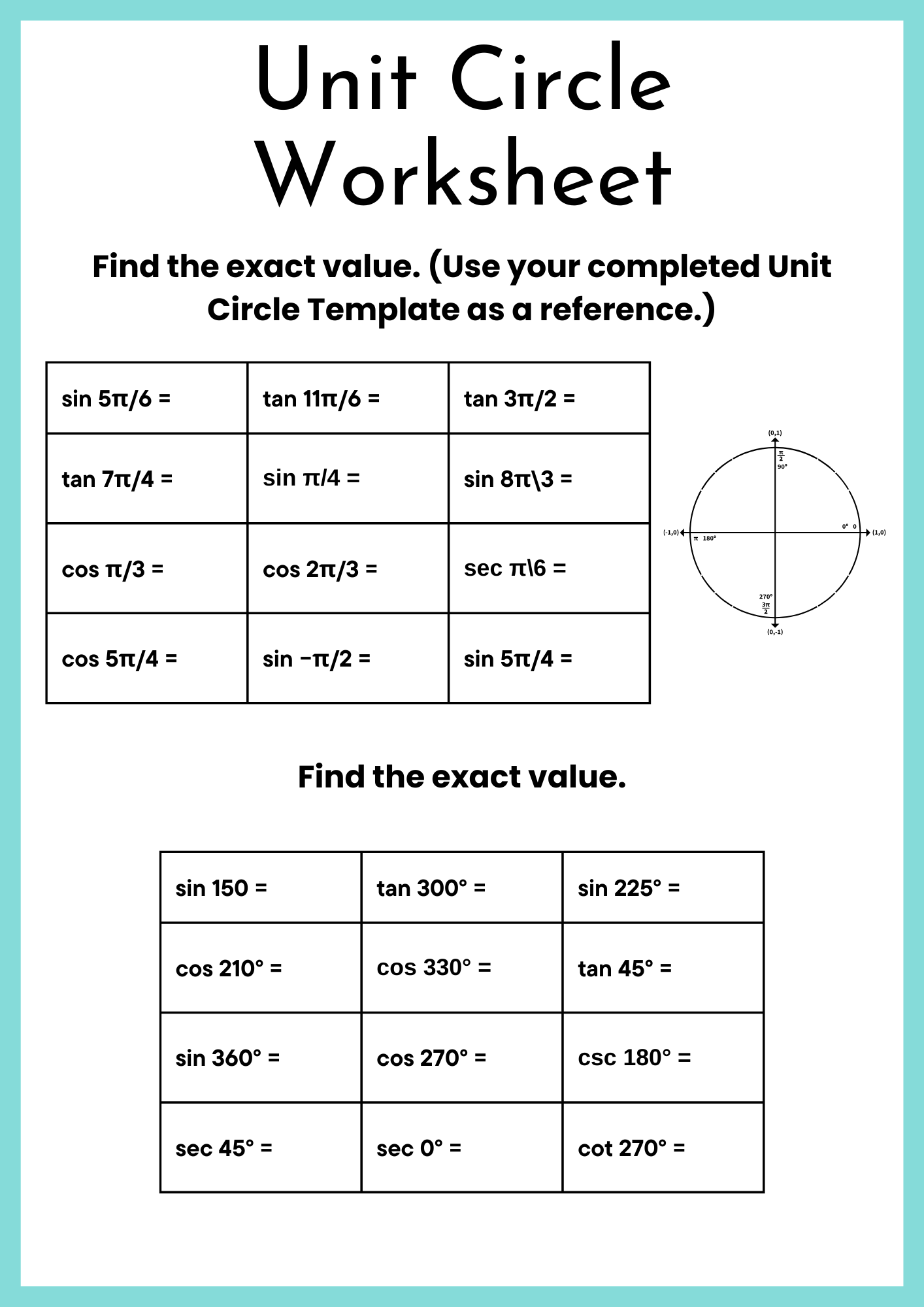
Complete Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Degree Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
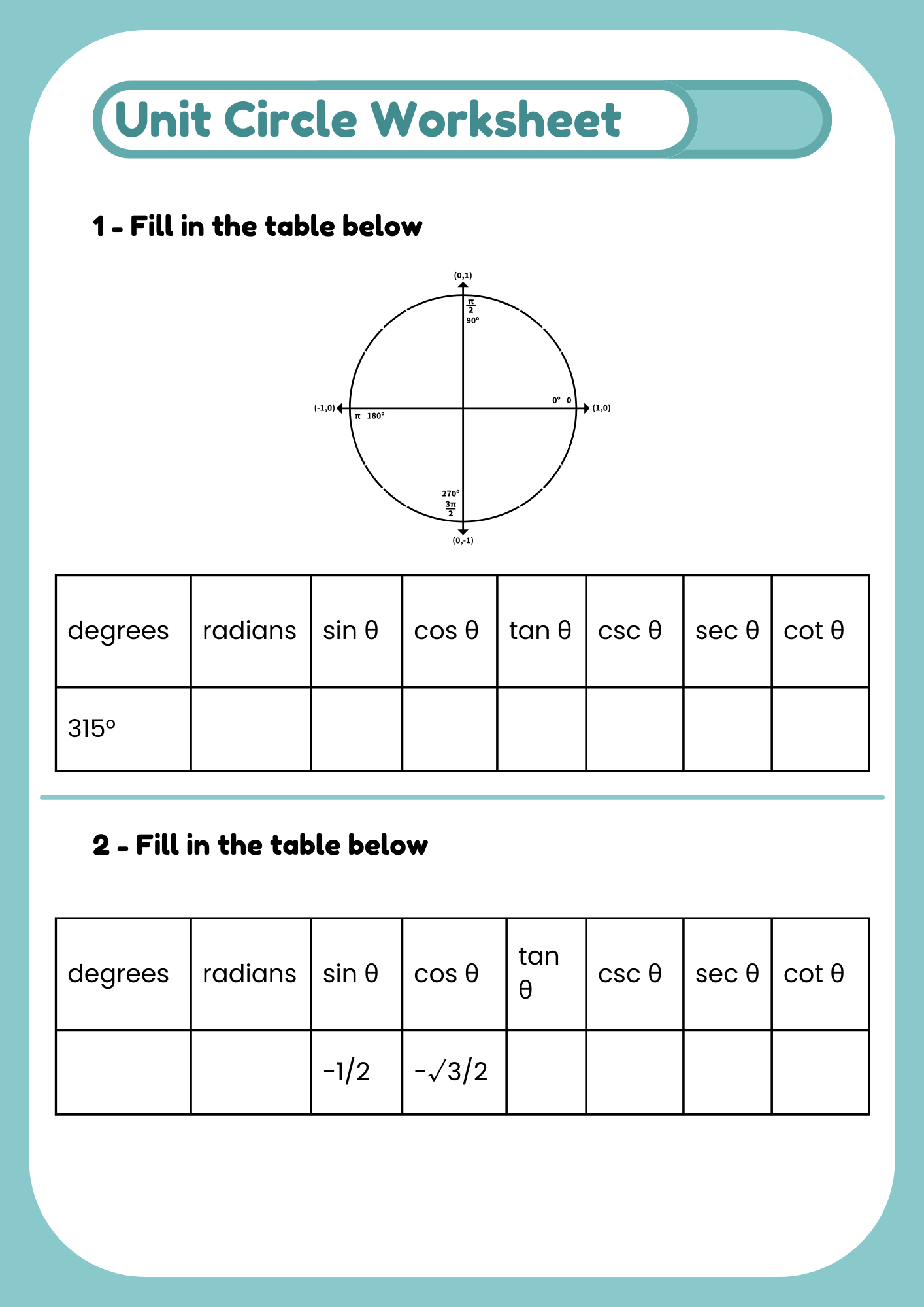
Unit Circle Worksheet with Coordinate Points
download now -

Identification Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
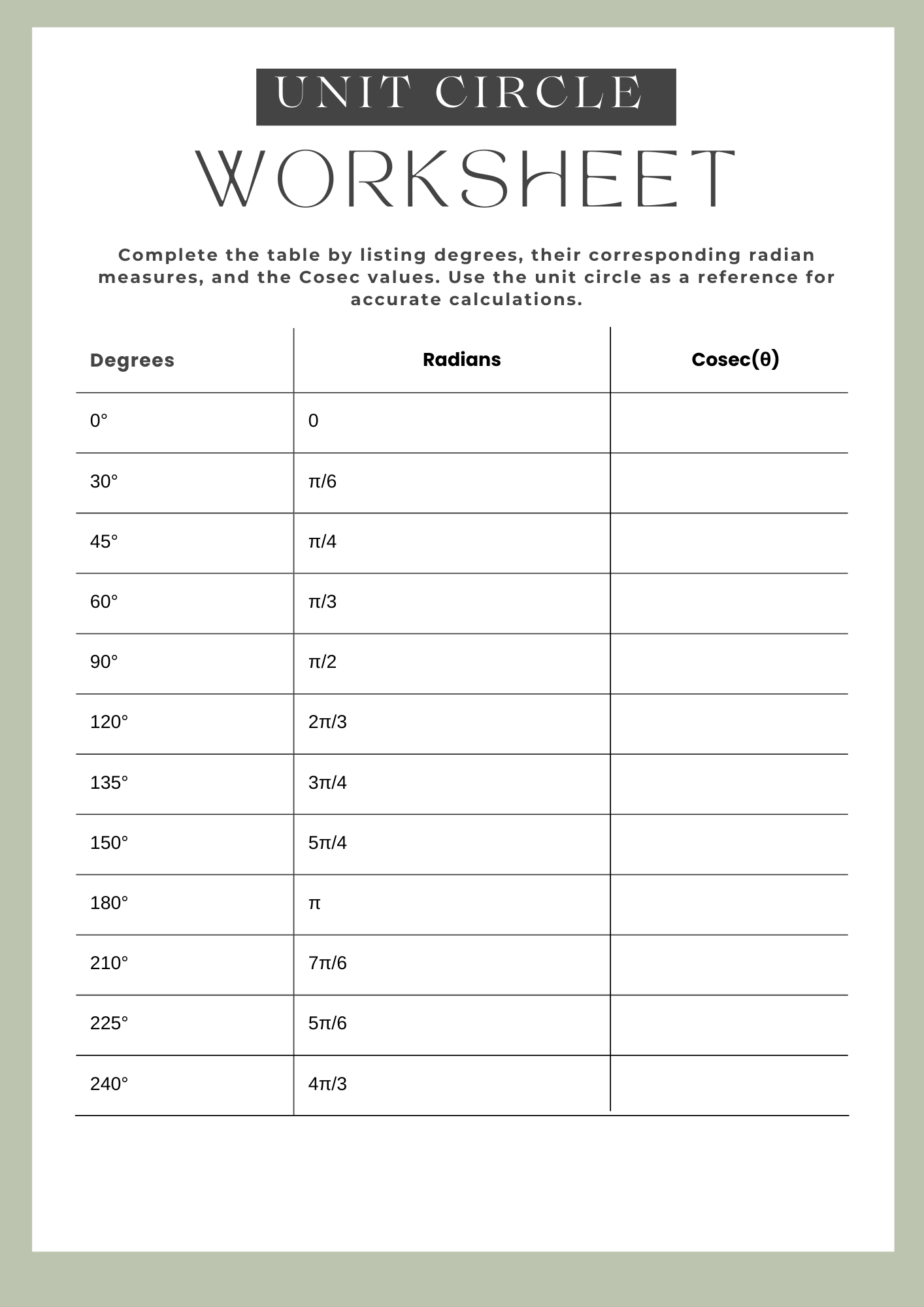
Trigonometry Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Worksheet Lesson
download now -

Unit Circle Worksheet for Exam Preparation
download now -

Easy Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Theoretical Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Assessment Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -
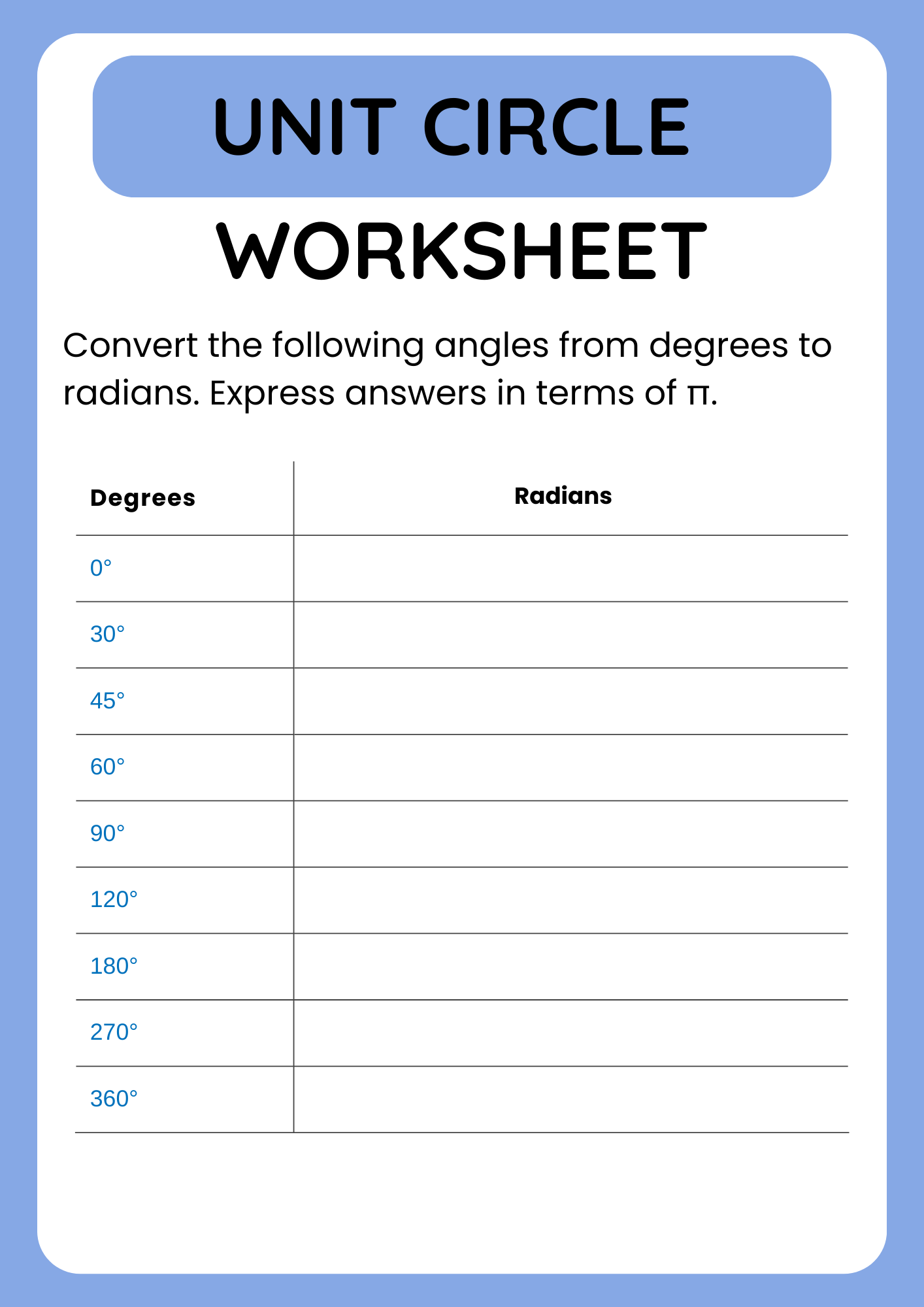
Unit Circle Worksheet with Degree and Radians
download now -

5th Grade Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Quiz Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

4th Grade Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

9th Grade Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

10th Grade Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Worksheet for Trigonometric Function
download now -

Unit Unit Circle Practice Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Worksheet for Homework
download now -
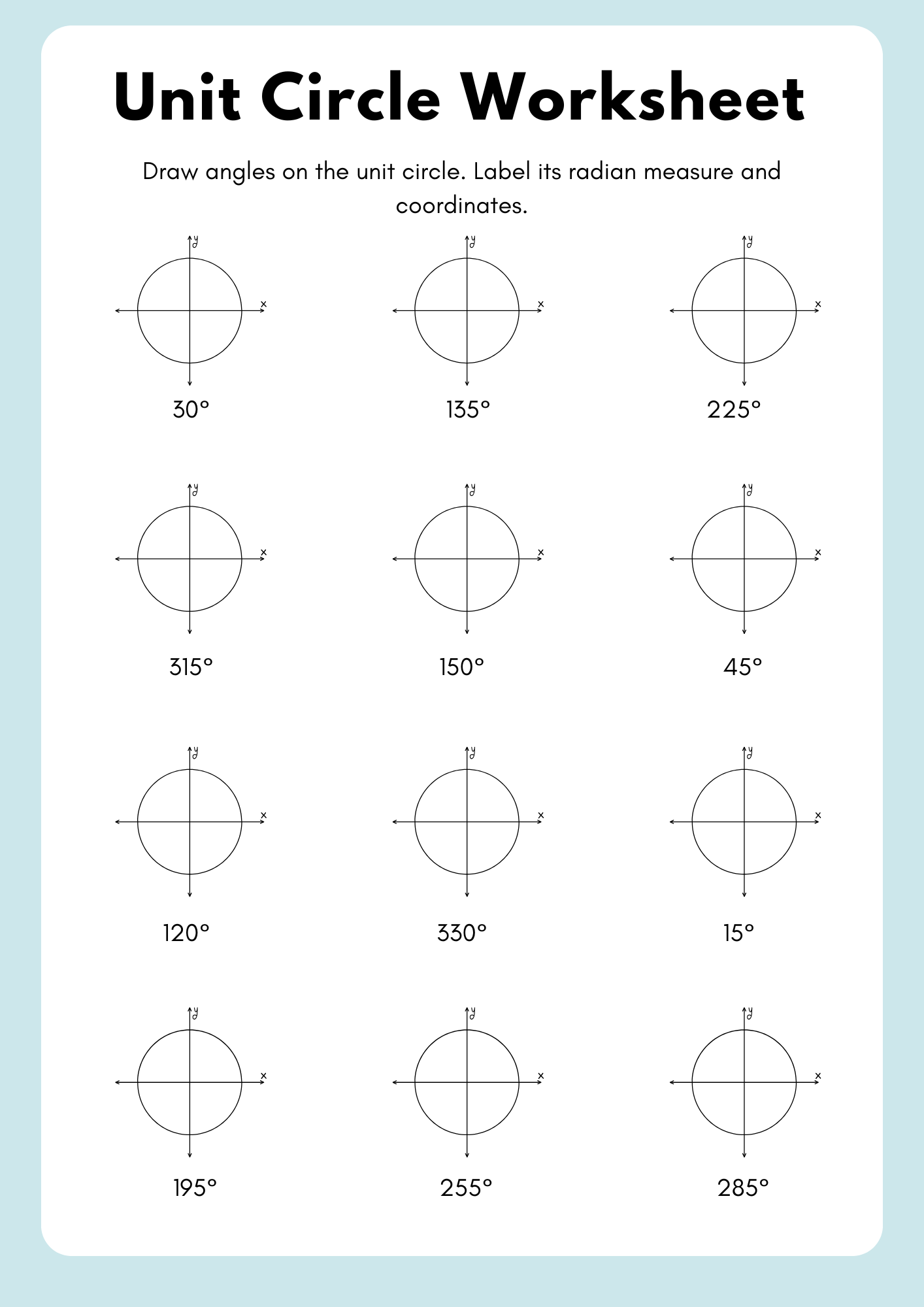
Unit Circle Worksheet for Classroom
download now -

Unit Circle Fill in Worksheet
download now -
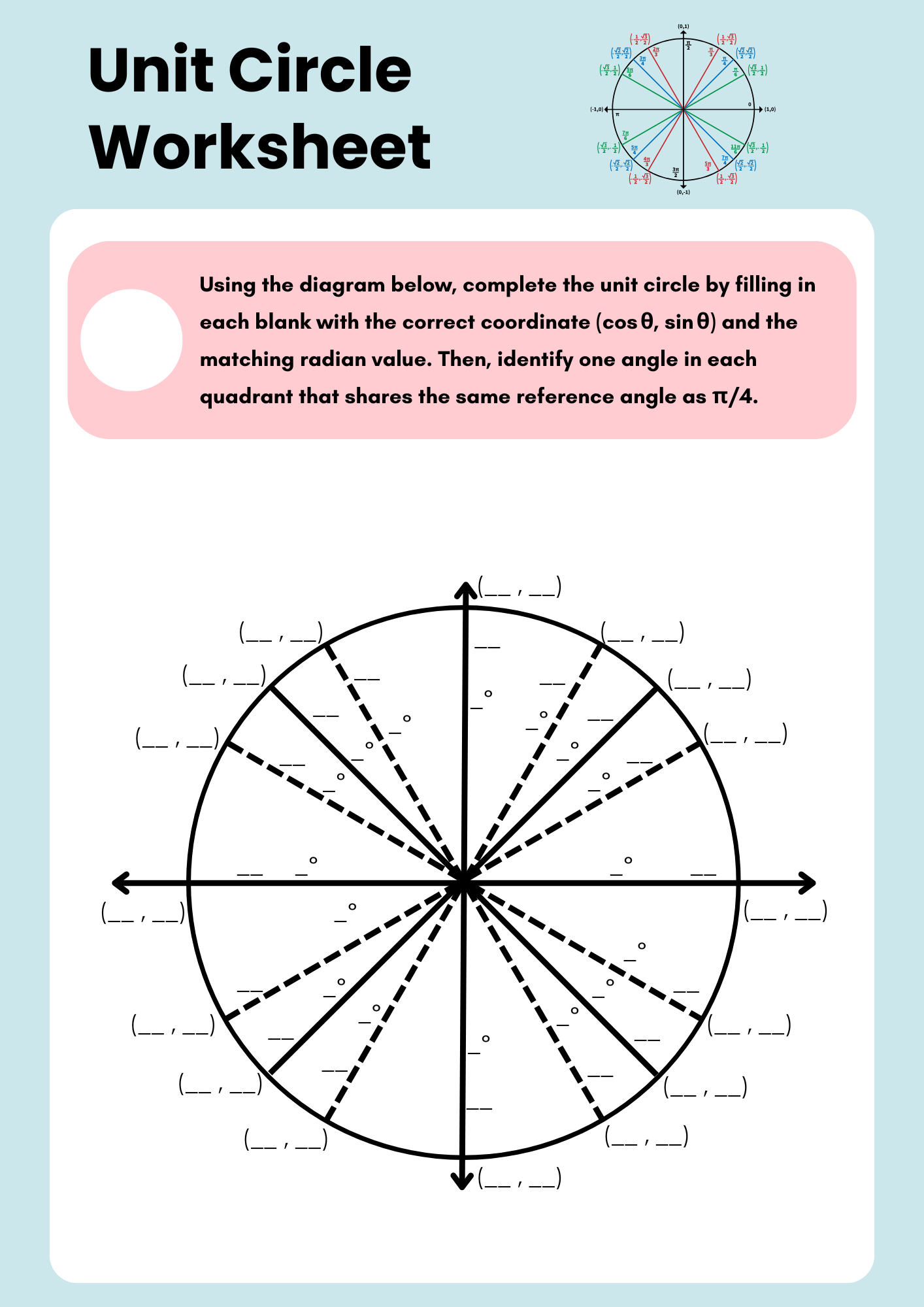
Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Worksheet With Answers PDF
download now -
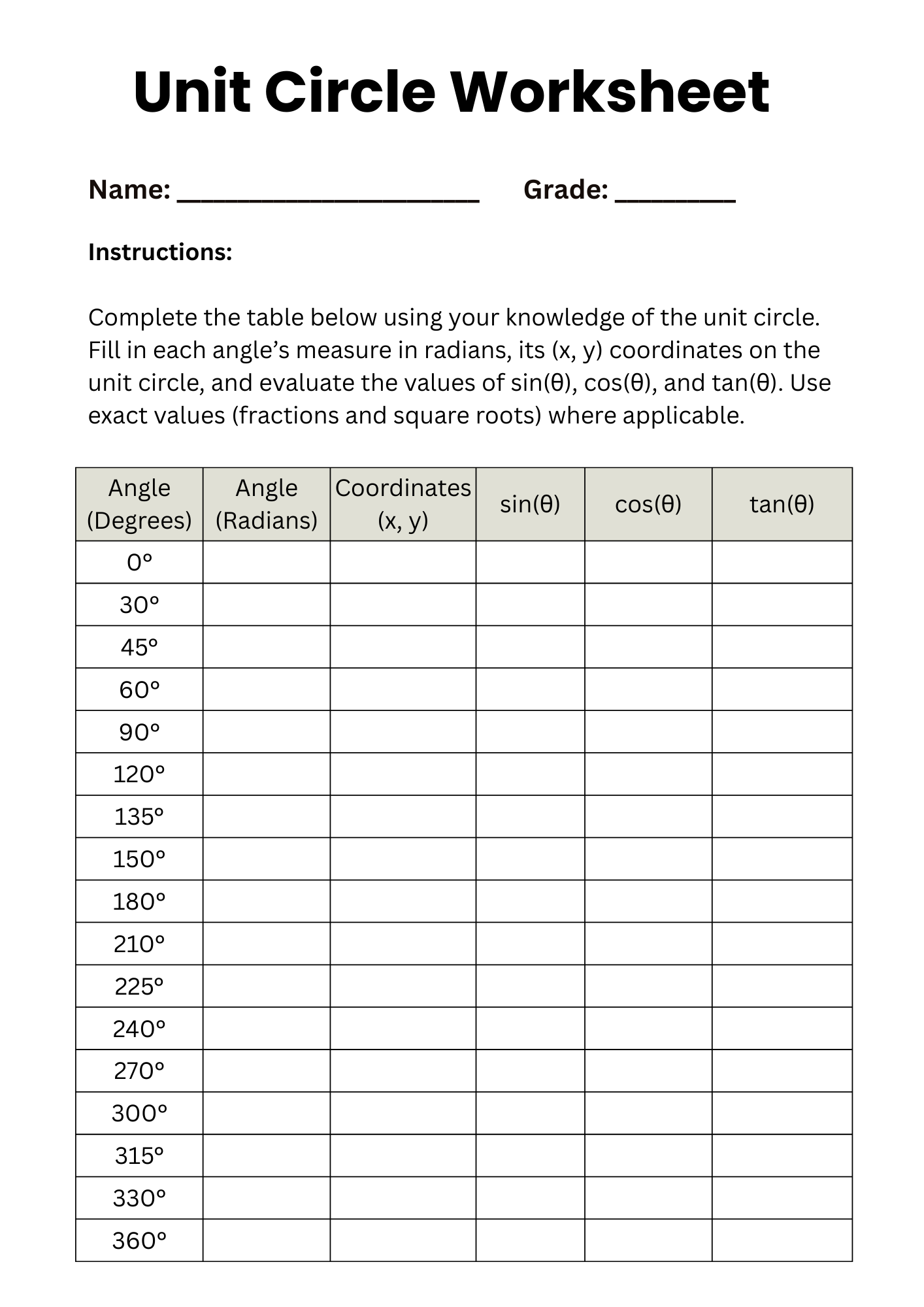
Unit Circle Worksheet Table
download now -
Blank Unit Circle Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Sin Cos Tan Worksheet
download now -

Unit Circle Worksheet Answer Key
download now
Free Printable Unit Circle Worksheet s to Download
50+ Unit Circle Worksheets (Trigonometric, Radians, Geometry, Degree, Interactive, Algebra 2, Math)
What is a Unit Circle Worksheet?
Key Components of a Unit Circle Worksheet
Why Use Unit Circle Worksheet?
How to Use a Unit Circle Worksheet?
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Unit Circle Calculations
What is a Unit Circle Worksheet?
A Unit Circle Worksheet is a structured learning tool designed to help students practice and understand the relationships between angles, radians, trigonometric functions, and coordinates on the unit circle. It typically includes exercises such as degree-to-radian conversions, labeling unit circle points, identifying sine, cosine, and tangent values, solving trigonometric equations, and applying unit circle properties in different quadrants.
Key Components of a Unit Circle Worksheet
✅ Degree to Radian Conversion – Converting angles from degrees to radians for better trigonometric calculations.
✅ Labeling the Unit Circle – Identifying and marking angles, coordinates, and quadrants on the unit circle.
✅ Trigonometric Function Values – Finding sine, cosine, and tangent values for common angles.
✅ Quadrants and Signs of Trigonometric Functions – Understanding where sine, cosine, and tangent are positive or negative.
✅ True or False Questions – Assessing knowledge with statements about the unit circle and its properties.
✅ Fill-in-the-Blank Exercises – Completing missing values for angles, coordinates, and function values.
✅ Matching Questions – Pairing angles with their corresponding coordinates, radians, or trigonometric values.
✅ Problem-Solving Questions – Applying unit circle concepts to real-world and mathematical scenarios.
✅ Reference Angles – Identifying and using reference angles to simplify calculations.
✅ Graphing Trigonometric Functions – Understanding sine and cosine waveforms using unit circle concepts.
Why Use Unit Circle Worksheet?
✔️ Improves Understanding of Trigonometric Functions – Helps visualize sine, cosine, and tangent values at different angles.
✔️ Strengthens Radian and Degree Conversions – Provides practice converting between radians and degrees for accuracy in calculations.
✔️ Enhances Problem-Solving Skills – Encourages applying unit circle concepts to real-world and mathematical problems.
✔️ Clarifies Quadrant-Based Sign Rules – Reinforces when sine, cosine, and tangent are positive or negative in different quadrants.
✔️ Builds Speed and Accuracy in Calculations – Repeated practice improves efficiency in solving trigonometric equations.
✔️ Provides Structured Learning – Organizes exercises systematically for step-by-step learning.
✔️ Helps with Memorization of Key Values – Encourages retention of unit circle coordinates and trigonometric identities.
✔️ Supports Exam Preparation – Essential for tests and standardized exams that involve trigonometry.
✔️ Makes Learning Interactive and Engaging – Uses various question types like matching, fill-in-the-blank, and true/false to keep learning dynamic.
✔️ Foundation for Advanced Math and Physics – Serves as a crucial tool for calculus, physics, and engineering applications.
How to Use a Unit Circle Worksheet?

1️⃣ 📖 Start with Basics – Begin by understanding the unit circle, its quadrants, and key angles in degrees and radians.
2️⃣ ✍️ Practice Conversions – Convert angles between degrees and radians to reinforce your understanding of different angle measures.
3️⃣ 📌 Label the Circle – Fill in missing coordinates, reference angles, and trigonometric values to strengthen memorization.
4️⃣ 🧠 Solve Questions – Work on multiple-choice, true/false, and problem-solving exercises to apply your knowledge.
5️⃣ ✅ Check and Review – Go over your answers, correct mistakes, and repeat tricky exercises to improve accuracy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Unit Circle Calculations
✔️ Misplacing Coordinates – Mixing up sine (y-value) and cosine (x-value) when labeling points.
✔️ Incorrect Quadrant Signs – Forgetting that sine, cosine, and tangent have different signs in each quadrant.
✔️ Wrong Radian Conversions – Confusing degree-to-radian conversions, especially for non-standard angles.
✔️ Forgetting Reference Angles – Not using reference angles correctly for trigonometric function values.
✔️ Dividing by Zero in Tangent – Not recognizing when cosine is zero, making tangent undefined at 90° and 270°.
